|
MEN2
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (also known as "Pheochromocytoma and amyloid producing medullary thyroid carcinoma", "PTC syndrome," and "Sipple syndrome") is a group of medical disorders associated with tumors of the endocrine system. The tumors may be benign or malignant (cancer). They generally occur in endocrine organs (e.g. thyroid, parathyroid, and adrenals), but may also occur in endocrine tissues of organs not classically thought of as endocrine. MEN2 is a sub-type of MEN (multiple endocrine neoplasia) and itself has sub-types, as discussed below. Signs and symptoms MEN2 can present with a sign or symptom related to a tumor or, in the case of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2b, with characteristic musculoskeletal and/or lip and/or gastrointestinal findings. Medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) represents the most frequent initial diagnosis. Occasionally pheochromocytoma or primary hyperparathyroidism may be the initial diagnosis. Pheochromocytoma occurs in 33-50% o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MEN2A
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (also known as "Pheochromocytoma and amyloid producing medullary thyroid carcinoma", "PTC syndrome," and "Sipple syndrome") is a group of medical disorders associated with tumors of the endocrine system. The tumors may be benign or malignant (cancer). They generally occur in endocrine organs (e.g. thyroid, parathyroid, and adrenals), but may also occur in endocrine tissues of organs not classically thought of as endocrine. MEN2 is a sub-type of MEN (multiple endocrine neoplasia) and itself has sub-types, as discussed below. Signs and symptoms MEN2 can present with a sign or symptom related to a tumor or, in the case of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2b, with characteristic musculoskeletal and/or lip and/or gastrointestinal findings. Medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) represents the most frequent initial diagnosis. Occasionally pheochromocytoma or primary hyperparathyroidism may be the initial diagnosis. Pheochromocytoma occurs in 33-50% o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RET Proto-oncogene
The ''RET'' proto-oncogene encodes a receptor tyrosine kinase for members of the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) family of extracellular signalling molecules. ''RET'' loss of function mutations are associated with the development of Hirschsprung's disease, while gain of function mutations are associated with the development of various types of human cancer, including medullary thyroid carcinoma, multiple endocrine neoplasias type 2A and 2B, pheochromocytoma and parathyroid hyperplasia. Structure ''RET'' is an abbreviation for "rearranged during transfection", as the DNA sequence of this gene was originally found to be rearranged within a 3T3 fibroblast cell line following its transfection with DNA taken from human lymphoma cells. The human gene ''RET'' is localized to chromosome 10 (10q11.2) and contains 21 exons. The natural alternative splicing of the ''RET'' gene results in the production of 3 different isoforms of the protein RET. RET51, RET43 and RET9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia
Multiple endocrine neoplasia (abbreviated MEN) is a condition which encompasses several distinct syndromes featuring tumors of endocrine glands, each with its own characteristic pattern. In some cases, the tumors are malignant, in others, benign. Benign or malignant tumors of nonendocrine tissues occur as components of some of these tumor syndromes. MEN syndromes are inherited as autosomal dominant disorders. Presentation Related conditions Although not officially categorized as multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes, Von Hippel–Lindau disease and Carney complex are two other autosomal dominant endocrine tumor syndromes with features that overlap the clinical features of the MEN syndromes. Although not transmitted in the germline, McCune–Albright syndrome is a genetic disorder characterized by endocrine neoplastic features involving endocrine glands that overlap with those involved in MEN1 or MEN2. Comparison Percentages in the table below refer to the percentage of peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia
Multiple endocrine neoplasia (abbreviated MEN) is a condition which encompasses several distinct syndromes featuring tumors of endocrine glands, each with its own characteristic pattern. In some cases, the tumors are malignant, in others, benign. Benign or malignant tumors of nonendocrine tissues occur as components of some of these tumor syndromes. MEN syndromes are inherited as autosomal dominant disorders. Presentation Related conditions Although not officially categorized as multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes, Von Hippel–Lindau disease and Carney complex are two other autosomal dominant endocrine tumor syndromes with features that overlap the clinical features of the MEN syndromes. Although not transmitted in the germline, McCune–Albright syndrome is a genetic disorder characterized by endocrine neoplastic features involving endocrine glands that overlap with those involved in MEN1 or MEN2. Comparison Percentages in the table below refer to the percentage of peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma (PHEO or PCC) is a rare tumor of the adrenal medulla composed of chromaffin cells, also known as pheochromocytes. When a tumor composed of the same cells as a pheochromocytoma develops outside the adrenal gland, it is referred to as a paraganglioma. These neuroendocrine tumors are capable of producing and releasing massive amounts of catecholamines, metanephrines, or methoxytyramine, which result in the most common symptoms, including hypertension (high blood pressure), tachycardia (fast heart rate), and diaphoresis (sweating). However, not all of these tumors will secrete catecholamines. Those that do not are referred to as biochemically silent, and are predominantly located in the head and neck. While patients with biochemically silent disease will not develop the typical disease manifestations described above, the tumors grow and compress the surrounding structures of the head and neck, and can result in pulsatile tinnitus (ringing of the ear), hearing loss, au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
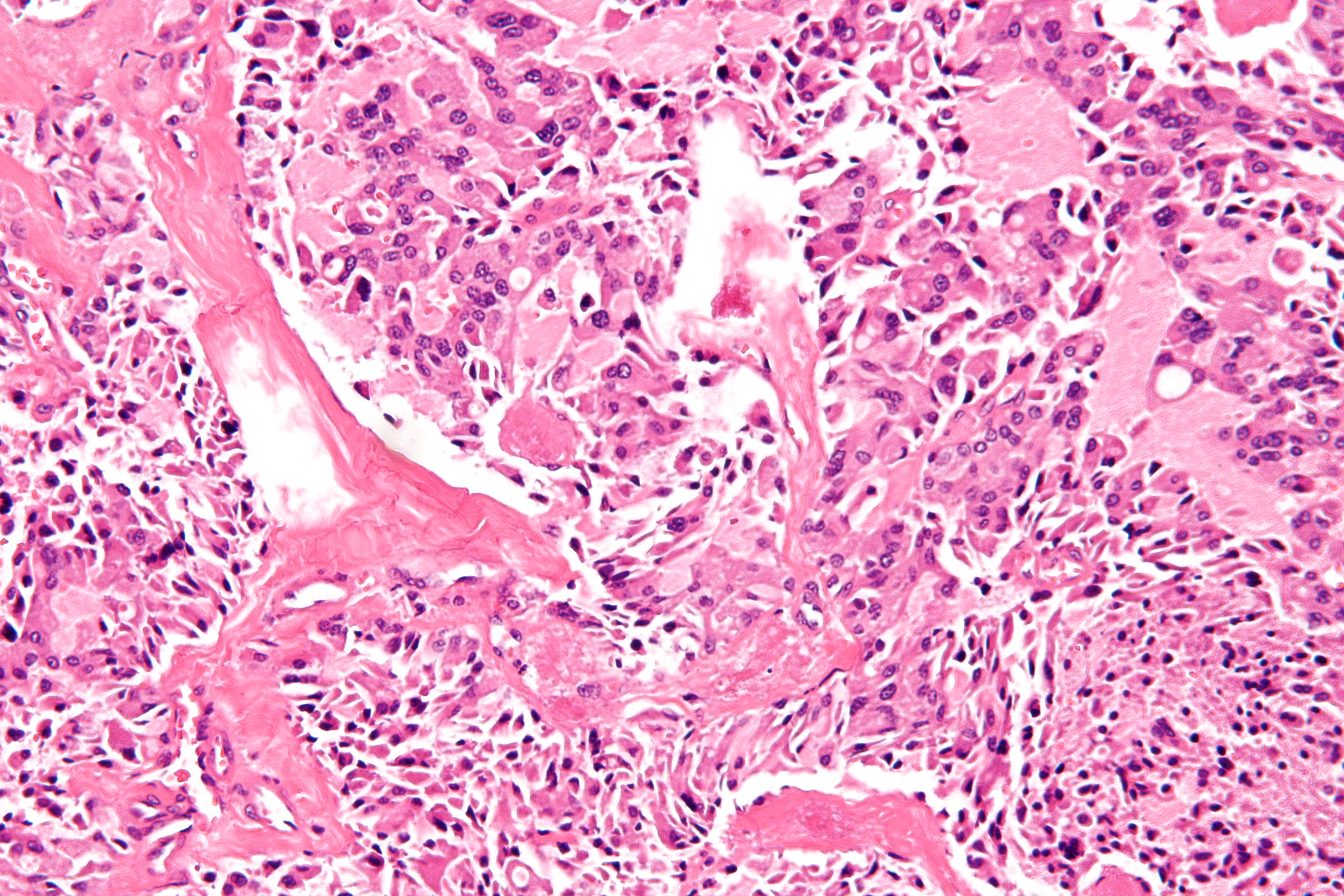
Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Medullary thyroid cancer is a form of Thyroid cancer, thyroid carcinoma which originates from the parafollicular cells (C cells), which produce the hormone calcitonin.Hu MI, Vassilopoulou-Sellin R, Lustig R, Lamont JP"Thyroid and Parathyroid Cancers"in Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins WJ (EdsCancer Management: A Multidisciplinary Approach 11 ed. 2008. Medullary tumors are the third most common of all thyroid cancers and together make up about 3% of all thyroid cancer cases. MTC was first characterized in 1959. Approximately 25% of medullary thyroid cancer cases are Genetic disorder, genetic in nature, caused by a mutation in the RET proto-oncogene. When MTC occurs by itself it is termed sporadic medullary thyroid cancer. Medullary thyroid cancer is seen in people with Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2, multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A and Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2B, 2B. When medullary thyroid cancer due to a hereditary genetic disorder occurs without othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma (PHEO or PCC) is a rare tumor of the adrenal medulla composed of chromaffin cells, also known as pheochromocytes. When a tumor composed of the same cells as a pheochromocytoma develops outside the adrenal gland, it is referred to as a paraganglioma. These neuroendocrine tumors are capable of producing and releasing massive amounts of catecholamines, metanephrines, or methoxytyramine, which result in the most common symptoms, including hypertension (high blood pressure), tachycardia (fast heart rate), and diaphoresis (sweating). However, not all of these tumors will secrete catecholamines. Those that do not are referred to as biochemically silent, and are predominantly located in the head and neck. While patients with biochemically silent disease will not develop the typical disease manifestations described above, the tumors grow and compress the surrounding structures of the head and neck, and can result in pulsatile tinnitus (ringing of the ear), hearing loss, au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Medullary thyroid cancer is a form of thyroid carcinoma which originates from the parafollicular cells (C cells), which produce the hormone calcitonin.Hu MI, Vassilopoulou-Sellin R, Lustig R, Lamont JP"Thyroid and Parathyroid Cancers"in Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins WJ (EdsCancer Management: A Multidisciplinary Approach 11 ed. 2008. Medullary tumors are the third most common of all thyroid cancers and together make up about 3% of all thyroid cancer cases. MTC was first characterized in 1959. Approximately 25% of medullary thyroid cancer cases are genetic in nature, caused by a mutation in the RET proto-oncogene. When MTC occurs by itself it is termed sporadic medullary thyroid cancer. Medullary thyroid cancer is seen in people with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A and 2B. When medullary thyroid cancer due to a hereditary genetic disorder occurs without other endocrine tumours it is termed familial medullary thyroid cancer. Signs and symptoms The major clinical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hirschsprung Disease
Hirschsprung's disease (HD or HSCR) is a birth defect in which nerves are missing from parts of the intestine. The most prominent symptom is constipation. Other symptoms may include vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea and slow growth. Symptoms usually become apparent in the first two months of life. Complications may include enterocolitis, megacolon, bowel obstruction and intestinal perforation. The disorder may occur by itself or in association with other genetic disorders such as Down syndrome or Waardenburg syndrome. About half of isolated cases are linked to a specific genetic mutation, and about 20% occur within families. Some of these occur in an autosomal dominant manner. The cause of the remaining cases is unclear. If otherwise normal parents have one child with the condition, the next child has a 4% risk of being affected. The condition is divided into two main types, short-segment and long-segment, depending on how much of the bowel is affected. Rarely, the small bowel m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Familial Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Medullary thyroid cancer is a form of thyroid carcinoma which originates from the parafollicular cells (C cells), which produce the hormone calcitonin.Hu MI, Vassilopoulou-Sellin R, Lustig R, Lamont JP"Thyroid and Parathyroid Cancers"in Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins WJ (EdsCancer Management: A Multidisciplinary Approach 11 ed. 2008. Medullary tumors are the third most common of all thyroid cancers and together make up about 3% of all thyroid cancer cases. MTC was first characterized in 1959. Approximately 25% of medullary thyroid cancer cases are genetic in nature, caused by a mutation in the RET proto-oncogene. When MTC occurs by itself it is termed sporadic medullary thyroid cancer. Medullary thyroid cancer is seen in people with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2A and 2B. When medullary thyroid cancer due to a hereditary genetic disorder occurs without other endocrine tumours it is termed familial medullary thyroid cancer. Signs and symptoms The major clinical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Dominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomplete d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscular Hypotonia
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are Organ (biology), organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as Skeletal muscle#Skeletal muscle cells, muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated muscle tissue, striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |