|
Melee Weapons
A melee weapon, hand weapon or close combat weapon is any handheld weapon used in hand-to-hand combat, i.e. for use within the direct physical reach of the weapon itself, essentially functioning as an additional (and more impactful) extension of the user's limbs. By contrast, a ranged weapon is any other weapon capable of engaging targets at a distance beyond immediate physical contact. Etymology The term ''melee'' originates in the 1640s from the French word ', which refers to disorganized hand-to-hand combat, a close-quarters battle, a brawl, or a confused fight; especially involving many combatants. The 1812 tabletop war game ''Kriegsspiel'' referred to the hand-combat stage of the game as a ''melee''. Later war games would follow this pattern. From there, gamers would eventually begin to call the weapons used in that stage ''melee weapons''. Categories Melee weapons can be broadly divided into three categories : * Pointed weapons, which cover spears, pikes, lances, and mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weapon
A weapon, arm or armament is any implement or device that can be used to deter, threaten, inflict physical damage, harm, or kill. Weapons are used to increase the efficacy and efficiency of activities such as hunting, crime, law enforcement, self-defense, warfare, or suicide. In broader context, weapons may be construed to include anything used to gain a tactical, strategic, material or mental advantage over an adversary or enemy target. While ordinary objects – sticks, rocks, bottles, chairs, vehicles – can be used as weapons, many objects are expressly designed for the purpose; these range from simple implements such as clubs, axes and swords, to complicated modern firearms, tanks, intercontinental ballistic missiles, biological weapons, and cyberweapons. Something that has been re-purposed, converted, or enhanced to become a weapon of war is termed weaponized, such as a weaponized virus or weaponized laser. History The use of weapons is a major driver of cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
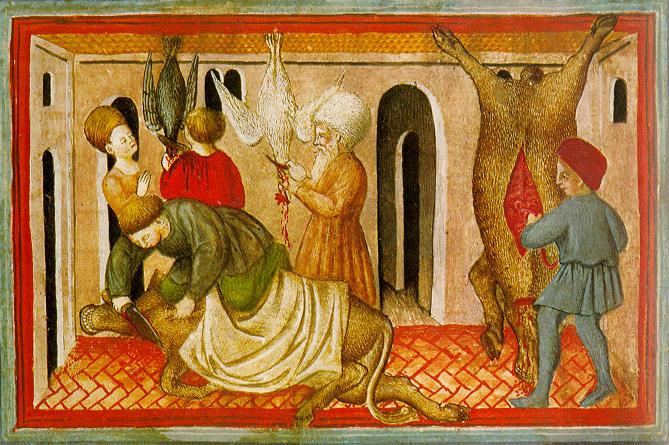
Exsanguination
Exsanguination is death caused by loss of blood. Depending upon the health of the individual, people usually die from losing half to two-thirds of their blood; a loss of roughly one-third of the blood volume is considered very serious. Even a single deep cut can warrant suturing and hospitalization, especially if trauma, a vein or artery, or another comorbidity is involved. The word comes from the Latin 'sanguis', meaning blood. Slaughtering of animals Exsanguination is used as a method of slaughter. Before the fatal incision is made, the animal will be rendered insensible to pain by various methods, including captive bolt, electricity, or chemical. Electricity is used mostly to incapacitate swine, poultry, and domestic sheep, whereas a chemical is used for injured livestock. Without prior sedation, stunning, or anesthetic, this method of slaughter may cause a high degree of anxiety, depending on the process. The way animals are handled and restrained prior to slaughter lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falx
The ''falx'' was a weapon with a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge used by the Thracians and Dacians. The name was later applied to a siege hook used by the Romans. Etymology ''Falx'' is a Latin word originally meaning 'sickle' but was later used to mean any of a number of tools that had a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge like a sickle. ''Falx'' was thus also used to mean the weapon of the Thracians and Dacians, and the Roman siege hook. Dacian ''falx'' In Latin texts, the weapon was described as an ' (whence ''falcata'') by Ovid in ''Metamorphose'' and as a ' by Juvenal in ''Satiriae''. The Dacian ''falx'' came in two sizes: one-handed and two-handed. The shorter variant was called ''sica'' (sickle) in the Dacian language (Valerius Maximus, III, 2.12) with a blade length that varied but was usually around long with a handle 1/3 longer than the blade. The two-handed ''falx'' was a polearm. It consisted of a long wooden shaft with a long curved i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauchard
A fauchard is a type of polearm weapon which was used in Europe from the 11th through the 17th centuries. In later use fauchards became ornamental and ceremonial (''fauchard de parade''), growing in size until some examples were almost too heavy to carry, let alone use. The design consisted of a curved blade atop a long pole, although in some portrayals, it is shown on a shorter pole. The blade bore a moderate to strong curve along its length. The cutting edge was only on the convex side of the blade, unlike the guisarme or bill. The fauchard was likely developed from the war scythe (and is from the scythe (falx) family in general) with the cutting edge turned opposite, convex instead of concave, so that the weapon was good for both thrusting and slashing attacks. Pole arms developed from relatively few early tools (axe, scythe/wide-bladed knife, and the pruning hook) and the spear. Thus naming, particularly of early forms, is difficult. Fauchard, as a name, is from early Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Billhook
A billhook or bill hook, also called a pruning knife or spar hook, is a versatile cutting tool used widely in agriculture and forestry for cutting woody material such as shrubs, small trees and branches. It is distinct from the sickle. It was commonly used in Europe with an important variety of traditional local patterns. Elsewhere, it was also developed locally such as in the Indian subcontinent, or introduced regionally as in the Americas, South Africa and Oceania by European settlers. Design The blade is usually made from a medium- carbon steel in varying weights and lengths, but typically long. Blades are straight near the handle but have an increasingly strong curve towards the end. The blade is generally sharpened only on the inside of the curve, but double-edged billhooks, or "broom hooks", also have a straight secondary edge on the back. The blade is fixed to a wooden handle, in Europe usually made from ash due to its strength and ability to deal with repeated impac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hook
A hook is a tool consisting of a length of material, typically metal, that contains a portion that is curved or indented, such that it can be used to grab onto, connect, or otherwise attach itself onto another object. In a number of uses, one end of the hook is pointed, so that this end can pierce another material, which is then held by the curved or indented portion. Some kinds of hooks, particularly fish hooks, also have a barb, a backwards-pointed projection near the pointed end of the hook to ensure that once the hook is embedded in its target, it can not easily be removed. Variations * Bagging hook, a large sickle or reaping hook used for harvesting grain * Bondage hook, used in sexual bondage play * Cabin hook, a hooked bar that engages into an eye screw, used on doors * Cap hook, hat ornament of the 15th and 16th centuries * Cargo hook (helicopter), different types of hook systems for helicopters * Crochet hook, used for crocheting thread or yarn * Drapery hook, for ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guisarme
A guisarme (sometimes gisarme, giserne or bisarme) is a pole weapon used in Europe primarily between 1000 and 1400. Its origin is likely Germanic, from the Old High German , literally "weeding iron". Like many medieval polearms, the exact early form of the weapon is hard to define from literary references, and the identification of surviving weapons can be speculative. Possible interpretations of form Two main modern schools of thought exist: # Like most polearms the guisarme was developed by peasants by combining hand tools with long poles: in this case by putting a pruning hook onto a spear shaft. According to Sir Guy Francis Laking, among the polearms, the guisarme was second only to the spear in importance for the medieval soldier class. In fact, it was so effective by the 13th century there was active support for its banishment from the battlefield. While early designs were simply a hook on the end of a long pole, later designs implemented a small reverse spike on the back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
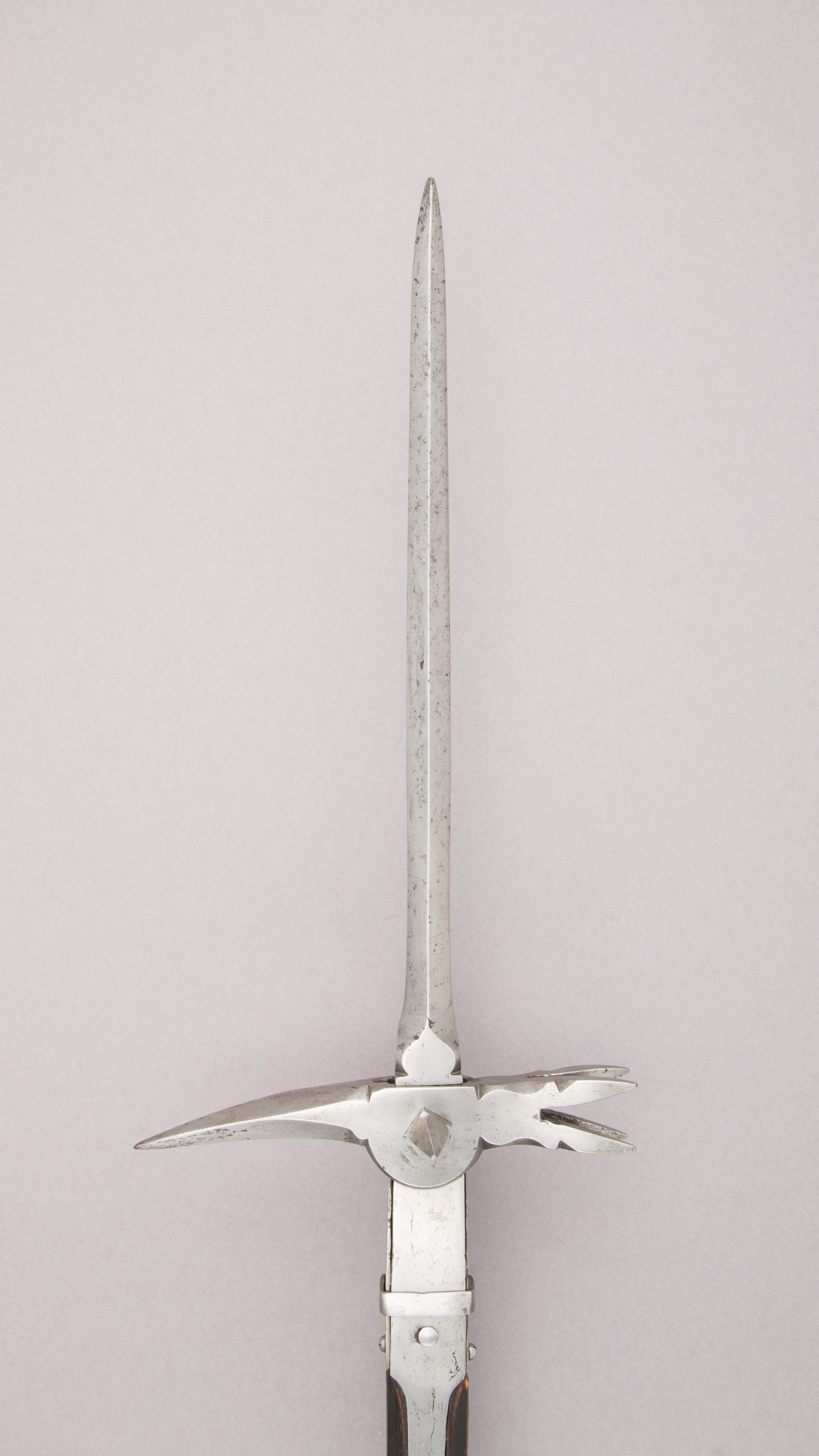
Lucerne Hammer
The Lucerne hammer ( ) is a type of polearm which was popular in Swiss armies during the 15th to 17th centuries. It was a combination of the bec de corbin and a pronged war hammer. Origins The weapon originates from Switzerland, and the name comes from a discovery of many of these weapons in Lucerne, Switzerland. Design The hammer-part of the Lucerne hammer is a three-to-four-pronged head mounted atop a 2-meter-long (7 foot) polearm shaft. It bears a long spike on its reverse, and an even longer spike extending from the top. They are occasionally found to have spikes on the side of the head as well. Use The Lucerne hammer requires both hands for effective handling. As a modified polearm, Lucerne hammers have multiple functions in battle. The forward-pointing spike could be used for spearing, while the hammer proved effective at puncturing or smashing armour. Like many other polearms, the Lucerne hammer was also used for dismounting the enemy. The long pole increased the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halberd
A halberd (also called halbard, halbert or Swiss voulge) is a two-handed pole weapon that came to prominent use during the 13th, 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries. The word ''halberd'' is cognate with the German word ''Hellebarde'', deriving from Middle High German ''halm'' (handle) and ''barte'' (battleaxe) joined to form ''helmbarte''. Troops that used the weapon were called halberdiers. The halberd consists of an axe blade topped with a spike mounted on a long shaft. It always has a hook or thorn on the back side of the axe blade for grappling mounted combatants. It is very similar to certain forms of the voulge in design and usage. The halberd was usually 1.5 to 1.8 metres (5 to 6 feet) long. The word has also been used to describe a weapon of the Early Bronze Age in Western Europe. This consisted of a blade mounted on a pole at a right angle. History The halberd was inexpensive to produce and very versatile in battle. As the halberd was eventually refined, its point was mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blunt Trauma
Blunt trauma, also known as blunt force trauma or non-penetrating trauma, is physical traumas, and particularly in the elderly who fall. It is contrasted with penetrating trauma which occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body, creating an open wound and bruise. Blunt trauma can result in contusions, abrasions, lacerations, internal hemorrhages, bone fractures, as well as death. Blunt trauma represents a significant cause of disability and death in people under the age of 35 years worldwide. Classification Blunt abdominal trauma Blunt abdominal trauma (BAT) represents 75% of all blunt trauma and is the most common example of this injury. 75% of BAT occurs in motor vehicle crashes, in which rapid deceleration may propel the driver into the steering wheel, dashboard, or seatbelt, causing contusions in less serious cases, or rupture of internal organs from briefly increased intraluminal pressure in the more serious, depending on the force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flail (weapon)
A flail is a weapon consisting of a striking head attached to a handle by a flexible rope, strap, or chain. The chief tactical virtue of the flail was its capacity to strike around a defender's shield or parry. Its chief liability was a lack of precision and the difficulty of using it in close combat, or closely-ranked formations. There are two broad types of flail: a long, two-handed infantry weapon with a cylindrical head, and a shorter weapon with a round metal striking head. The longer cylindrical-headed flail is a hand weapon derived from the agricultural tool of the same name, commonly used in threshing. It was primarily considered a peasant's weapon, and while not common, they were deployed in Germany and Central Europe in the later Late Middle Ages. The smaller, more spherical-headed flail appears to be even less common; it appears occasionally in artwork from the 15th century onward, but many historians have expressed doubts that it ever saw use as an actual military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
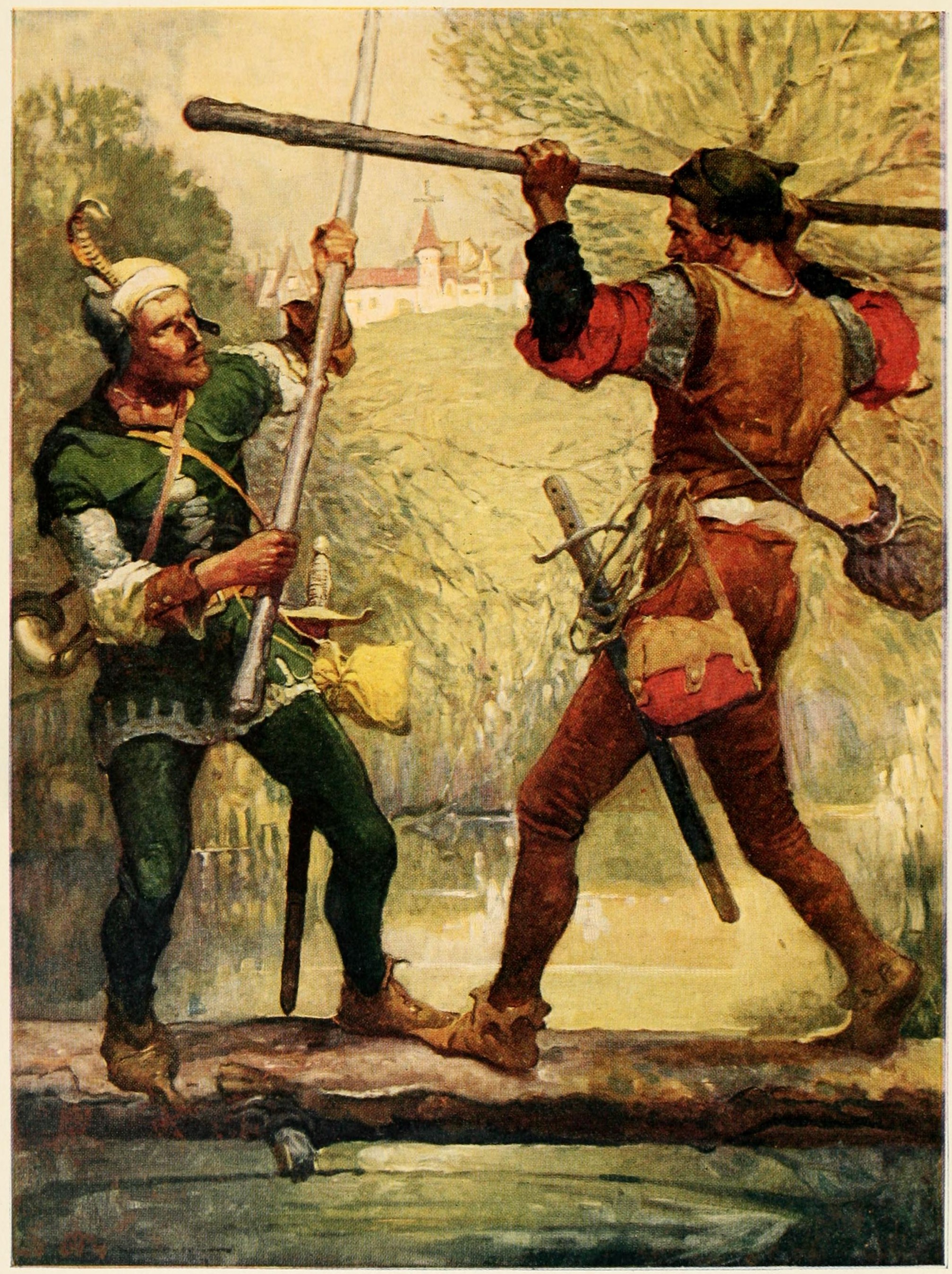
Quarterstaff
A quarterstaff (plural quarterstaffs or quarterstaves), also short staff or simply staff is a traditional European pole weapon, which was especially prominent in England during the Early Modern period. The term is generally accepted to refer to a shaft of hardwood from long, sometimes with a metal tip, ferrule, or spike at one or both ends. The term "short staff" compares this to the "long staff" based on the pike with a length in excess of . The height of the staff should be around the same as the user plus their hand set upright on their head (approximately ). Etymology The name "quarterstaff" is first attested in the mid-16th century. The "quarter" possibly refers to the means of production, the staff being made from quartersawn hardwood (as opposed to a staff of lower quality made from conventionally sawn lumber or from a tree branch).OED; The possibility that the name derives from the way the staff is held, the right hand grasping it one-quarter of the distance from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)