|
Megaliths In The Netherlands
Megalithic architecture appeared in what is now the Netherlands during the Neolithic period, especially in the northeast. Megalithic structures, i.e. buildings made of large upright stones, occur in various forms and functions, mainly as Grave, burial sites, temples or menhirs (stones standing alone or in a formation). In the Netherlands, only burial complexes are known. These large stone tombs () were built between 3470 and 3250 BC by members of the Western Group of the Funnelbeaker culture (''TBK'') and were used until about 2760 BC. After the end of the Funnelbeaker culture in the Late Neolithic, the sites were reused by the Single Grave culture and the Bell Beaker culture during the ensuing Early Bronze Age and, to a lesser extent, into the Middle Ages.Of the original 100 megalithic tombs in the Netherlands, 54 are still preserved today. Of these, 52 are located in the province of Drenthe. Two more are in the Groningen (province), province of Groningen, one of which has been tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunebed D27 2020
A dolmen () or portal tomb is a type of single-chamber megalithic tomb, usually consisting of two or more upright megaliths supporting a large flat horizontal capstone or "table". Most date from the early Neolithic (40003000 BCE) and were sometimes covered with earth or smaller stones to form a tumulus (burial mound). Small pad-stones may be wedged between the cap and supporting stones to achieve a level appearance.Murphy (1997), 43 In many instances, the covering has eroded away, leaving only the stone "skeleton". The Korean Peninsula is home to the world's highest concentration of dolmens,UNESCO World Heritage List. "Gochang, Hwasun and Ganghwa Dolmen Sites." https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/977 including "cemeteries" consisting of 30–100 examples located in close proximity to each other; with over 35,000 dolmens, Korea alone (for unknown reasons) accounts for approximately 40% of the global total. History It remains unclear when, why and by whom the earliest dolmens wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overijssel
Overijssel (, ; nds, Oaveriessel ; german: Oberyssel) is a Provinces of the Netherlands, province of the Netherlands located in the eastern part of the country. The province's name translates to "across the IJssel", from the perspective of the Bishopric of Utrecht, Episcopal principality of Utrecht by which it was held until 1528. The capital city of Overijssel is Zwolle (pop. 127,497) and the largest city is Enschede (pop. 158,986). The province had a population of 1,162,215 as of November 2019. The land mostly consists of grasslands and some forests (including Sallandse Heuvelrug National Park); it also borders a small part of the IJsselmeer to the west. Geography Overijssel is bordered by Germany (Lower Saxony and North Rhine-Westphalia) to the east, the Achterhoek region of Gelderland to the south, the Veluwe region of Gelderland and Flevoland to the west, and Friesland and the former moors of Drenthe to the north. Overijssel comprises three regions: Kop van Overijssel in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacial Erratic
A glacial erratic is glacially deposited rock differing from the type of rock native to the area in which it rests. Erratics, which take their name from the Latin word ' ("to wander"), are carried by glacial ice, often over distances of hundreds of kilometres. Erratics can range in size from pebbles to large boulders such as Big Rock () in Alberta. Geologists identify erratics by studying the rocks surrounding the position of the erratic and the composition of the erratic itself. Erratics are significant because: *They can be transported by glaciers, and they are thereby one of a series of indicators which mark the path of prehistoric glacier movement. Their lithographic origin can be traced to the parent bedrock, allowing for confirmation of the ice flow route. *They can be transported by ice rafting. This allows quantification of the extent of glacial flooding resulting from ice dam failure which release the waters stored in proglacial lakes such as Lake Missoula. Erratics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or ''granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) contain almost no dark minerals. Granite is nearly alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
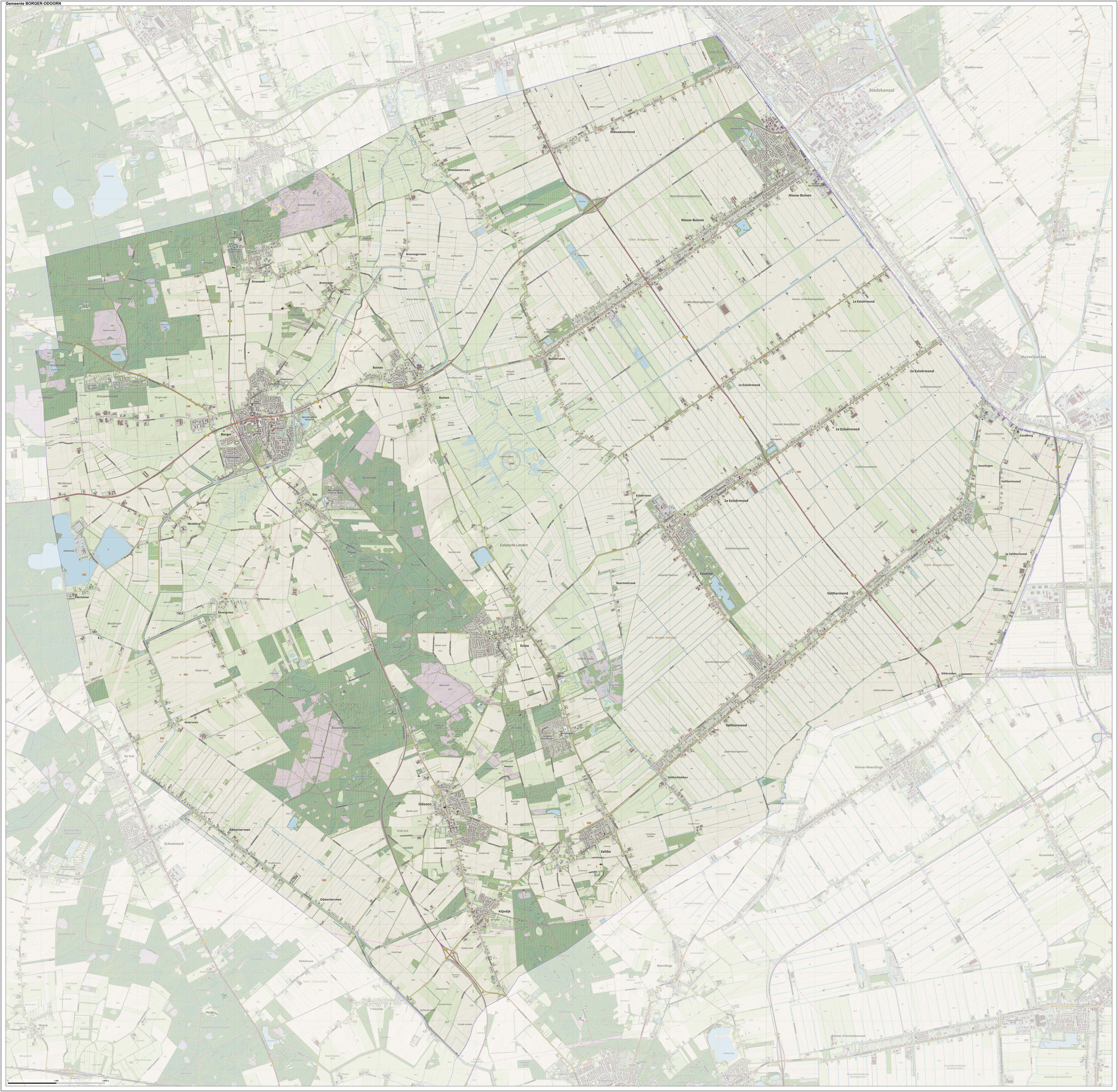
Borger-Odoorn
Borger-Odoorn () is a municipality in the northeastern Netherlands in the province of Drenthe. The local Hunebedcentrum Borger features several megaliths (or 'hunebeds') associated with the neolithic and mesolithic Funnelbeaker culture, as well as recreations of historical houses. Population centers Topography ''Dutch Topographic map of the municipality of Borger-Odoorn, June 2015.'' Notable people * Albert Meems (1888 in Nieuw-Buinen – after 1957) a Dutch spy for Germany in the Second World War * Pieter van Boven (1898 – 1952) a Dutch fencer, competed at the 1924 Summer Olympics * Egbert Schuurman (born 1937 in Borger) a Dutch engineer, philosopher and politician * Henk Nienhuis (1941 in Nieuw-Buinen – 2017) a Dutch footballer and manager. * Henk G. Sol (born 1951 in Borger) a Dutch organizational theorist and academic * Carsten de Dreu (born 1966 in Borger) Professor of Psychology at Leiden University and Behavioral Economics at the University of Amsterda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Egges Van Giffen
Albert Egges van Giffen (14 March 1884 – 31 May 1973) was a Dutch archaeologist. Van Giffen worked at the University of Groningen and University of Amsterdam, where he was a professor of Prehistory and Germanic archaeology. He worked most of his career in the Northern provinces of the Netherlands, where he specialized in hunebeds and tumuli. Career Van Giffen was born on 14 March 1884 in Noordhorn to Jan van Giffen, a predikant, and Hendrika Post. He attended the gymnasium in Zutphen and Sneek. Van Giffen studied zoology and biology at the University of Groningen between 1904 and 1910. He obtained his doctorate there in 1913 with a German-language thesis titled: "Die Fauna der Wurten" under supervision of J.F. van Bemmelen. Van Giffen was employed as curator at the Rijksmuseum van Oudheden in Leiden from 1912 to 1917. He then moved back to Groningen to work at the zoological laboratory. Van Giffen was employed by the University of Groningen as lector Prehistory and Germanic A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Hendrik Holwerda
Jan, JaN or JAN may refer to: Acronyms * Jackson, Mississippi (Amtrak station), US, Amtrak station code JAN * Jackson-Evers International Airport, Mississippi, US, IATA code * Jabhat al-Nusra (JaN), a Syrian militant group * Japanese Article Number, a barcode standard compatible with EAN * Japanese Accepted Name, a Japanese nonproprietary drug name * Job Accommodation Network, US, for people with disabilities * ''Joint Army-Navy'', US standards for electronic color codes, etc. * '' Journal of Advanced Nursing'' Personal name * Jan (name), male variant of ''John'', female shortened form of ''Janet'' and ''Janice'' * Jan (Persian name), Persian word meaning 'life', 'soul', 'dear'; also used as a name * Ran (surname), romanized from Mandarin as Jan in Wade–Giles * Ján, Slovak name Other uses * January, as an abbreviation for the first month of the year in the Gregorian calendar * Jan (cards), a term in some card games when a player loses without taking any tricks or scoring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the adven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Collings Lukis
Rev. William Collings Lukis MA. FSA (8 April 1817 in Guernsey – 7 December 1892 in Wath, North Riding of Yorkshire) was a British antiquarian, archeologist and polymath. William Collings Lukis was the third son of Frederick Corbin Lukis, the Colonel of Guernsey Militia. He was educated at Trinity College, Cambridge. He was married to Lucy Adelaide, daughter of Admiral Sir Thomas Fellowes. Lukis is best remembered in England for his work on Church Bells which was published in 1857. He was the first person to publish a collection of bell descriptions, chiefly from Wiltshire. He was a founder member of the Wiltshire Archaeological and Natural History Society and an authority on perspective drawing. It is his drawings of the Saxon church in Bradford on Avon, where he was curate from 1841 to 1846, that formed the basis for the illustrations for WH Jones's article on the Saxon Church in WAM V, and acknowledged by Jones in WAM XIII. Lukis is also remembered for his work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonhardt Johannes Friedrich (1921–2014), German political author, publicist, and historian
{{surname, Leonhardt ...
Leonhardt is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * David Leonhardt (born 1973), a business journalist, and Pulitzer Prize winner with the New York Times * Fritz Leonhardt (1909–1999), German civil engineer * Gustav Leonhardt (1928–2012), Dutch musician * Paul Saladin Leonhardt, (1877–1934), German chess master * Robert Leonhardt (1877–1923), Austria-born baritone * Wolfgang Leonhard Wolfgang Leonhard (16 April 1921 – 17 August 2014) was a German political author and historian of the Soviet Union, the German Democratic Republic and Communism. A German Communist whose family had fled Hitler's Germany and who was educat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titia Brongersma
Titia Brongersma (Dokkum, Friesland, 1650 – Groningen, 1700) was a Frisians, Frisian poet of the late 17th century. Her book, ''De bron-swaan'', was published in 1686 and is virtually the only trace of her literary activity. She also gained prominence for excavating a dolmen at Borger, Netherlands in 1685. Brongersma became widely known for her excavation of the dolmen in Borger, Netherlands, Borger in Drenthe. She heard about the dolmen (these are called ''hunebed'' in Dutch, plural ''hunebedden'') when she visited Jan Laurens Lenting(h), the ''schout'' of Borger, around Pentecost 1685. In July she had one of the ''hunebedden'' excavated; to everyone's surprise the dolmen was a grave site, rather than just a heap of rocks created by giants. She wrote a poem on the topic, "Ode on the hunebed". Selected works * ''De bron-swaan of mengeldigten van Titia Brongersma'', 1686 ** Eric Miller, ''The Swan of the Well by Titia Brongersma''. 2020, McGill-Queen’s University Press, Montre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant
In folklore, giants (from Ancient Greek: '' gigas'', cognate giga-) are beings of human-like appearance, but are at times prodigious in size and strength or bear an otherwise notable appearance. The word ''giant'' is first attested in 1297 from Robert of Gloucester's chronicle. It is derived from the ''Gigantes'' ( grc-gre, Γίγαντες) of Greek mythology. Fairy tales such as '' Jack the Giant Killer'' have formed the modern perception of giants as dimwitted ogres, sometimes said to eat humans, while other giants tend to eat the livestock. The antagonist in ''Jack and the Beanstalk'' is often described as a giant. In some more recent portrayals, like those of Jonathan Swift and Roald Dahl, some giants are both intelligent and friendly. Literary and cultural analysis Giants appear in the folklore of cultures worldwide as they represent a relatively simple concept. Representing the human body enlarged to the point of being monstrous, giants evoke terror and remind humans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

