|
Medial Temporal Lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain. The temporal lobe is involved in processing sensory input into derived meanings for the appropriate retention of visual memory, language comprehension, and emotion association. ''Temporal'' refers to the head's temples. Structure The temporal lobe consists of structures that are vital for declarative or long-term memory. Declarative (denotative) or explicit memory is conscious memory divided into semantic memory (facts) and episodic memory (events). Medial temporal lobe structures that are critical for long-term memory include the hippocampus, along with the surrounding hippocampal region consisting of the perirhinal, parahippocampal, and entorhinal neocortical regions. The hippocampus is critical for memory formation, and the surrounding medial temporal cortex is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrum
The cerebrum, telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb. In the human brain, the cerebrum is the uppermost region of the central nervous system. The cerebrum develops prenatally from the forebrain (prosencephalon). In mammals, the dorsal telencephalon, or pallium, develops into the cerebral cortex, and the ventral telencephalon, or subpallium, becomes the basal ganglia. The cerebrum is also divided into approximately symmetric left and right cerebral hemispheres. With the assistance of the cerebellum, the cerebrum controls all voluntary actions in the human body. Structure The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. Depending upon the position of the animal it lies either in front or on top of the brainstem. In humans, the cerebrum is the largest and best-developed of the five majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Memory
Semantic memory refers to general world knowledge that humans have accumulated throughout their lives. This general knowledge (word meanings, concepts, facts, and ideas) is intertwined in experience and dependent on culture. We can learn about new concepts by applying our knowledge learned from things in the past. Semantic memory is distinct from episodic memory, which is our memory of experiences and specific events that occur during our lives, from which we can recreate at any given point. For instance, semantic memory might contain information about what a cat is, whereas episodic memory might contain a specific memory of petting a particular cat. Semantic memory and episodic memory are both types of explicit memory (or declarative memory), that is, memory of facts or events that can be consciously recalled and "declared". The counterpart to declarative or explicit memory is nondeclarative memory or implicit memory. History The idea of semantic memory was first int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
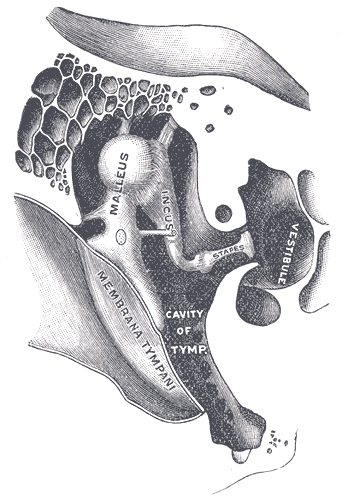
Cochlea
The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the Organ of Corti, the sensory organ of hearing, which is distributed along the partition separating the fluid chambers in the coiled tapered tube of the cochlea. The name cochlea derives . Structure The cochlea (plural is cochleae) is a spiraled, hollow, conical chamber of bone, in which waves propagate from the base (near the middle ear and the oval window) to the apex (the top or center of the spiral). The spiral canal of the cochlea is a section of the bony labyrinth of the inner ear that is approximately 30 mm long and makes 2 turns about the modiolus. The cochlear structures include: * Three ''scalae'' or chambers: ** the vestibular duct or ''scala vestibuli'' (containing perilymph), which lies superior to the cochlear duct and abuts the oval window ** the ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
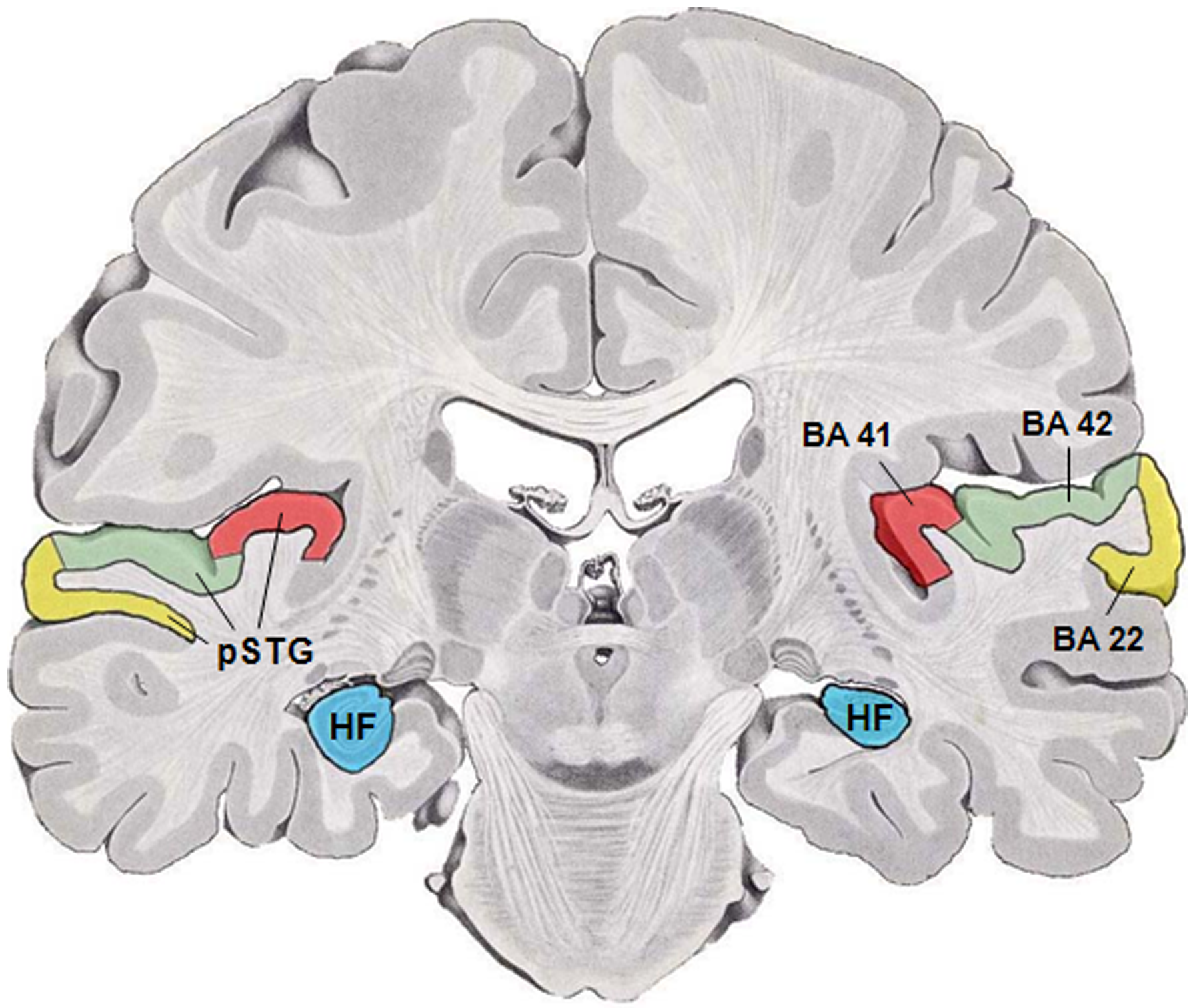
Superior Temporal Gyrus
The superior temporal gyrus (STG) is one of three (sometimes two) gyri in the temporal lobe of the human brain, which is located laterally to the head, situated somewhat above the external ear. The superior temporal gyrus is bounded by: * the lateral sulcus above; * the superior temporal sulcus (not always present or visible) below; * an imaginary line drawn from the preoccipital notch to the lateral sulcus posteriorly. The superior temporal gyrus contains several important structures of the brain, including: * Brodmann areas 41 and 42, marking the location of the auditory cortex, the cortical region responsible for the sensation of sound; * Wernicke's area, Brodmann 22p, an important region for the processing of speech so that it can be understood as language. The superior temporal gyrus contains the auditory cortex, which is responsible for processing sounds. Specific sound frequencies map precisely onto the auditory cortex. This auditory (or tonotopic) map is similar to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Auditory Cortex
The auditory cortex is the part of the temporal lobe that processes auditory information in humans and many other vertebrates. It is a part of the auditory system, performing basic and higher functions in hearing, such as possible relations to language switching.Cf. Pickles, James O. (2012). ''An Introduction to the Physiology of Hearing'' (4th ed.). Bingley, UK: Emerald Group Publishing Limited, p. 238. It is located bilaterally, roughly at the upper sides of the temporal lobes – in humans, curving down and onto the medial surface, on the superior temporal plane, within the lateral sulcus and comprising parts of the transverse temporal gyri, and the superior temporal gyrus, including the planum polare and planum temporale (roughly Brodmann areas 41 and 42, and partially 22). The auditory cortex takes part in the spectrotemporal, meaning involving time and frequency, analysis of the inputs passed on from the ear. The cortex then filters and passes on the information to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearing (sense)
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science. Sound may be heard through solid, liquid, or gaseous matter. It is one of the traditional five senses. Partial or total inability to hear is called hearing loss. In humans and other vertebrates, hearing is performed primarily by the auditory system: mechanical waves, known as vibrations, are detected by the ear and transduced into nerve impulses that are perceived by the brain (primarily in the temporal lobe). Like touch, audition requires sensitivity to the movement of molecules in the world outside the organism. Both hearing and touch are types of mechanosensation. Hearing mechanism There are three main components of the human auditory system: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. Outer ear The outer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amygdala
The amygdala (; plural: amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is one of two almond-shaped clusters of nuclei located deep and medially within the temporal lobes of the brain's cerebrum in complex vertebrates, including humans. Shown to perform a primary role in the processing of memory, decision making, and emotional responses (including fear, anxiety, and aggression), the amygdalae are considered part of the limbic system. The term "amygdala" was first introduced by Karl Friedrich Burdach in 1822. Structure The regions described as amygdala nuclei encompass several structures of the cerebrum with distinct connectional and functional characteristics in humans and other animals. Among these nuclei are the basolateral complex, the cortical nucleus, the medial nucleus, the central nucleus, and the intercalated cell clusters. The basolateral complex can be further subdivided into the lateral, the basal, and the accessory ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-term Memory
Long-term memory (LTM) is the stage of the Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model in which informative knowledge is held indefinitely. It is defined in contrast to short-term and working memory, which persist for only about 18 to 30 seconds. Long-term memory is commonly labelled as explicit memory ( declarative), as well as episodic memory, semantic memory, autobiographical memory, and implicit memory ( procedural memory). Dual-store memory model According to Miller, whose paper in 1956 popularized the theory of the "magic number seven", short-term memory is limited to a certain number of chunks of information, while long-term memory has a limitless store. Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model According to the dual store memory model proposed by Richard C. Atkinson and Richard Shiffrin in 1968, memories can reside in the short-term "buffer" for a limited time while they are simultaneously strengthening their associations in long-term memory. When items are first presented, they en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prefrontal Cortex
In mammalian brain anatomy, the prefrontal cortex (PFC) covers the front part of the frontal lobe of the cerebral cortex. The PFC contains the Brodmann areas BA8, BA9, BA10, BA11, BA12, BA13, BA14, BA24, BA25, BA32, BA44, BA45, BA46, and BA47. The basic activity of this brain region is considered to be orchestration of thoughts and actions in accordance with internal goals. Many authors have indicated an integral link between a person's will to live, personality, and the functions of the prefrontal cortex. This brain region has been implicated in executive functions, such as planning, decision making, short-term memory, personality expression, moderating social behavior and controlling certain aspects of speech and language. Executive function relates to abilities to differentiate among conflicting thoughts, determine good and bad, better and best, same and different, future consequences of current activities, working toward a defined goal, prediction of outc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entorhinal Cortex
The entorhinal cortex (EC) is an area of the brain's allocortex, located in the medial temporal lobe, whose functions include being a widespread network hub for memory, navigation, and the perception of time.Integrating time from experience in the lateral entorhinal cortex Albert Tsao, Jørgen Sugar, Li Lu, Cheng Wang, James J. Knierim, May-Britt Moser & Edvard I. Moser Naturevolume 561, pages57–62 (2018) The EC is the main interface between the hippocampus and neocortex. The EC-hippocampus system plays an important role in declarative (autobiographical/episodic/semantic) memories and in particular spatial memories including memory formation, memory consolidation, and memory optimization in sleep. The EC is also responsible for the pre-processing (familiarity) of the input signals in the reflex nictitating membrane response of classical trace conditioning; the association of impulses from the eye and the ear occurs in the entorhinal cortex. Structure In rodents, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parahippocampal Gyrus
The parahippocampal gyrus (or hippocampal gyrus') is a grey matter cortical region of the brain that surrounds the hippocampus and is part of the limbic system. The region plays an important role in memory encoding and retrieval. It has been involved in some cases of hippocampal sclerosis. Asymmetry has been observed in schizophrenia. Structure The anterior part of the gyrus includes the perirhinal and entorhinal cortices. The term parahippocampal cortex is used to refer to an area that encompasses both the posterior parahippocampal gyrus and the medial portion of the fusiform gyrus. Function Scene recognition The parahippocampal place area (PPA) is a sub-region of the parahippocampal cortex that lies medially in the inferior temporo-occipital cortex. PPA plays an important role in the encoding and recognition of environmental scenes (rather than faces). fMRI studies indicate that this region of the brain becomes highly active when human subjects view topographical scene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perirhinal Cortex
The perirhinal cortex is a cortical region in the medial temporal lobe that is made up of Brodmann areas 35 and 36. It receives highly processed sensory information from all sensory regions, and is generally accepted to be an important region for memory. It is bordered caudally by postrhinal cortex or parahippocampal cortex (homologous regions in rodents and primates, respectively) and ventrally and medially by entorhinal cortex. Structure The perirhinal cortex is composed of two regions: areas 36 and 35. Area 36 is sometimes divided into three subdivisions: 36d is the most rostral and dorsal, 36r ventral and caudal, and 36c the most caudal. Area 35 can be divided in the same manner, into 35d and 35v (for dorsal and ventral, respectively). Area 36 is six-layered, dysgranular, meaning that its layer IV is relatively sparse. Area 35 is agranular cortex (lacking any cells in layer IV). Function The perirhinal cortex is involved in both visual perception and memory; it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |