|
Mauritius Sheldgoose
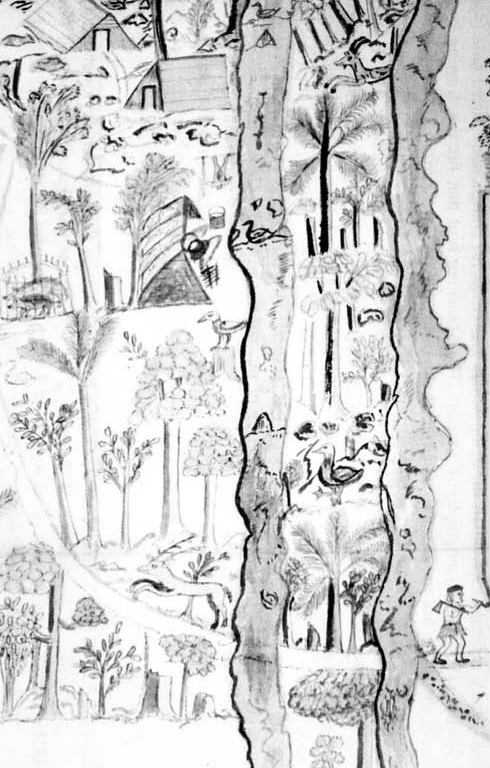
The Mauritius sheldgoose (''Alopochen mauritiana''), also known as the Mauritius shelduck, is an extinct species of sheldgoose that was endemic to the island of Mauritius. While geese were mentioned by visitors to Mauritius in the 17th century, few details were provided by these accounts. In 1893, a carpometacarpus wing-bone and a pelvis from the Mare aux Songes swamp were used to name a new species of comb duck, ''Sarcidiornis mauritianus''. These bones were connected to the contemporary accounts of geese and later determined to belong to a species related to the Egyptian goose, and placed in the sheldgoose genus ''Alopochen''. The Mauritius and Réunion sheldgoose may have descended from Egyptian geese that colonised the Mascarene islands. One contemporary account states that the Mauritius sheldgoose had wings that were half black and half white, and that they were not very large. It may also be depicted in one illustration. Fossil elements show that it was smaller than the Eg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
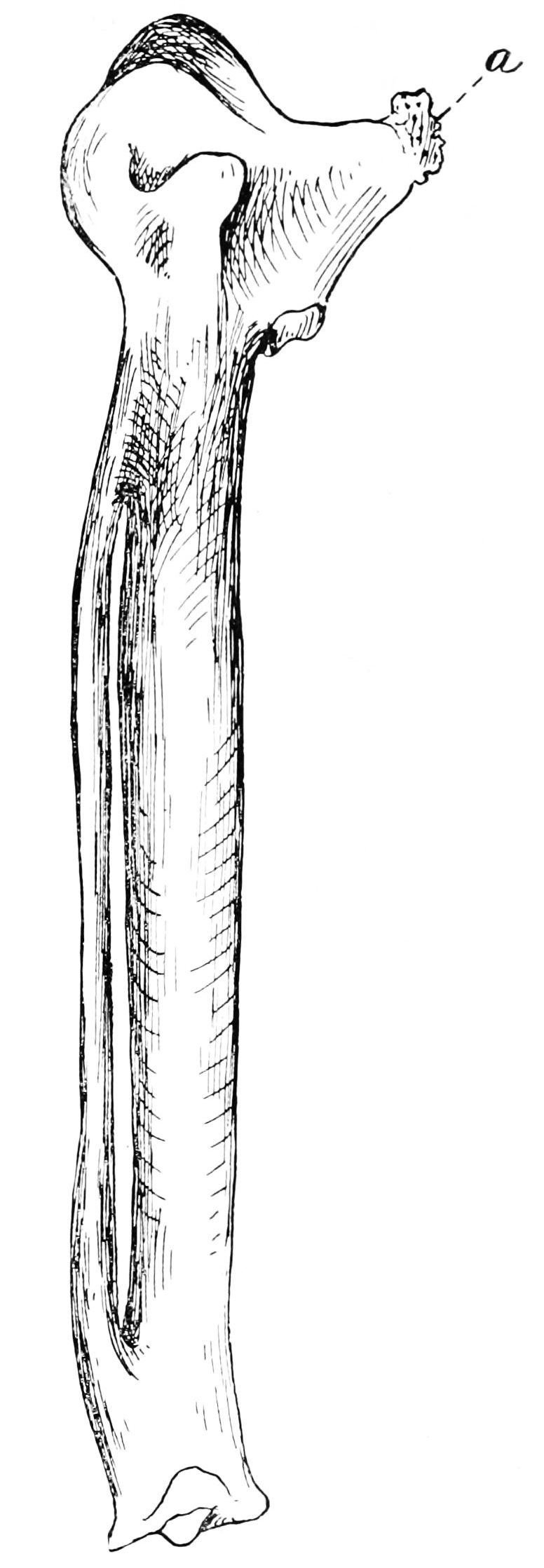
Carpometacarpus
The carpometacarpus is a bone found in the hands of birds. It results from the fusion of the carpal and metacarpal bone, and is essentially a single fused bone between the wrist and the knuckles. It is a smallish bone in most birds, generally flattened and with a large hole in the middle. In flightless birds, however, its shape may be slightly different, or it might be absent entirely. It forms the tip of the wing skeleton in birds. To it, most of the primary remiges attach. The alula, by contrast, is formed by the thumb, which does not completely fuse with the other hand-bones. Likewise, the tipmost primaries attach to the phalanx bones. To non-biologists the carpometacarpus may be best known from buffalo wings. Buffalo wings come in two basic sizes, a large angled one containing three major bones, and a smaller flat one containing only two. The bone missing in the latter is the carpometacarpus. See also * Carpometacarpal joint The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are five joint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geese
A goose (plural, : geese) is a bird of any of several waterfowl species in the family (biology), family Anatidae. This group comprises the genera ''Anser (bird), Anser'' (the grey geese and white geese) and ''Branta'' (the black geese). Some other birds, mostly related to the shelducks, have "goose" as part of their names. More distantly related members of the family Anatidae are swans, most of which are larger than true geese, and ducks, which are smaller. The term "goose" may refer to either a male or female bird, but when paired with "gander", refers specifically to a female one (the latter referring to a male). Young birds before fledging are called goslings. The List of collective nouns, collective noun for a group of geese on the ground is a gaggle; when in flight, they are called a skein, a team, or a wedge; when flying close together, they are called a plump. Etymology The word "goose" is a direct descendant of,''*ghans-''. In Germanic languages, the root gave Old E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles William Andrews
Charles William Andrews (30 October 1866 – 25 May 1924) F.R.S., was a British palaeontologist whose career as a vertebrate paleontologist, both as a curator and in the field, was spent in the services of the British Museum, Department of Geology. Biography Andrews was born in Hampstead, Middlesex . A graduate of the University of London, Andrews was awarded an assistant's position at the British Museum, after a competitive exam, in 1892. His first concerns were with fossil birds, and he described '' Aepyornis titan'', the extinct "Elephant Bird" of Madagascar (1894). He noticed the connections among widely separated flightless rails of Mauritius, the Chatham Islands and New Zealand and deduced that their flightless character had been independently evolved on the spot. Alfred Nicholson Leeds' gifts to the British Museum of Jurassic marine reptiles from the Oxford Clay of Peterborough elicited his interest in plesiosaurs and other sea-reptiles which culminated in a catalo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa across the Mozambique Channel. At Madagascar is the world's List of island countries, second-largest island country, after Indonesia. The nation is home to around 30 million inhabitants and consists of the island of Geography of Madagascar, Madagascar (the List of islands by area, fourth-largest island in the world), along with numerous smaller peripheral islands. Following the prehistoric breakup of the supercontinent Gondwana, Madagascar split from the Indian subcontinent around 90 million years ago, allowing native plants and animals to evolve in relative isolation. Consequently, Madagascar is a biodiversity hotspot; over 90% of wildlife of Madagascar, its wildlife is endemic. Human settlement of Madagascar occurred during or befo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malagasy Sheldgoose
The Malagasy sheldgoose (''Centrornis majori'') is an extinct monotypic species of large goose in the shelduck subfamily. It was described from subfossil remains radiocarbon dated to about 17,000 years ago, found in central Madagascar Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa .... References Malagasy sheldgoose Pleistocene birds of Africa Extinct birds of Madagascar Malagasy sheldgoose Fossil taxa described in 1897 {{duck-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emile Oustalet
Emil or Emile may refer to: Literature *''Emile, or On Education'' (1762), a treatise on education by Jean-Jacques Rousseau * ''Émile'' (novel) (1827), an autobiographical novel based on Émile de Girardin's early life *''Emil and the Detectives'' (1929), a children's novel *"Emil", nickname of the Kurt Maschler Award for integrated text and illustration (1982–1999) *''Emil i Lönneberga'', a series of children's novels by Astrid Lindgren Military *Emil (tank), a Swedish tank developed in the 1950s * Sturer Emil, a German tank destroyer People *Emil (given name), including a list of people with the given name ''Emil'' or ''Emile'' *Aquila Emil (died 2011), Papua New Guinean rugby league footballer Other * ''Emile'' (film), a Canadian film made in 2003 by Carl Bessai *Emil (river), in China and Kazakhstan See also * * *Aemilius (other) *Emilio (other) *Emílio (other) *Emilios (other) Emilios, or Aimilios, (Greek: Αιμίλιος) is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
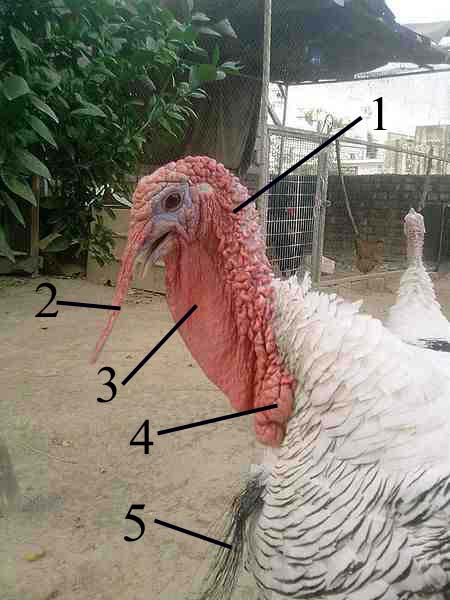
Caruncle (bird Anatomy)
A caruncle is defined as 'a small, fleshy excrescence that is a normal part of an animal's anatomy'. Within this definition, caruncles in birds include wattles (or dewlaps), combs, snoods, and earlobes. The term ''caruncle'' is derived from Latin ''caruncula'', the diminutive of ''carō'', "flesh". Taxonomy Caruncles are carnosities, often of bright colors such as red, blue, yellow or white. They can be present on the head, neck, throat, cheeks or around the eyes of some birds. They may be present as combs or crests and other structures near the beak, or, hanging from the throat or neck. Caruncles may be featherless, or, have small scattered feathers. In some species, they may form pendulous structures of erectile tissue, such as the snood of the domestic turkey. Caruncles are sometimes secondary sexual characteristics, having a more intense color or even a different color, developing as the male reaches sexual maturity. Function Caruncles are also ornamental elements used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs (sex organs) and the rectum, while the pelvic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcidiornis
''Sarkidiornis'' is a genus within the family ''Anatidae''. ''Sarkidiornis'' is sometimes considered a monotypic genus with its sole member the knob-billed duck The knob-billed duck (''Sarkidiornis melanotos''), or African comb duck, is a duck found in tropical wetlands in Sub-Saharan Africa, Madagascar and the Indian Subcontinent from northern India to Laos and extreme southern China. Most taxonomic au ... (''S. melanotos''), a cosmopolitan species. Most taxonomic authorities, however, split the species into two: References * https://www.itis.gov/servlet/SingleRpt/SingleRpt?search_topic=TSN&search_value=175243#null ITIS reference {{Taxonbar, from=Q2712557 Taxa named by Thomas Campbell Eyton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype Specimen
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessarily "typi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Gadow
Hans Friedrich Gadow (8 March 1855 – 16 May 1928) was a German-born ornithologist who worked in Britain. His work on the classification of birds based on anatomical and morphological characters was influential and made use of by Alexander Wetmore in his classification of North American birds. Gadow was born in Stary Kraków (Pomerania), the son of an inspector of the Prussian royal forests. He studied at the universities of Berlin, Jena and Heidelberg. At Jena he studied under Ernst Haeckel and at Heidelberg University under the anatomist Karl Gegenbaur. After graduation he travelled to the Natural History Museum in London in 1880 at the request of Albert Günther, to work on the museum's ''Catalogue of Birds''. Gadow also established the first new sequence of bird orders and families that departed from earlier works in being based on phylogenetic principles based on a comparison of anatomical and morphological features and made use of the studies made by Max Fürbringer. This se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Newton
Sir Edward Newton (10 November 1832 – 25 April 1897) was a British colonial administrator and ornithologist. He was born at Elveden Hall, Suffolk the sixth and youngest son of William Newton (MP for Ipswich), William Newton, MP. He was the brother of ornithologist Alfred Newton. He graduated from Magdelene College, Cambridge in 1857 and was one of the twenty founding members of the British Ornithologists' Union. Newton was the Chief Secretary (British Empire), Colonial Secretary for Mauritius from 1859 to 1877. From there he sent his brother a number of specimens, including the dodo and the Rodrigues solitaire, both already extinct. In 1878, Newton initiated the first laws anywhere specifically designed to protect indigenous land birds from persecution. Edward was later Colonial Secretary and Lieutenant-Governor of Jamaica (1877–1883). He married Mary Louisa Cranstoun, daughter of W.W.R. Kerr in 1869. She died the following year. He is commemorated in the binomial of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

_male.jpg)
