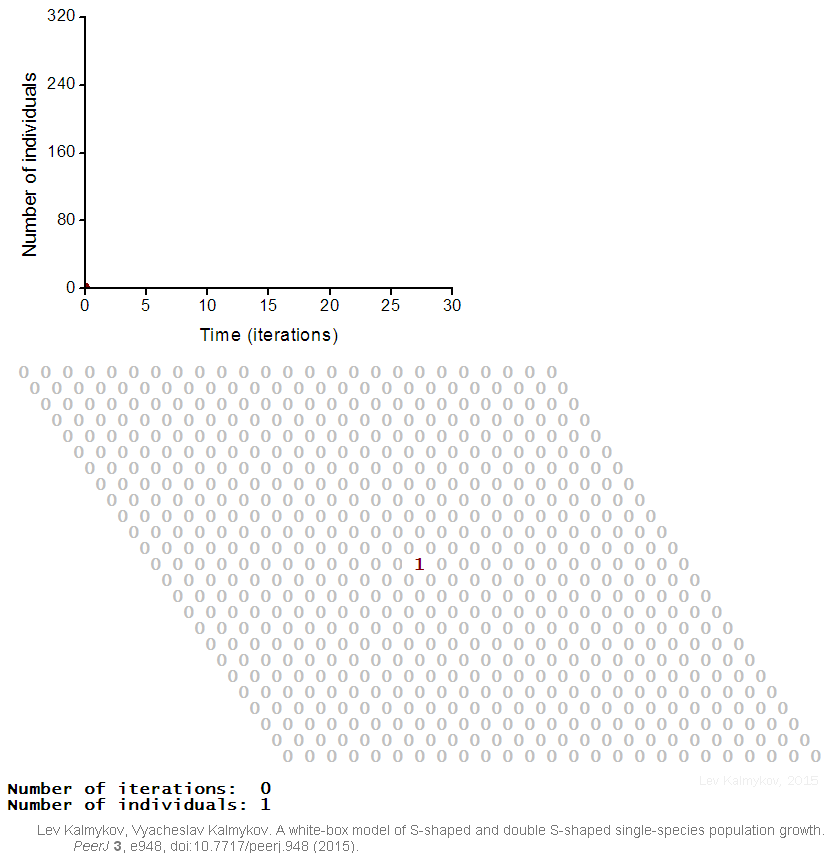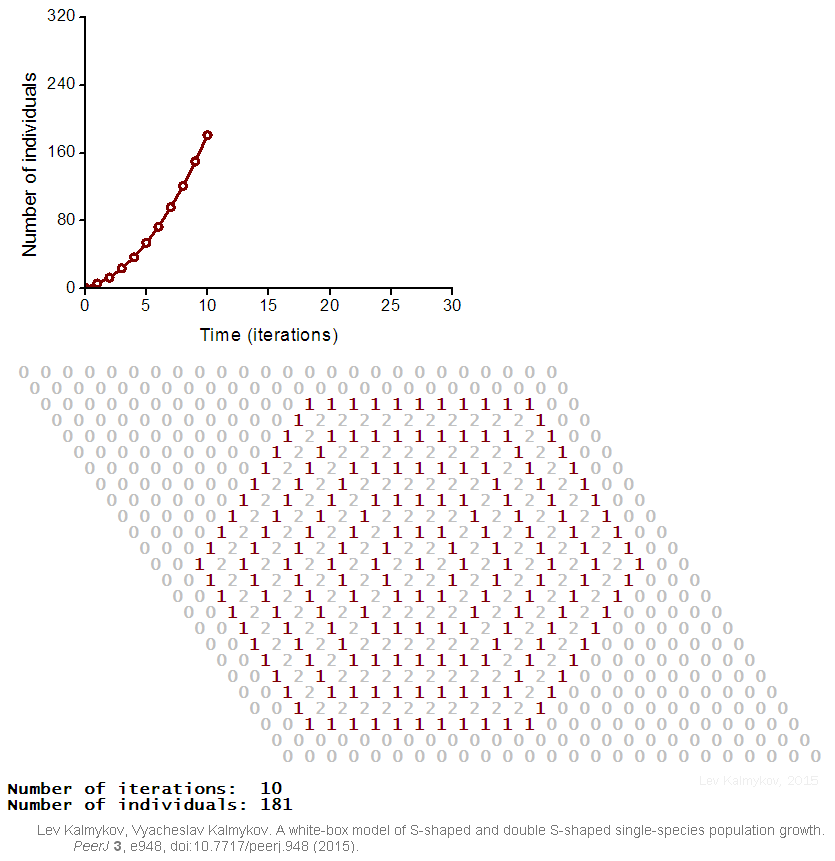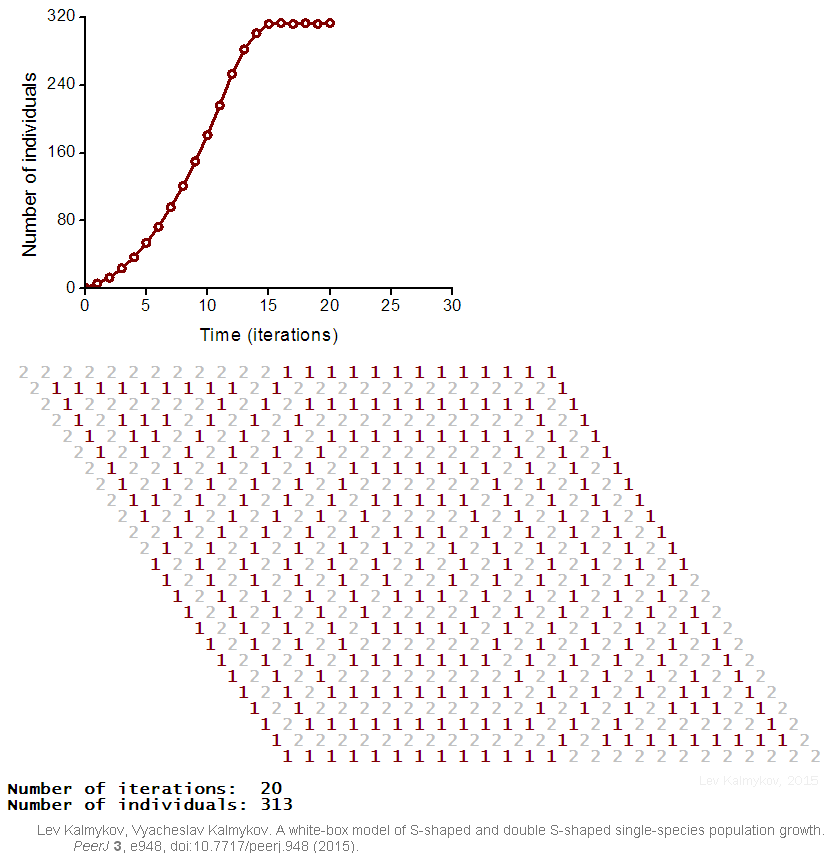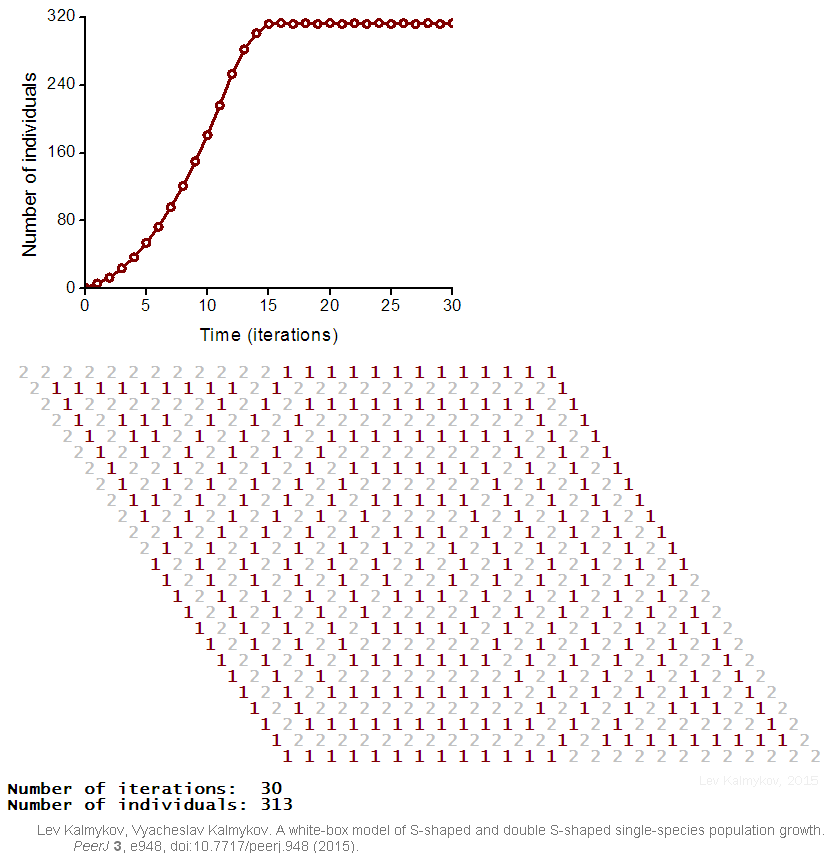
|
Matrix Population Models
Matrix population models are a specific type of population model that uses matrix algebra. Population models are used in population ecology to model the dynamics of wildlife or human populations. Matrix algebra, in turn, is simply a form of algebraic shorthand for summarizing a larger number of often repetitious and tedious algebraic computations. All populations can be modeled :N_=N_+B-D+I-E, where: *Nt+1 = abundance at time t+1 *Nt = abundance at time t *B = number of births within the population between Nt and Nt+1 *D = number of deaths within the population between Nt and Nt+1 *I = number of individuals immigrating into the population between Nt and Nt+1 *E = number of individuals emigrating from the population between Nt and Nt+1 This equation is called a BIDE model (Birth, Immigration, Death, Emigration model). Although BIDE models are conceptually simple, reliable estimates of the 5 variables contained therein (N, B, D, I and E) are often difficult to obtain. Usually a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Model
A population model is a type of mathematical model that is applied to the study of population dynamics. Rationale Models allow a better understanding of how complex interactions and processes work. Modeling of dynamic interactions in nature can provide a manageable way of understanding how numbers change over time or in relation to each other. Many patterns can be noticed by using population modeling as a tool. Ecological population modeling is concerned with the changes in parameters such as population size and age distribution within a population. This might be due to interactions with the environment, individuals of their own species, or other species. Population models are used to determine maximum harvest for agriculturists, to understand the dynamics of biological invasions, and for environmental conservation. Population models are also used to understand the spread of parasites, viruses, and disease. Another way populations models are useful are when species become enda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix Algebra
In abstract algebra, a matrix ring is a set of matrices with entries in a ring ''R'' that form a ring under matrix addition and matrix multiplication . The set of all matrices with entries in ''R'' is a matrix ring denoted M''n''(''R'')Lang, ''Undergraduate algebra'', Springer, 2005; V.§3. (alternative notations: Mat''n''(''R'') and ). Some sets of infinite matrices form infinite matrix rings. Any subring of a matrix ring is a matrix ring. Over a rng, one can form matrix rngs. When ''R'' is a commutative ring, the matrix ring M''n''(''R'') is an associative algebra over ''R'', and may be called a matrix algebra. In this setting, if ''M'' is a matrix and ''r'' is in ''R'', then the matrix ''rM'' is the matrix ''M'' with each of its entries multiplied by ''r''. Examples * The set of all matrices over ''R'', denoted M''n''(''R''). This is sometimes called the "full ring of ''n''-by-''n'' matrices". * The set of all upper triangular matrices over ''R''. * The set of al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Ecology
Population ecology is a sub-field of ecology that deals with the dynamics of species populations and how these populations interact with the environment, such as birth and death rates, and by immigration and emigration. The discipline is important in conservation biology, especially in the development of population viability analysis which makes it possible to predict the long-term probability of a species persisting in a given patch of habitat. Although population ecology is a subfield of biology, it provides interesting problems for mathematicians and statisticians who work in population dynamics. History In the 1940s ecology was divided into autecology—the study of individual species in relation to the environment—and synecology—the study of groups of species in relation to the environment. The term autecology (from Ancient Greek: αὐτο, ''aúto'', "self"; οίκος, ''oíkos'', "household"; and λόγος, ''lógos'', "knowledge"), refers to roughly the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Dynamics
Population dynamics is the type of mathematics used to model and study the size and age composition of populations as dynamical systems. History Population dynamics has traditionally been the dominant branch of mathematical biology, which has a history of more than 220 years,Malthus, Thomas Robert. An Essay on the Principle of Population: Library of Economics although over the last century the scope of mathematical biology has greatly expanded. The beginning of population dynamics is widely regarded as the work of Malthus, formulated as the Malthusian growth model. According to Malthus, assuming that the conditions (the environment) remain constant ('' ceteris paribus''), a population will grow (or decline) exponentially. This principle provided the basis for the subsequent predictive theories, such as the demographic studies such as the work of Benjamin Gompertz and Pierre François Verhulst in the early 19th century, who refined and adjusted the Malthusian demographic m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populations
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a census, a process of collecting, analysing, compiling, and publishing data regarding a population. Perspectives of various disciplines Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined criterion in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Demography is a social science which entails the statistical study of populations. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species who inhabit the same particular geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark And Recapture
Mark and recapture is a method commonly used in ecology to estimate an animal population's size where it is impractical to count every individual. A portion of the population is captured, marked, and released. Later, another portion will be captured and the number of marked individuals within the sample is counted. Since the number of marked individuals within the second sample should be proportional to the number of marked individuals in the whole population, an estimate of the total population size can be obtained by dividing the number of marked individuals by the proportion of marked individuals in the second sample. Other names for this method, or closely related methods, include capture-recapture, capture-mark-recapture, mark-recapture, sight-resight, mark-release-recapture, multiple systems estimation, band recovery, the Petersen method, and the Lincoln method. Another major application for these methods is in epidemiology, where they are used to estimate the completeness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Survival Rate
Survival rate is a part of survival analysis. It is the proportion of people in a study or treatment group still alive at a given period of time after diagnosis. It is a method of describing prognosis in certain disease conditions, and can be used for the assessment of standards of therapy. The survival period is usually reckoned from date of diagnosis or start of treatment. Survival rates are based on the population as a whole and cannot be applied directly to an individual. There are various types of survival rates (discussed below). They often serve as endpoints of clinical trials and should not be confused with mortality rates, a population metric. Overall survival Patients with a certain disease (for example, colorectal cancer) can die directly from that disease or from an unrelated cause (for example, a car accident). When the precise cause of death is not specified, this is called the overall survival rate or observed survival rate. Doctors often use mean overall surviv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leslie Matrix
The Leslie matrix is a discrete, age-structured model of population growth that is very popular in population ecology named after Patrick H. Leslie. The Leslie matrix (also called the Leslie model) is one of the most well-known ways to describe the growth of populations (and their projected age distribution), in which a population is closed to migration, growing in an unlimited environment, and where only one sex, usually the female, is considered. The Leslie matrix is used in ecology to model the changes in a population of organisms over a period of time. In a Leslie model, the population is divided into groups based on age classes. A similar model which replaces age classes with ontogenetic stages is called a Lefkovitch matrix, whereby individuals can both remain in the same stage class or move on to the next one. At each time step, the population is represented by a vector with an element for each age class where each element indicates the number of individuals currently in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Dynamics Of Fisheries
A fishery is an area with an associated fish or aquatic population which is harvested for its commercial or recreational value. Fisheries can be wild or farmed. Population dynamics describes the ways in which a given population grows and shrinks over time, as controlled by birth, death, and migration. It is the basis for understanding changing fishery patterns and issues such as habitat destruction, predation and optimal harvesting rates. The population dynamics of fisheries is used by fisheries scientists to determine sustainable yields. The basic accounting relation for population dynamics is the BIDE (Birth, Immigration, Death, Emigration) model, shown as: : ''N''1 = ''N''0 + ''B'' − ''D'' + ''I'' − ''E'' where ''N''1 is the number of individuals at time 1, ''N''0 is the number of individuals at time 0, ''B'' is the number of individuals born, ''D'' the number that died, ''I'' the number that immigrated, and ''E'' the number that emigrated between time 0 and time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Dynamics
Population dynamics is the type of mathematics used to model and study the size and age composition of populations as dynamical systems. History Population dynamics has traditionally been the dominant branch of mathematical biology, which has a history of more than 220 years,Malthus, Thomas Robert. An Essay on the Principle of Population: Library of Economics although over the last century the scope of mathematical biology has greatly expanded. The beginning of population dynamics is widely regarded as the work of Malthus, formulated as the Malthusian growth model. According to Malthus, assuming that the conditions (the environment) remain constant ('' ceteris paribus''), a population will grow (or decline) exponentially. This principle provided the basis for the subsequent predictive theories, such as the demographic studies such as the work of Benjamin Gompertz and Pierre François Verhulst in the early 19th century, who refined and adjusted the Malthusian demographic m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |