|
Mathieu Wavelet
The Mathieu equation is a linear second-order differential equation with periodic coefficients. The French mathematician, E. Léonard Mathieu, first introduced this family of differential equations, nowadays termed Mathieu equations, in his “Memoir on vibrations of an elliptic membrane” in 1868. "Mathieu functions are applicable to a wide variety of physical phenomena, e.g., diffraction, amplitude distortion, inverted pendulum, stability of a floating body, radio frequency quadrupole, and vibration in a medium with modulated density" Elliptic-cylinder wavelets This is a wide family of wavelet system that provides a multiresolution analysis. The magnitude of the detail and smoothing filters corresponds to first-kind Mathieu functions with odd characteristic exponent. The number of notches of these filters can be easily designed by choosing the characteristic exponent. Elliptic-cylinder wavelets derived by this method possess potential application in the fields of optics and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second-order Differential Equation
In mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more unknown functions and their derivatives. In applications, the functions generally represent physical quantities, the derivatives represent their rates of change, and the differential equation defines a relationship between the two. Such relations are common; therefore, differential equations play a prominent role in many disciplines including engineering, physics, economics, and biology. Mainly the study of differential equations consists of the study of their solutions (the set of functions that satisfy each equation), and of the properties of their solutions. Only the simplest differential equations are solvable by explicit formulas; however, many properties of solutions of a given differential equation may be determined without computing them exactly. Often when a closed-form expression for the solutions is not available, solutions may be approximated numerically using computers. The theory of dy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microstrip Antenna
In telecommunication, a microstrip antenna (also known as a printed antenna) usually means an antenna fabricated using photolithographic techniques on a printed circuit board (PCB). It is a kind of internal antenna. They are mostly used at microwave frequencies. An individual microstrip antenna consists of a patch of metal foil of various shapes (a patch antenna) on the surface of a PCB ( printed circuit board), with a metal foil ground plane on the other side of the board. Most microstrip antennas consist of multiple patches in a two-dimensional array. The antenna is usually connected to the transmitter or receiver through foil microstrip transmission lines. The radio frequency current is applied (or in receiving antennas the received signal is produced) between the antenna and ground plane. Microstrip antennas have become very popular in recent decades due to their thin planar profile which can be incorporated into the surfaces of consumer products, aircraft and missil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compact Support
In mathematics, the support of a real-valued function f is the subset of the function domain containing the elements which are not mapped to zero. If the domain of f is a topological space, then the support of f is instead defined as the smallest closed set containing all points not mapped to zero. This concept is used very widely in mathematical analysis. Formulation Suppose that f : X \to \R is a real-valued function whose domain is an arbitrary set X. The of f, written \operatorname(f), is the set of points in X where f is non-zero: \operatorname(f) = \. The support of f is the smallest subset of X with the property that f is zero on the subset's complement. If f(x) = 0 for all but a finite number of points x \in X, then f is said to have . If the set X has an additional structure (for example, a topology), then the support of f is defined in an analogous way as the smallest subset of X of an appropriate type such that f vanishes in an appropriate sense on its complement. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
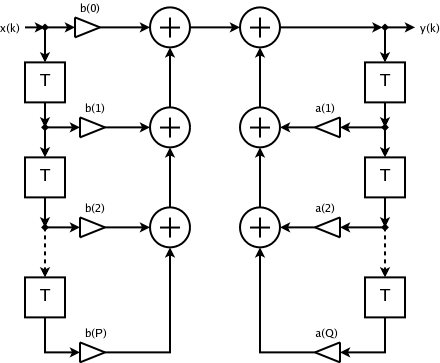
IIR Filter
Infinite impulse response (IIR) is a property applying to many linear time-invariant systems that are distinguished by having an impulse response h(t) which does not become exactly zero past a certain point, but continues indefinitely. This is in contrast to a finite impulse response (FIR) system in which the impulse response ''does'' become exactly zero at times t>T for some finite T, thus being of finite duration. Common examples of linear time-invariant systems are most electronic and digital filters. Systems with this property are known as ''IIR systems'' or ''IIR filters''. In practice, the impulse response, even of IIR systems, usually approaches zero and can be neglected past a certain point. However the physical systems which give rise to IIR or FIR responses are dissimilar, and therein lies the importance of the distinction. For instance, analog electronic filters composed of resistors, capacitors, and/or inductors (and perhaps linear amplifiers) are generally IIR filte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cascade Algorithm
In the mathematical topic of wavelet theory, the cascade algorithm is a numerical method for calculating function values of the basic scaling and wavelet functions of a discrete wavelet transform In numerical analysis and functional analysis, a discrete wavelet transform (DWT) is any wavelet transform for which the wavelets are discretely sampled. As with other wavelet transforms, a key advantage it has over Fourier transforms is temporal ... using an iterative algorithm. It starts from values on a coarse sequence of sampling points and produces values for successively more densely spaced sequences of sampling points. Because it applies the same operation over and over to the output of the previous application, it is known as the ''cascade algorithm''. Successive approximation The iterative algorithm generates successive approximations to ψ(''t'') or φ(''t'') from and filter coefficients. If the algorithm converges to a fixed point, then that fixed point is the basic scali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figura Mathieu2
Figura may refer to: * Bella Figura, one act ballet by Jiří Kylián * Fgura, town in the south of Malta * Figura etymologica, rhetoric al figure * Figura Serpentinata, style in painting and sculpture * Oliva figura, species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Olividae (olives) * translation of figure in some languages *Typology, a new testament theory of interpretation of events, people and sacraments of the Hebrew bible as figurative *''Figura,'' a 1938 essay by Erich Auerbach People * Anna Figura Anna Figura (born 6 February 1990) is a Polish ski mountaineer. Figura is born in Zakopane, and studies forestry at the University of Krakow.Monika StrojnyTrzy medale Polki na Mistrzostwach Europy . She is member of the ''Klub Skialpinistyczny K ... (b. 1990), Polish ski mountaineer * Katarzyna Figura (b. 1962), Polish actress * Paulina Figura (b. 1991), Polish ski mountaineer {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiresolution Analysis
A multiresolution analysis (MRA) or multiscale approximation (MSA) is the design method of most of the practically relevant discrete wavelet transforms (DWT) and the justification for the algorithm of the fast wavelet transform (FWT). It was introduced in this context in 1988/89 by Stephane Mallat and Yves Meyer and has predecessors in the microlocal analysis in the theory of differential equations (the ''ironing method'') and the pyramid methods of image processing as introduced in 1981/83 by Peter J. Burt, Edward H. Adelson anJames L. Crowley Definition A multiresolution analysis of the Lebesgue space L^2(\mathbb) consists of a sequence of nested subspaces ::\\dots\subset V_1\subset V_0\subset V_\subset\dots\subset V_\subset V_\subset\dots\subset L^2(\R) that satisfies certain self-similarity relations in time-space and scale-frequency, as well as completeness and regularity relations. * ''Self-similarity'' in ''time'' demands that each subspace ''Vk'' is invariant under sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelet
A wavelet is a wave-like oscillation with an amplitude that begins at zero, increases or decreases, and then returns to zero one or more times. Wavelets are termed a "brief oscillation". A taxonomy of wavelets has been established, based on the number and direction of its pulses. Wavelets are imbued with specific properties that make them useful for signal processing. For example, a wavelet could be created to have a frequency of Middle C and a short duration of roughly one tenth of a second. If this wavelet were to be convolved with a signal created from the recording of a melody, then the resulting signal would be useful for determining when the Middle C note appeared in the song. Mathematically, a wavelet correlates with a signal if a portion of the signal is similar. Correlation is at the core of many practical wavelet applications. As a mathematical tool, wavelets can be used to extract information from many different kinds of data, including but not limited to au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelets
A wavelet is a wave-like oscillation with an amplitude that begins at zero, increases or decreases, and then returns to zero one or more times. Wavelets are termed a "brief oscillation". A taxonomy of wavelets has been established, based on the number and direction of its pulses. Wavelets are imbued with specific properties that make them useful for signal processing. For example, a wavelet could be created to have a frequency of Middle C and a short duration of roughly one tenth of a second. If this wavelet were to be convolved with a signal created from the recording of a melody, then the resulting signal would be useful for determining when the Middle C note appeared in the song. Mathematically, a wavelet correlates with a signal if a portion of the signal is similar. Correlation is at the core of many practical wavelet applications. As a mathematical tool, wavelets can be used to extract information from many different kinds of data, including but not limited to aud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Figura Mathieu1
Figura may refer to: * Bella Figura, one act ballet by Jiří Kylián * Fgura, town in the south of Malta * Figura etymologica, rhetoric al figure * Figura Serpentinata, style in painting and sculpture * Oliva figura, species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Olividae (olives) * translation of figure in some languages *Typology, a new testament theory of interpretation of events, people and sacraments of the Hebrew bible as figurative *''Figura,'' a 1938 essay by Erich Auerbach People * Anna Figura Anna Figura (born 6 February 1990) is a Polish ski mountaineer. Figura is born in Zakopane, and studies forestry at the University of Krakow.Monika StrojnyTrzy medale Polki na Mistrzostwach Europy . She is member of the ''Klub Skialpinistyczny K ... (b. 1990), Polish ski mountaineer * Katarzyna Figura (b. 1962), Polish actress * Paulina Figura (b. 1991), Polish ski mountaineer {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horn Antenna
A horn antenna or microwave horn is an antenna that consists of a flaring metal waveguide shaped like a horn to direct radio waves in a beam. Horns are widely used as antennas at UHF and microwave frequencies, above 300 MHz. They are used as feed antennas (called feed horns) for larger antenna structures such as parabolic antennas, as standard calibration antennas to measure the gain of other antennas, and as directive antennas for such devices as radar guns, automatic door openers, and microwave radiometers. Their advantages are moderate directivity, low standing wave ratio (SWR), broad bandwidth, and simple construction and adjustment. One of the first horn antennas was constructed in 1897 by Bengali-Indian radio researcher Jagadish Chandra Bose in his pioneering experiments with microwaves. reprinted in The modern horn antenna was invented independently in 1938 by Wilmer Barrow and G. C. Southworth The development of radar in World War 2 stimulated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiresolution Analysis
A multiresolution analysis (MRA) or multiscale approximation (MSA) is the design method of most of the practically relevant discrete wavelet transforms (DWT) and the justification for the algorithm of the fast wavelet transform (FWT). It was introduced in this context in 1988/89 by Stephane Mallat and Yves Meyer and has predecessors in the microlocal analysis in the theory of differential equations (the ''ironing method'') and the pyramid methods of image processing as introduced in 1981/83 by Peter J. Burt, Edward H. Adelson anJames L. Crowley Definition A multiresolution analysis of the Lebesgue space L^2(\mathbb) consists of a sequence of nested subspaces ::\\dots\subset V_1\subset V_0\subset V_\subset\dots\subset V_\subset V_\subset\dots\subset L^2(\R) that satisfies certain self-similarity relations in time-space and scale-frequency, as well as completeness and regularity relations. * ''Self-similarity'' in ''time'' demands that each subspace ''Vk'' is invariant under sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |