|
Market Fundamentalism
Market fundamentalism, also known as free-market fundamentalism, is a term applied to a strong belief in the ability of unregulated ''laissez-faire'' or free-market capitalist policies to solve most economic and social problems. It is often used as pejorative by critics of said beliefs.''market fundemmentalism'', UNESCWA/ref> Origins and use Palagummi Sainath believes Jeremy Seabrook, a journalist and campaigner, first used the term. The term was used by Jonathan Benthall in an ''Anthropology Today'' editorial in 1991 and by John Langmore and John Quiggin in their 1994 book ''Work for All''. According to economist John Quiggin, the standard features of economic fundamentalist rhetoric are dogmatic assertions combined with the claim that anyone who holds contrary views is not a real economist. Quiggin, John. ''Rationalism and Rationality in Economics'', 1999, On Line Opinion,www.onlineopinion.com.au However, Kozul-Wright states in his book ''The Resistible Rise of Market Fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulatory Economics
Regulatory economics is the economics of regulation. It is the application of law by government or regulatory agencies for various purposes, including remedying market failure, protecting the environment and economic management. Regulation Regulation is generally defined as legislation imposed by a government on individuals and private sector firms in order to regulate and modify economic behaviors. Conflict can occur between public services and commercial procedures (e.g. maximizing profit), the interests of the people using these services (see market failure), and also the interests of those not directly involved in transactions (externalities). Most governments, therefore, have some form of control or regulation to manage these possible conflicts. The ideal goal of economic regulation is to ensure the delivery of a safe and appropriate service, while not discouraging the effective functioning and development of businesses. For example, in most countries, regulation controls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a major financial agency of the United Nations, and an international financial institution, headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of 190 countries. Its stated mission is "working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world." Formed in 1944, started on 27 December 1945, at the Bretton Woods Conference primarily by the ideas of Harry Dexter White and John Maynard Keynes, it came into formal existence in 1945 with 29 member countries and the goal of reconstructing the international monetary system. It now plays a central role in the management of balance of payments difficulties and international financial crises. Countries contribute funds to a pool through a quota system from which countries experiencing balance of payments problems can borrow money. , the fund had XDR 477 billion (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Externality
In economics, an externality or external cost is an indirect cost or benefit to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another party's (or parties') activity. Externalities can be considered as unpriced goods involved in either consumer or producer market transactions. Air pollution from motor vehicles is one example. The cost of air pollution to society is not paid by either the producers or users of motorized transport to the rest of society. Water pollution from mills and factories is another example. All consumers are all made worse off by pollution but are not compensated by the market for this damage. A positive externality is when an individual's consumption in a market increases the well-being of others, but the individual does not charge the third party for the benefit. The third party is essentially getting a free product. An example of this might be the apartment above a bakery receiving the benefit of enjoyment from smelling fresh pastries every mornin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Times
The ''Financial Times'' (''FT'') is a British daily newspaper printed in broadsheet and published digitally that focuses on business and economic current affairs. Based in London, England, the paper is owned by a Japanese holding company, Nikkei, with core editorial offices across Britain, the United States and continental Europe. In July 2015, Pearson sold the publication to Nikkei for £844 million (US$1.32 billion) after owning it since 1957. In 2019, it reported one million paying subscriptions, three-quarters of which were digital subscriptions. The newspaper has a prominent focus on financial journalism and economic analysis over generalist reporting, drawing both criticism and acclaim. The daily sponsors an annual book award and publishes a " Person of the Year" feature. The paper was founded in January 1888 as the ''London Financial Guide'' before rebranding a month later as the ''Financial Times''. It was first circulated around metropolitan London by James Sherid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward E
Edward is an English given name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortune; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”. History The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Saxon England, but the rule of the Norman and Plantagenet dynasties had effectively ended its use amongst the upper classes. The popularity of the name was revived when Henry III named his firstborn son, the future Edward I, as part of his efforts to promote a cult around Edward the Confessor, for whom Henry had a deep admiration. Variant forms The name has been adopted in the Iberian peninsula since the 15th century, due to Edward, King of Portugal, whose mother was English. The Spanish/Portuguese forms of the name are Eduardo and Duarte. Other variant forms include French Édouard, Italian Edoardo and Odoardo, German, Dutch, Czech and Romanian Eduard (name), Eduard and Scandinavian Edvard. Short forms include Ed, Eddy, Eddie, Ted, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornell University
Cornell University is a private statutory land-grant research university based in Ithaca, New York. It is a member of the Ivy League. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell and Andrew Dickson White, Cornell was founded with the intention to teach and make contributions in all fields of knowledge—from the classics to the sciences, and from the theoretical to the applied. These ideals, unconventional for the time, are captured in Cornell's founding principle, a popular 1868 quotation from founder Ezra Cornell: "I would found an institution where any person can find instruction in any study." Cornell is ranked among the top global universities. The university is organized into seven undergraduate colleges and seven graduate divisions at its main Ithaca campus, with each college and division defining its specific admission standards and academic programs in near autonomy. The university also administers three satellite campuses, two in New York City and one in Education City, Qatar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Krugman
Paul Robin Krugman ( ; born February 28, 1953) is an American economist, who is Distinguished Professor of Economics at the Graduate Center of the City University of New York, and a columnist for ''The New York Times''. In 2008, Krugman was the winner of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his contributions to New Trade Theory and New Economic Geography. The Prize Committee cited Krugman's work explaining the patterns of international trade and the geographic distribution of economic activity, by examining the effects of economies of scale and of consumer preferences for diverse goods and services. Krugman was previously a professor of economics at MIT, and later at Princeton University. He retired from Princeton in June 2015, and holds the title of professor emeritus there. He also holds the title of Centennial Professor at the London School of Economics. Krugman was President of the Eastern Economic Association in 2010, and is among the most influential economi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Soros
George Soros ( name written in eastern order), (born György Schwartz, August 12, 1930) is a Hungarian-American businessman and philanthropist. , he had a net worth of US$8.6 billion, Note that this site is updated daily. having donated more than $32 billion to the Open Society Foundations, of which $15 billion has already been distributed, representing 64% of his original fortune. ''Forbes'' called him the "most generous giver" (in terms of percentage of net worth). Born in Budapest to a non-observant Jewish family, Soros survived the Nazi occupation of Hungary and moved to the United Kingdom in 1947. He studied at the London School of Economics and was awarded a BSc in philosophy in 1951, and then a Master of Science degree, also in philosophy, in 1954. Soros began his business career by taking various jobs at merchant banks in the United Kingdom and then the United States, before starting his first hedge fund, Double Eagle, in 1969. Profits from his first fund furnis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protectionism
Protectionism, sometimes referred to as trade protectionism, is the economic policy of restricting imports from other countries through methods such as tariffs on imported goods, import quotas, and a variety of other government regulations. Proponents argue that protectionist policies shield the producers, businesses, and workers of the Import substitution industrialization, import-competing sector in the country from foreign competitors. Opponents argue that protectionist policies reduce trade and adversely affect consumers in general (by raising the cost of imported goods) as well as the producers and workers in export sectors, both in the country implementing protectionist policies and in the countries protected against. Protectionism is advocated mainly by parties that hold Economic nationalism, economic nationalist or left-wing positions, while economically right-wing political parties generally support free trade. There is a consensus among economists that protectioni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed Economy
A mixed economy is variously defined as an economic system blending elements of a market economy with elements of a planned economy, markets with state interventionism, or private enterprise with public enterprise. Common to all mixed economies is a combination of free-market principles and principles of socialism. While there is no single definition of a mixed economy, one definition is about a mixture of markets with state interventionism, referring specifically to a capitalist market economy with strong regulatory oversight and extensive interventions into markets. Another is that of active collaboration of capitalist and socialist visions. Yet another definition is apolitical in nature, strictly referring to an economy containing a mixture of private enterprise with public enterprise. Alternatively, a mixed economy can refer to a reformist transitionary phase to a socialist economy that allows a substantial role for private enterprise and contracting within a dominant econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
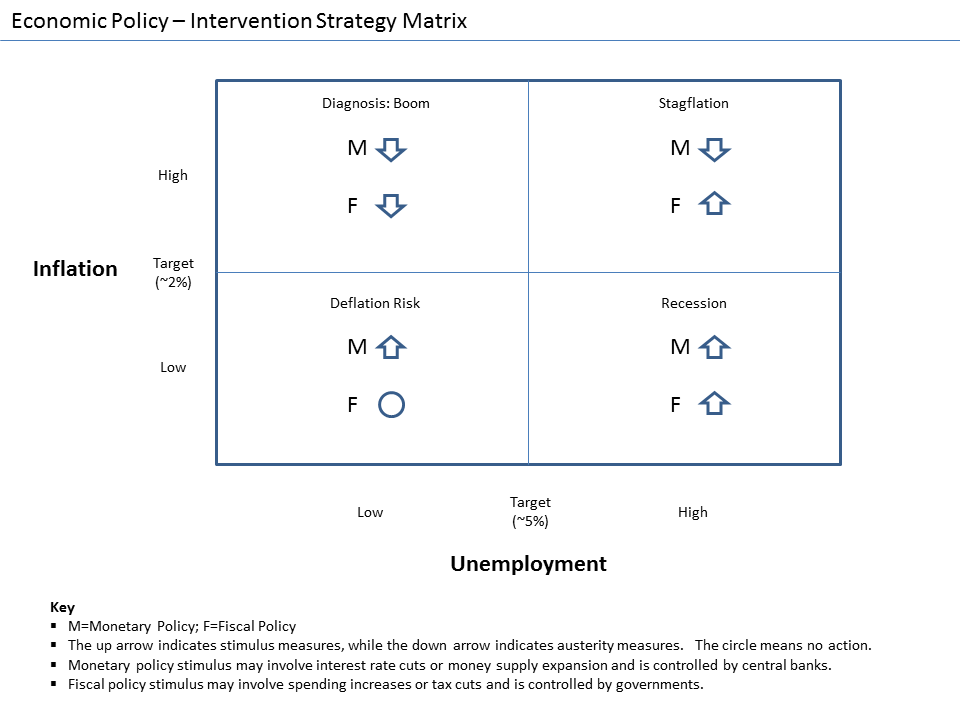
Economic Interventionism
Economic interventionism, sometimes also called state interventionism, is an economic policy position favouring government intervention in the market process with the intention of correcting market failures and promoting the general welfare of the people. An economic intervention is an action taken by a government or international institution in a market economy in an effort to impact the economy beyond the basic regulation of fraud, enforcement of contracts, and provision of public goods and services. Economic intervention can be aimed at a variety of political or economic objectives, such as promoting economic growth, increasing employment, raising wages, raising or reducing prices, promoting income equality, managing the money supply and interest rates, increasing profits, or addressing market failures. The term ''intervention'' is typically used by advocates of ''laissez-faire'' and free market capitalism, and assumes that, on a philosophical level, the state and econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitalist
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, private property, property rights recognition, voluntary exchange, and wage labor. In a market economy, decision-making and investments are determined by owners of wealth, property, or ability to maneuver capital or production ability in capital and financial markets—whereas prices and the distribution of goods and services are mainly determined by competition in goods and services markets. Economists, historians, political economists and sociologists have adopted different perspectives in their analyses of capitalism and have recognized various forms of it in practice. These include ''laissez-faire'' or free-market capitalism, anarcho-capitalism, state capitalism and welfare capitalism. Different forms of capitalism feature varying deg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |