|
Mariannelund
Mariannelund is a locality situated in Hässleby parish in Eksjö Municipality, Jönköping County, in the region of Småland, Sweden with 1,468 inhabitants in 2010. Mariannelund is situated in the Småland highlands (elevation 118–280 metres above sea level), 39 km east of Eksjö. A railway running from Jönköping by lake Vättern to the Baltic Sea crosses through Mariannelund as well as the coast to coast road number 40. The river Bruza floats through Mariannelund and is part of the greater Em river system. The industry is dominated by forest and building companies. Together with the neighbouring parish of Kråkshult Mariannelund formed its own municipality (township) until it joined with Eksjö in 1971. Mariannelund is probably mostly known through the stories of Astrid Lindgren, mostly her books about Emil i Lönneberga. Mariannelund is home to the Doctor, whom the people of the Katthult farm need to visit regularly. The movies based on the books about Emil were fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mariannelund Railway Station
Mariannelund is a locality situated in Hässleby parish in Eksjö Municipality, Jönköping County, in the region of Småland, Sweden with 1,468 inhabitants in 2010. Mariannelund is situated in the Småland highlands (elevation 118–280 metres above sea level), 39 km east of Eksjö. A railway running from Jönköping by lake Vättern to the Baltic Sea crosses through Mariannelund as well as the coast to coast road number 40. The river Bruza floats through Mariannelund and is part of the greater Em river system. The industry is dominated by forest and building companies. Together with the neighbouring parish of Kråkshult Mariannelund formed its own municipality (township) until it joined with Eksjö in 1971. Mariannelund is probably mostly known through the stories of Astrid Lindgren, mostly her books about Emil i Lönneberga. Mariannelund is home to the Doctor, whom the people of the Katthult farm need to visit regularly. The movies based on the books about Emil were filme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kvill Oak
The Rumskulla oak, also known as the Kvill oak, is an oak tree (''Quercus robur'')"Rumskullaeken—Sveriges grövsta träd" Naturreservat, Vimmerby, Länsstyrelsen Kalmar län, retrieved 17 November 2013 (pdf) near Norra Kvill National Park in Rumskulla , , |
Eksjö Municipality
Eksjö Municipality (''Eksjö kommun'') is a municipality in Jönköping County, southern Sweden, where the town Eksjö is seat. The present municipality was created in 1971 when the former ''City of Eksjö'' was amalgamated with three neighboring municipalities. Localities There are 6 urban areas (also called a Tätort or locality) in Eksjö Municipality. In the table the localities are listed according to the size of the population as of December 31, 2005. The municipal seat is in bold characters. Natives Albert Engström (1869-1940) was an author, poet and drawer and subsequently member of the Swedish Academy, who grew up in a small village outside of the city Eksjö. Sister cities *Marstal, in Denmark *Barlinek, in Poland (See sister city A sister city or a twin town relationship is a form of legal or social agreement between two geographically and politically distinct localities for the purpose of promoting cultural and commercial ties. While there are early examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emil I Lönneberga
''Emil of Lönneberga'' (from Swedish: ''Emil i Lönneberga'') is a series of children's novels, written by Astrid Lindgren in 1963, 1966 and 1970 respectively, about the prankster Emil Svensson who lives on a farm in the Lönneberga village of Småland, Sweden. In total twelve books were written between 1963 and 1997, which have appeared in 44 languages (2014), in most cases with the original Swedish illustrations by Björn Berg. There are three Swedish movie adaptations, released in 1971–1973. Emil the character Emil Svensson lives on the farm Katthult ("Catholt"), set in the village of Lönneberga in Småland around the year 1900, with his younger sister Ida, mother Alma and father Anton, the farmhand Alfred who loves Emil and the farm maid Lina who, however, is unable to tolerate Emil's pranks (''"hyss"''). Sometimes Krösa-Maja ("Lingonberry-Maia") comes to Katthult to help with domestic work and tell Emil and Ida stories about "mylingar", ghosts, murders and similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Industry
Heavy industry is an industry that involves one or more characteristics such as large and heavy products; large and heavy equipment and facilities (such as heavy equipment, large machine tools, huge buildings and large-scale infrastructure); or complex or numerous processes. Because of those factors, heavy industry involves higher capital intensity than light industry does, and it is also often more heavily cyclical in investment and employment. Though important to economic development and industrialization of economies, heavy industry can also have significant negative side effects: both local communities and workers frequently encounter health risks, heavy industries tend to produce byproducts that both pollute the air and water, and the industrial supply chain is often involved in other environmental justice issues from mining and transportation. Because of their intensity, heavy industries are also significant contributors to greenhouse gas emissions that cause climat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrid Lindgren
Astrid Anna Emilia Lindgren (; ; 14 November 1907 – 28 January 2002) was a Swedish writer of fiction and screenplays. She is best known for several children's book series, featuring Pippi Longstocking, Emil of Lönneberga, Karlsson-on-the-Roof, and the Six Bullerby Children (''Children of Noisy Village'' in the US), and for the children's fantasy novels '' Mio, My Son'', ''Ronia the Robber's Daughter'', and '' The Brothers Lionheart''. Lindgren worked on the Children's Literature Editorial Board at the Rabén & Sjögren publishing house in Stockholm and wrote more than 30 books for children. In January 2017, she was calculated to be the world's 18th most translated author, and the fourth most translated children's writer after Enid Blyton, Hans Christian Andersen and the Brothers Grimm. Lindgren has so far sold roughly 167 million books worldwide. In 1994, she was awarded the Right Livelihood Award for "her unique authorship dedicated to the rights of children and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emån
Emån is a river in southern Sweden, rising just north of Bodafors in the highlands of Småland and running approximately 229 kilometers to the Baltic Sea just south of Oskarshamn. Emån is popular among canoeists, as it is easily navigated and provides opportunities to experience Swedish flora and fauna up close. Emån is the home to more than 30 species of fish and is prized among anglers for its very large seatrout. Noteworthy settlements along the stream include Holsbybrunn, Kvillsfors, Målilla and Högsby Högsby is a Urban areas in Sweden, locality and the seat of Högsby Municipality, Kalmar County, Sweden with 1,881 inhabitants in 2010. Other towns in the Högsby Municipality are Långemåla, Fågelfors, Berga and Fagerhult, of which Långemåla .... References Småland Rivers of Kalmar County Drainage basins of the Baltic Sea Ramsar sites in Sweden {{Sweden-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Areas Of Sweden
An urban area or () in Sweden has a minimum of 200 inhabitants and may be a city, town or larger village. It is a purely statistical concept, not defined by any municipal or county boundaries. Larger urban areas synonymous with cities or towns ( sv, stad for both terms) for statistical purposes have a minimum of 10,000 inhabitants.. The same statistical definition is also used for urban areas in the other Nordic countries. In 2018, there were nearly two thousand urban areas in Sweden, which were inhabited by 87% of the Swedish population. ''Urban area'' is a common English translation of the Swedish term . The official term in English used by Statistics Sweden is, however, "locality" ( sv, ort). It could be compared with "census-designated places" in the United States. History Until the beginning of the 20th century, only the towns/cities were regarded as urban areas. The built-up area and the municipal entity were normally almost congruent. Urbanization and industrialization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters (for their latitude), with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature. Oceanic climates can be found in both hemispheres generally between 45 and 63 latitude, most notably in northwestern Europe, northwestern America, as well as New Zealand. Precipitation Locations with oceanic climates tend to feature frequent cloudy conditions with precipitation, low hanging clouds, and frequent fronts and storms. Thunderstorms are normally few, since strong daytime heating and hot and cold air masses meet infrequently in the region. In most areas with an oceanic climate, precipitation comes in the form of rain for the majority of the year. However, some areas with this climate see some snowfall annually during winter. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central European Time
Central European Time (CET) is a standard time which is 1 hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). The time offset from UTC can be written as UTC+01:00. It is used in most parts of Europe and in a few North African countries. CET is also known as Middle European Time (MET, German: MEZ) and by colloquial names such as Amsterdam Time, Berlin Time, Brussels Time, Madrid Time, Paris Time, Rome Time, Warsaw Time or even Romance Standard Time (RST). The 15th meridian east is the central axis for UTC+01:00 in the world system of time zones. As of 2011, all member states of the European Union observe summer time (daylight saving time), from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October. States within the CET area switch to Central European Summer Time (CEST, UTC+02:00) for the summer. In Africa, UTC+01:00 is called West Africa Time (WAT), where it is used by several countries, year round. Algeria, Morocco, and Tunisia also refer to it as ''Central European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central European Summer Time
Central European Summer Time (CEST), sometimes referred to as Central European Daylight Time (CEDT), is the standard clock time observed during the period of summer daylight-saving in those European countries which observe Central European Time (CET; UTC+01:00) during the other part of the year. It corresponds to UTC+02:00, which makes it the same as Eastern European Time, Central Africa Time, South African Standard Time, Egypt Standard Time and Kaliningrad Time in Russia. Names Other names which have been applied to Central European Summer Time are Middle European Summer Time (MEST), Central European Daylight Saving Time (CEDT), and Bravo Time (after the second letter of the NATO phonetic alphabet). Period of observation Since 1996, European Summer Time has been observed between 01:00 UTC (02:00 CET and 03:00 CEST) on the last Sunday of March, and 01:00 UTC on the last Sunday of October; previously the rules were not uniform across the European Union. There were proposals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


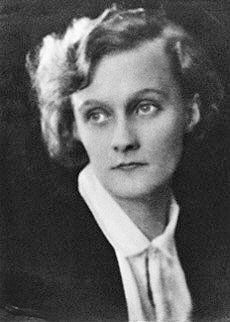
.png)