|
Marathi Grammar
The grammar of the Marathi language shares similarities with other modern Indo-Aryan languages such as Odia, Gujarati or Punjabi. The first modern book exclusively about the grammar of Marathi was printed in 1805 by Willam Carey. The principal word order in Marathi is SOV (subject–object–verb). Nouns inflect for gender (masculine, feminine, neuter), number (singular, plural), and case. Marathi preserves the neuter gender found in Sanskrit, a feature further distinguishing it from many Indo-Aryan languages. Typically, Marathi adjectives do not inflect unless they end in an () vowel, in which case they inflect for gender and number. Marathi verbs inflect for tense (past, present, future). Verbs can agree with their subjects, yielding an active voice construction, or with their objects, yielding a passive voice construction. A third type of voice, not found in English for example, is produced when the verb agrees with neither subject nor object. Affixation is largely s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marathi Language
Marathi (; , 𑘦𑘨𑘰𑘙𑘲, , ) is a Classical languages of India, classical Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language predominantly spoken by Marathi people in the Indian state of Maharashtra and is also spoken in Goa, and parts of Gujarat, Karnataka and the territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. It is the official language of Maharashtra, and an additional official language in the state of Goa, where it is used for replies, when requests are received in Marathi. It is one of the 22 scheduled languages of India, with 83 million speakers as of 2011. Marathi ranks 13th in the List of languages by number of native speakers, list of languages with most native speakers in the world. Marathi has the List of languages by number of native speakers in India, third largest number of native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
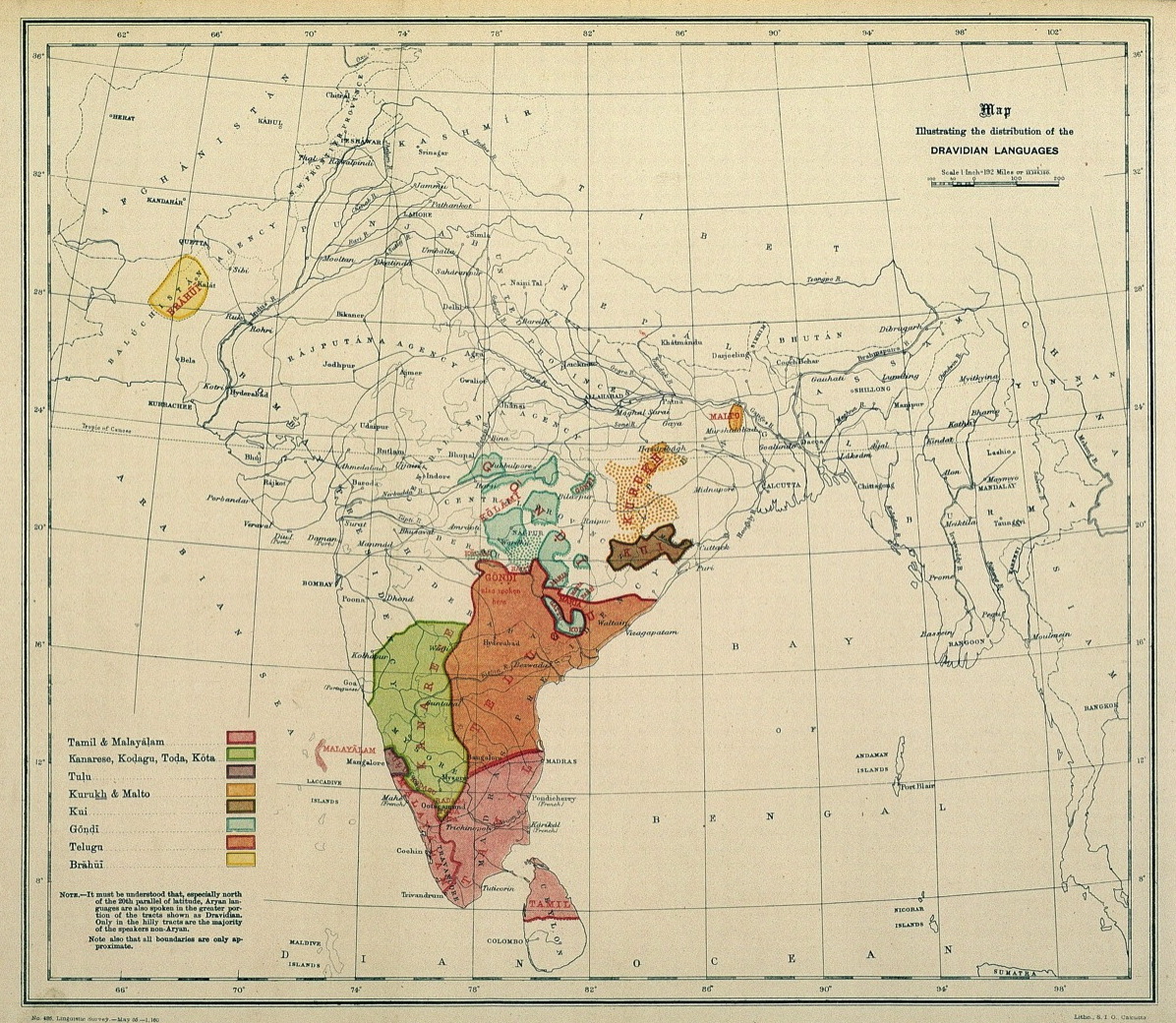
Dravidian Languages
The Dravidian languages are a language family, family of languages spoken by 250 million people, primarily in South India, north-east Sri Lanka, and south-west Pakistan, with pockets elsewhere in South Asia. The most commonly spoken Dravidian languages are (in descending order) Telugu language, Telugu, Tamil language, Tamil, Kannada, and Malayalam, all of which Classical languages of India, have long literary traditions. Smaller literary languages are Tulu language, Tulu and Kodava language, Kodava. Together with several smaller languages such as Gondi language, Gondi, these languages cover the southern part of India and the northeast of Sri Lanka, and account for the overwhelming majority of speakers of Dravidian languages. Malto language, Malto and Kurukh language, Kurukh are spoken in isolated pockets in eastern India. Kurukh is also spoken in parts of Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh. Brahui language, Brahui is mostly spoken in the Balochistan region of Pakistan, Sistan and Baluc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preposition And Postposition
Adpositions are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in, under, towards, behind, ago'', etc.) or mark various semantic roles (''of, for''). The most common adpositions are prepositions (which precede their complement) and postpositions (which follow their complement). An adposition typically combines with a noun phrase, this being called its complement, or sometimes object. English generally has prepositions rather than postpositions – words such as ''in, under'' and ''of'' precede their objects, such as "in England", "under the table", "of Jane" – although there are a few exceptions including ''ago'' and ''notwithstanding'', as in "three days ago" and "financial limitations notwithstanding". Some languages that use a different word order have postpositions instead (like Turkic languages) or have both types (like Finnish). The phrase formed by an adposition together with its complement is called an adpositional phrase (or prepositional phras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjunction (grammar)
In grammar, a conjunction (List of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated or ) is a part of speech that connects Word, words, phrases, or Clause, clauses'','' which are called its conjuncts. That description is vague enough to overlap with those of other parts of speech because what constitutes a "conjunction" must be defined for each language. In English language, English, a given word may have several Word sense, senses and in some contexts be a Preposition and postposition, preposition but a conjunction in others, depending on the syntax. For example, ''after'' is a preposition in "he left after the fight" but a conjunction in "he left after they fought". In general, a conjunction is an invariant (non-Inflection, inflecting) grammatical particle that stands between conjuncts. A conjunction may be placed at the beginning of a sentence, but some superstition about the practice persists. The definition may be extended to idiomatic phrases that behave as a unit and perform the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adverb
An adverb is a word or an expression that generally modifies a verb, an adjective, another adverb, a determiner, a clause, a preposition, or a sentence. Adverbs typically express manner, place, time, frequency, degree, or level of certainty by answering questions such as ''how'', ''in what way'', ''when'', ''where'', ''to what extent''. This is called the adverbial function and may be performed by an individual adverb, by an adverbial phrase, or by an adverbial clause. Adverbs are traditionally regarded as one of the parts of speech. Modern linguists note that the term ''adverb'' has come to be used as a kind of "catch-all" category, used to classify words with various types of syntactic behavior, not necessarily having much in common except that they do not fit into any of the other available categories (noun, adjective, preposition, etc.). Functions The English word ''adverb'' derives (through French) from Latin ''adverbium'', from ''ad-'' ('to'), ''verbum'' ('word', 'ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verb
A verb is a word that generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual description of English, the basic form, with or without the particle ''to'', is the infinitive. In many languages, verbs are inflected (modified in form) to encode tense, aspect, mood, and voice. A verb may also agree with the person, gender or number of some of its arguments, such as its subject, or object. In English, three tenses exist: present, to indicate that an action is being carried out; past, to indicate that an action has been done; and future, to indicate that an action will be done, expressed with the auxiliary verb ''will'' or ''shall''. For example: * Lucy ''will go'' to school. ''(action, future)'' * Barack Obama ''became'' the President of the United States in 2009. ''(occurrence, past)'' * Mike Trout ''is'' a center fielder. ''(state of bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjective
An adjective (abbreviations, abbreviated ) is a word that describes or defines a noun or noun phrase. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun. Traditionally, adjectives are considered one of the main part of speech, parts of speech of the English language, although historically they were classed together with Noun, nouns. Nowadays, certain words that usually had been classified as adjectives, including ''the'', ''this'', ''my'', etc., typically are classed separately, as Determiner (class), determiners. Examples: * That's a ''funny'' idea. (Prepositive attributive) * That idea is ''funny''. (Predicate (grammar), Predicative) * * The ''good'', the ''bad'', and the ''funny''. (Substantive adjective, Substantive) * Clara Oswald, completely ''fictional'', died three times. (Apposition, Appositive) Etymology ''Adjective'' comes from Latin ', a calque of (whence also English ''epithet''). In the grammatical tradition of Latin and Greek, because adjectives were I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (Interlinear gloss, glossed ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the part of speech, parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not consider them to form a single class, in view of the variety of functions they perform cross-linguistically. An example of a pronoun is "you", which can be either singular or plural. Sub-types include personal pronoun, personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive pronoun, reflexive and reciprocal pronoun, reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative pronoun, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. The use of pronouns often involves anaphora (linguistics), anaphora, where the meaning of the pronoun is dependent on an antecedent (grammar), antecedent. For example, in the sentence ''That poor man looks as if he needs a new coat'', the meaning of the pronoun ''he'' is dependent on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun
In grammar, a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, like living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an Object (grammar), object or Subject (grammar), subject within a phrase, clause, or sentence.Example nouns for: * Living creatures (including people, alive, dead, or imaginary): ''mushrooms, dogs, Afro-Caribbeans, rosebushes, Mandela, bacteria, Klingons'', etc. * Physical objects: ''hammers, pencils, Earth, guitars, atoms, stones, boots, shadows'', etc. * Places: ''closets, temples, rivers, Antarctica, houses, Uluru, utopia'', etc. * Actions of individuals or groups: ''swimming, exercises, cough, explosions, flight, electrification, embezzlement'', etc. * Physical qualities: ''colors, lengths, porosity, weights, roundness, symmetry, solidity,'' etc. * Mental or bodily states: ''jealousy, sleep, joy, headache, confusion'', etc. In linguistics, nouns constitute a lexical category (part of speech) defined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parts Of Speech
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech (abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class or grammatical category) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntactic behavior (they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences), sometimes similar morphological behavior in that they undergo inflection for similar properties and even similar semantic behavior. Commonly listed English parts of speech are noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, numeral, article, and determiner. Other terms than ''part of speech''—particularly in modern linguistic classifications, which often make more precise distinctions than the traditional scheme does—include word class, lexical class, and lexical category. Some authors restrict the term ''lexical category'' to refer only to a particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanskrit Language
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural diffusion, diffused there from the northwest in the late Bronze Age#South Asia, Bronze Age. Sanskrit is the sacred language of Hinduism, the language of classical Hindu philosophy, and of historical texts of Buddhism and Jainism. It was a lingua franca, link language in ancient and medieval South Asia, and upon transmission of Hindu and Buddhist culture to Southeast Asia, East Asia and Central Asia in the early medieval era, it became a language of religion and high culture, and of the political elites in some of these regions. As a result, Sanskrit had a lasting effect on the languages of South Asia, Southeast Asia and East Asia, especially in their formal and learned vocabularies. Sanskrit generally connotes several Indo-Aryan languages# ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatsama
Tatsama ( , lit. 'same as that') are Sanskrit loanwords in modern Indo-Aryan languages like Assamese, Bengali, Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Hindi, Gujarati, and Sinhala and in Dravidian languages like Tamil, Kannada and Telugu. They generally belong to a higher and more erudite register than common words, many of which are (in modern Indo-Aryan languages) directly inherited from Old Indo-Aryan ( tadbhava). The tatsama register can be compared to the use of loan words of Greek or Latin origin in English (e.g. ''hubris''). Eastern Indo-Aryan Bengali The origin of tatsama words () in Bengali is traced to 10th century poets. Another, more minor, wave of tatsama vocabulary entered the (Modern) Bengali language by Sanskrit scholars teaching at Fort William College in Kolkata at the start of the 19th century. Bengali's lexicon is now about 40% tatsama (with about 58% tadbhava vocabulary inherited from Old Indo-Aryan via the Prakrit languages such as Apabhramsha and Avahaṭṭh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |