|
Manus O'Donnell
Manus O'Donnell (Irish: ''Maghnas Ó Domhnaill'' or ''Manus Ó Domhnaill'', died 1564) was an Irish lord and son of Sir Hugh Dubh O'Donnell. He was an important member of the O'Donnell dynasty based in County Donegal in Ulster. Early life Hugh Dubh (pronounced in Ulster Irish as 'Hugh Doo') had been ''Rí'' (king) of the O'Donnells during one of the bitterest and most protracted of the feuds between his clan and the O'Neills, which in 1491 led to a war lasting more than ten years. He left his son to rule Tyrconnell, though still a boy, when he went on a pilgrimage to Rome about 1511. On his return from Rome (via England, where he was knighted by King Henry VIII) in broken health after two years' absence, his son Manus, who had proved himself a capable leader in defending his country against the O'Neills, retained the chief authority. When Sir Hugh Dubh O'Donnell, as he was now, appealed for aid against his son to the Maguires, Manus made an alliance with the O'Neills, by wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manus O'Donell
Manus O'Donnell, Irish soldier and noble, died 1737. O'Donnell (O Domhnaill in Irish) was the son of Rory or Rodger O Donnell of Lifford, grandson of Colonel Manus O'Donnell who was killed in action at the Battle of Benburb in 1646, and grandson of Niall Garbh O'Donnell the last Gaelic chieftain of the O'Donnell clan. Rory of Lifford was transported to Mayo as part of the final conquest circa 1654. Manus, the only known son of Rory of Lifford was a colonel in the service of the Irish forces during the Williamite wars. * Charles, who was the father of Count Manus O'Donell of Austria and Lewis O'Donell of Newcastle, County Mayo * a son, name unknown * Hugh, whose son, Sir Neal O'Donel Bt of Newport conformed to the Church of Ireland in 1763. This Neal gave evidence that lead to execution of the Fr Manus Sweeney a local Catholic priest who sided with the United Irishmen during the 1798 rebellion.Guy Beiner, "In Pursuit of a People’s Hero: Remembering Father Manus Sweeney and T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 census of Ireland, 2016 census it had a population of 1,173,179, while the preliminary results of the 2022 census of Ireland, 2022 census recorded that County Dublin as a whole had a population of 1,450,701, and that the population of the Greater Dublin Area was over 2 million, or roughly 40% of the Republic of Ireland's total population. A settlement was established in the area by the Gaels during or before the 7th century, followed by the Vikings. As the Kings of Dublin, Kingdom of Dublin grew, it became Ireland's principal settlement by the 12th century Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland. The city expanded rapidly from the 17th century and was briefly the second largest in the British Empire and sixt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
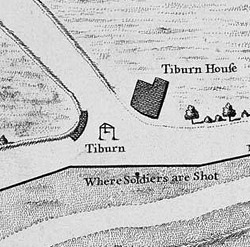
Tyburn
Tyburn was a manor (estate) in the county of Middlesex, one of two which were served by the parish of Marylebone. The parish, probably therefore also the manor, was bounded by Roman roads to the west (modern Edgware Road) and south (modern Oxford Street), the junction of these was the site of the famous Tyburn Gallows (known colloquially as the "Tyburn Tree"), now occupied by Marble Arch. For this reason, for many centuries, the name Tyburn was synonymous with capital punishment, it having been the principal place for execution of London criminals and convicted traitors, including many religious martyrs. It was also known as 'God's Tribunal', in the 18th century. Tyburn took its name from the Tyburn Brook, a tributary of the River Westbourne. The name Tyburn, from Teo Bourne, means 'boundary stream',Gover, J. E. B., Allen Mawer and F. M. Stenton ''The Place-Names of Middlesex''. Nottingham: English Place-Name Society, The, 1942: 6. but Tyburn Brook should not be confused wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas FitzGerald, 10th Earl Of Kildare
{{Infobox noble, type , name = Thomas FitzGerald , title = The Earl of Kildare , image = Thomas FitzGerald, 10th Earl of Kildare.jpg , caption = , alt = , CoA = , more = no , succession = , reign = 1534–1537 , reign-type = Reign , predecessor = Gerald FitzGerald , successor = Title forfeited , suc-type = , spouse = , spouse-type = , issue = , issue-link = , issue-pipe = , full name = , styles = , titles = , noble family = FitzGerald dynasty , house-type = , father = Gerald FitzGerald , mother = Elizabeth Zouche , birth_date = 1513 , birth_place = , christening_date = , christening_place = , death_date = 3 February 1537 (aged 23/24) , death_place = Tyburn, London, K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry VIII Of England
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disagreement with Pope Clement VII about such an annulment led Henry to initiate the English Reformation, separating the Church of England from papal authority. He appointed himself Supreme Head of the Church of England and dissolved convents and monasteries, for which he was excommunicated by the pope. Henry is also known as "the father of the Royal Navy" as he invested heavily in the navy and increased its size from a few to more than 50 ships, and established the Navy Board. Domestically, Henry is known for his radical changes to the English Constitution, ushering in the theory of the divine right of kings in opposition to papal supremacy. He also greatly expanded royal power during his reign. He frequently used charges of treason and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lordship Of Ireland
The Lordship of Ireland ( ga, Tiarnas na hÉireann), sometimes referred to retroactively as Norman Ireland, was the part of Ireland ruled by the King of England (styled as "Lord of Ireland") and controlled by loyal Anglo-Norman lords between 1177 and 1542. The lordship was created following the Norman invasion of Ireland in 1169–1171. It was a papal fief, granted to the Plantagenet kings of England by the Holy See, via ''Laudabiliter''. As the Lord of Ireland was also the King of England, he was represented locally by a governor, variously known as the Justiciar, Lieutenant, Lord Lieutenant or Lord Deputy. The kings of England claimed lordship over the whole island, but in reality the king's rule only ever extended to parts of the island. The rest of the island – referred to subsequently as Gaelic Ireland – remained under the control of various Gaelic Irish kingdoms or chiefdoms, who were often at war with the Anglo-Normans. The area under English rule and law grew and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Knockavoe
The Battle of Knockavoe (''Cnoc-Buidhbh'') was fought in 1522 between the O'Donnells, led by Hugh Dubh O'Donnell and Manus O'Donnell, both sons of Sir Hugh Dubh O'Donnell, against the O'Neills, in which the O'Neills and their supporters were surprised and routed. Knockavoe was not a lost pitched battle, rather it was in fact the result of a nighttime surprise attack on the O'Neill camp by the O'Donnells. Knockavoe is the hill just behind Strabane in County Tyrone. Background Conn Bacach O'Neill (who was later created Earl of Tyrone, in 1542) was determined to bring the O'Donnells under his rule and made a great gathering, determined to march into Tyrconnell. Forces arrived from Munster and Connacht, together with English contingents, and brought into O'Neill's army itself were the Scoto-Irish MacDonnells of Antrim, Bissetts, MacSheehys and others. The forces laid siege to and took Ballyshannon Castle, and later devastated a large part of Tyrconnell. Battle While encamped at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strabane
Strabane ( ; ) is a town in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland. Strabane had a population of 13,172 at the 2011 Census. It lies on the east bank of the River Foyle. It is roughly midway from Omagh, Derry and Letterkenny. The River Foyle marks the border between Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland. On the other side of the river (across Lifford Bridge) is the smaller town of Lifford, which is the county town of Donegal. The River Mourne flows through the centre of the town and meets the Finn to form the Foyle River. A large hill named Knockavoe, which marks the beginning of the Sperrin Mountains, forms the backdrop to the town. History Early history The locale was home to a group of northern Celts known as the Orighella as far back as the fourth century when the territories of Owen (later Tír Eoghain) and Connail (later Tír Chonaill - mostly modern County Donegal) were established, and Orighella were assimilated into the Cenél Conaill. With the arrival of Saint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballyshannon
Ballyshannon () is a town in County Donegal, Ireland. It is located at the southern end of the county where the N3 from Dublin ends and the N15 crosses the River Erne. Incorporated in 1613, it is one of the oldest towns in Ireland. Location Ballyshannon, which means "the mouth of Seannach's ford", after a fifth-century warrior, Seannach, who was slain there, lies at the mouth of the river Erne. Just west of the town, the Erne widens and its waters meander over a long sandy estuary. The northern bank of the river rises steeply away from the riverbank, while the southern bank is flat with a small cliff that runs parallel to the river. From its idyllic setting, the town looks out over the estuary and has panoramic views of mountains, lakes and forests. History Archaeological sites dating as far back as the Neolithic period (4000 BC – 2500 BC) have been excavated in Ballyshannon and surrounding areas, representing settlement and ritual activity from early periods of human settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Antrim
County Antrim (named after the town of Antrim, ) is one of six counties of Northern Ireland and one of the thirty-two counties of Ireland. Adjoined to the north-east shore of Lough Neagh, the county covers an area of and has a population of about 618,000. County Antrim has a population density of 203 people per square kilometre or 526 people per square mile. It is also one of the thirty-two traditional counties of Ireland, as well as part of the historic province of Ulster. The Glens of Antrim offer isolated rugged landscapes, the Giant's Causeway is a unique landscape and a UNESCO World Heritage Site, Bushmills produces whiskey, and Portrush is a popular seaside resort and night-life area. The majority of Belfast, the capital city of Northern Ireland, is in County Antrim, with the remainder being in County Down. According to the 2001 census, it is currently one of only two counties of the Island of Ireland in which a majority of the population are from a Protestant back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connacht
Connacht ( ; ga, Connachta or ), is one of the provinces of Ireland, in the west of Ireland. Until the ninth century it consisted of several independent major Gaelic kingdoms (Uí Fiachrach, Uí Briúin, Uí Maine, Conmhaícne, and Delbhna). Between the reigns of Conchobar mac Taidg Mór (died 882) and his descendant, Aedh mac Ruaidri Ó Conchobair (reigned 1228–33), it became a kingdom under the rule of the Uí Briúin Aí dynasty, whose ruling sept adopted the surname Ua Conchobair. At its greatest extent, it incorporated the often independent Kingdom of Breifne, as well as vassalage from the lordships of western Mide and west Leinster. Two of its greatest kings, Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair (1088–1156) and his son Ruaidri Ua Conchobair (c. 1115–1198) greatly expanded the kingdom's dominance, so much so that both became High King of Ireland. The Kingdom of Connacht collapsed in the 1230s because of civil war within the royal dynasty, which enabled widespread Hiber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |