|
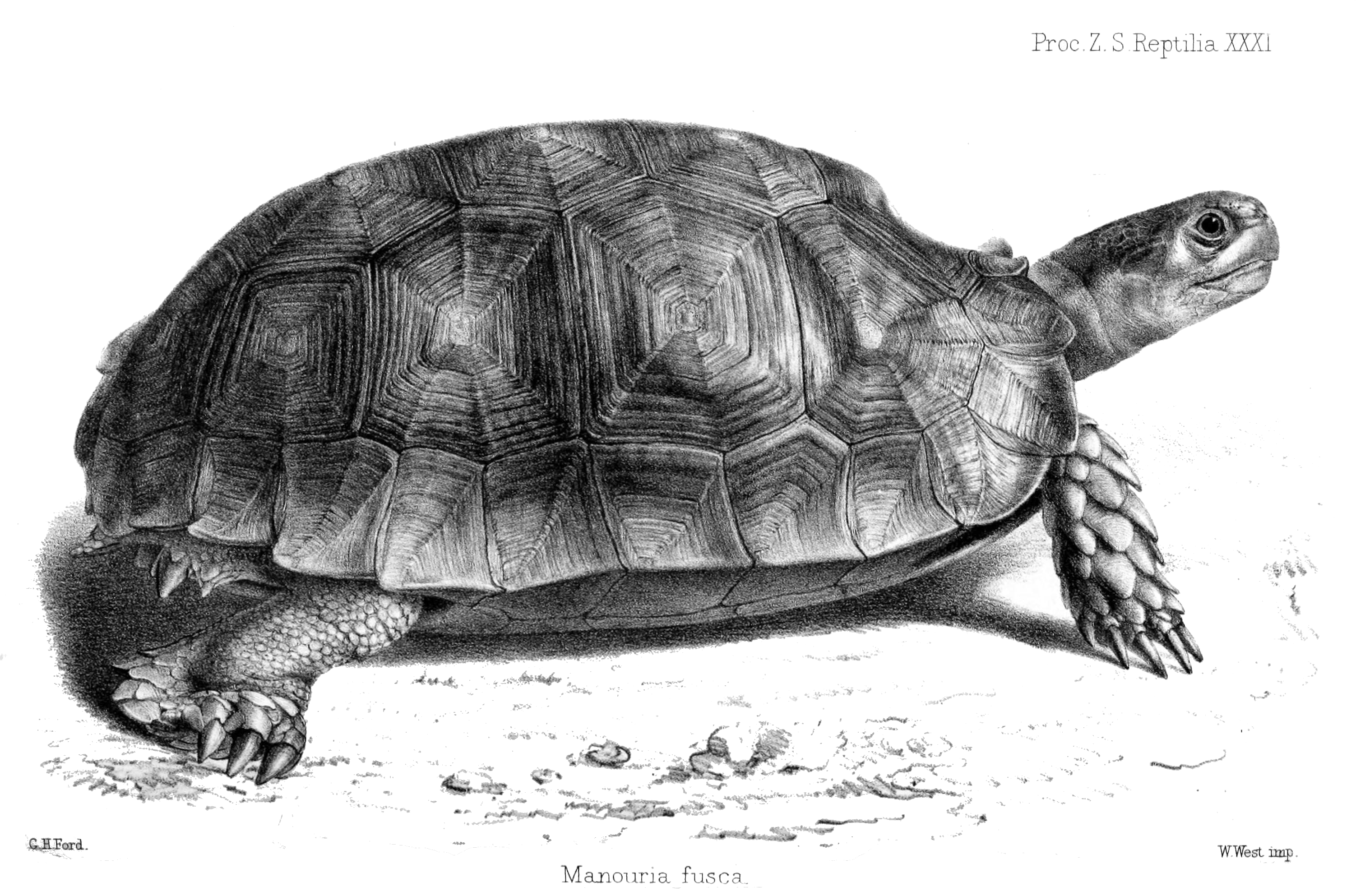
Manouria Oyamai
''Manouria'' is a genus of tortoises in the family Testudinidae. The genus was erected by John Edward Gray in 1854. Species The following five species are recognized as being valid, two of which are extant, and three of which are extinct: *''Manouria emys'' – Asian forest tortoise *''Manouria impressa'' – impressed tortoise *†'' Manouria sondaari'' – a giant land tortoise from Luzon Island, PhilippinesStaesche, Ulrich (coordinator) (2007). ''Fossile Schildkröten aus vier Ländern in drei Kontinenten: Deutschland, Türkei, Niger, Philippen'' Fossil Turtles from Four Countries on Three Continents: Germany, Turkey, Niger, and the Philippines ''Geologisches Jahrbuch, Reihe B, Heft 98'' Series B, Issue 98 197 pp. . http://www.schweizerbart.de/publications/detail/artno/186029800 (in German). however, Rhodin et al. (2015) transferred this species to the genus ''Megalochelys''. *†''Manouria punjabiensis'' – a fossil tortoise from Siwaliks, India *†'' Manouria oyama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manouria Emys
The Asian forest tortoise (''Manouria emys''), also known commonly as the Mountain tortoise, is a species of tortoise in the family Testudinidae. The species is endemic to Southeast Asia. It is believed to be among the most primitive of living tortoises, based on molecular and morphological studies. Taxonomy There are two recognized subspecies: ''M. e. emys'' occurring in southern Thailand, Malaysia, Sumatra, Borneo; and ''M. e. phayrei'', occurring from northwestern Thailand to northeastern India. The latter was named after Sir Arthur Purves Phayre (1812–1885), British Army officer in India who became Commissioner of British Burma. Based on a variety of phylogenetic characteristics, the genus ''Manouria'' is regarded as comparatively primitive and basal to other Testudinidae. Description The Asian forest tortoise is the largest tortoise in mainland Asia. The largest adults of the northern subspecies, ''Manouria emys phayrei'', can reach in the wild and much more than t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalochelys
''Megalochelys'' ("great turtle") is an extinct genus of cryptodiran tortoises that lived from the Miocene to Pleistocene. They are noted for their giant size, which is among the largest of any known testudine, with a maximum carapace length over 2 m (6.5 ft) in ''M. atlas''. During the dry glacial periods it ranged from western India and Pakistan (possibly even as far west as southern and eastern Europe) to as far east as Sulawesi and Timor in Indonesia, though the island specimens likely represent distinct species. Description One species of ''Megalochelys,'' ''M. atlas'', is the largest known tortoise, with a shell length of and even , and an approximate total height of . Popular weight estimates for this taxon have varied greatly with the highest estimates reaching up to in some instances.Orenstein, R. 2001. Survivors in Armor: Turtles, Tortoises, and Terrapins. Key Porter Books Ltd. However, weights based on volumetric displacement of the skeleton,Brown, B. 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turtle Genera
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked turtles), which differ in the way the head retracts. There are 360 living and recently extinct species of turtles, including land-dwelling tortoises and freshwater terrapins. They are found on most continents, some islands and, in the case of sea turtles, much of the ocean. Like other amniotes (reptiles, birds, and mammals) they breathe air and do not lay eggs underwater, although many species live in or around water. Turtle shells are made mostly of bone; the upper part is the domed carapace, while the underside is the flatter plastron or belly-plate. Its outer surface is covered in scales made of keratin, the material of hair, horns, and claws. The carapace bones develop from ribs that grow sideways and develop into broad flat plates th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manouria
''Manouria'' is a genus of tortoises in the family Testudinidae. The genus was erected by John Edward Gray in 1854. Species The following five species are recognized as being valid, two of which are extant, and three of which are extinct: *''Manouria emys'' – Asian forest tortoise *''Manouria impressa'' – impressed tortoise *†''Manouria sondaari'' – a giant land tortoise from Luzon Island, PhilippinesStaesche, Ulrich (coordinator) (2007). ''Fossile Schildkröten aus vier Ländern in drei Kontinenten: Deutschland, Türkei, Niger, Philippen'' Fossil Turtles from Four Countries on Three Continents: Germany, Turkey, Niger, and the Philippines ''Geologisches Jahrbuch, Reihe B, Heft 98'' Series B, Issue 98 197 pp. . http://www.schweizerbart.de/publications/detail/artno/186029800 (in German). however, Rhodin et al. (2015) transferred this species to the genus ''Megalochelys''. *†''Manouria punjabiensis'' – a fossil tortoise from Siwaliks, India *†''Manouria oyamai' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binomial Nomenclature
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name (which may be shortened to just "binomial"), a binomen, name or a scientific name; more informally it is also historically called a Latin name. The first part of the name – the '' generic name'' – identifies the genus to which the species belongs, whereas the second part – the specific name or specific epithet – distinguishes the species within the genus. For example, modern humans belong to the genus ''Homo'' and within this genus to the species ''Homo sapiens''. ''Tyrannosaurus rex'' is likely the most widely known binomial. The ''formal'' introduction of this system of naming species is credit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nota Bene
(, or ; plural form ) is a Latin phrase meaning "note well". It is often abbreviated as NB, n.b., or with the ligature and first appeared in English writing . In Modern English, it is used, particularly in legal papers, to draw the attention of the reader to a certain (side) aspect or detail of the subject being addressed. While ''NB'' is also often used in academic writing, ''note'' is a common substitute. The markings used to draw readers' attention in medieval manuscripts are also called marks. The common medieval markings do not, however, include the abbreviation ''NB''. The usual medieval equivalents are anagrams from the four letters in the word , the abbreviation DM from ("worth remembering"), or a symbol of a little hand (☞), called a manicule or index, with the index finger pointing towards the beginning of the significant passage.Raymond Clemens and Timothy Graham, Introduction to Manuscript Studies (Ithaca: Cornell University Press, 2007), p. 44. Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ryukyu Islands
The , also known as the or the , are a chain of Japanese islands that stretch southwest from Kyushu to Taiwan: the Ōsumi, Tokara, Amami, Okinawa, and Sakishima Islands (further divided into the Miyako and Yaeyama Islands), with Yonaguni the westernmost. The larger are mostly high islands and the smaller mostly coral. The largest is Okinawa Island. The climate of the islands ranges from humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification ''Cfa'') in the north to tropical rainforest climate (Köppen climate classification ''Af'') in the south. Precipitation is very high and is affected by the rainy season and typhoons. Except the outlying Daitō Islands, the island chain has two major geologic boundaries, the Tokara Strait (between the Tokara and Amami Islands) and the Kerama Gap (between the Okinawa and Miyako Islands). The islands beyond the Tokara Strait are characterized by their coral reefs. The Ōsumi and Tokara Islands, the northernmost of the islands, fall un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manouria Oyamai
''Manouria'' is a genus of tortoises in the family Testudinidae. The genus was erected by John Edward Gray in 1854. Species The following five species are recognized as being valid, two of which are extant, and three of which are extinct: *''Manouria emys'' – Asian forest tortoise *''Manouria impressa'' – impressed tortoise *†'' Manouria sondaari'' – a giant land tortoise from Luzon Island, PhilippinesStaesche, Ulrich (coordinator) (2007). ''Fossile Schildkröten aus vier Ländern in drei Kontinenten: Deutschland, Türkei, Niger, Philippen'' Fossil Turtles from Four Countries on Three Continents: Germany, Turkey, Niger, and the Philippines ''Geologisches Jahrbuch, Reihe B, Heft 98'' Series B, Issue 98 197 pp. . http://www.schweizerbart.de/publications/detail/artno/186029800 (in German). however, Rhodin et al. (2015) transferred this species to the genus ''Megalochelys''. *†''Manouria punjabiensis'' – a fossil tortoise from Siwaliks, India *†'' Manouria oyama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sivalik Hills
The Sivalik Hills, also known as the Shivalik Hills and Churia Hills, are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas that stretches over about from the Indus River eastwards close to the Brahmaputra River, spanning the northern parts of the Indian subcontinent. It is wide with an average elevation of . Between the Teesta and Raidāk Rivers in Assam is a gap of about . "Sivalik" literally means 'tresses of Shiva'. Sivalik region is home to the Soanian archaeological culture. Geology Geologically, the Sivalik Hills belong to the Tertiary deposits of the outer Himalayas. They are chiefly composed of sandstone and conglomerate rock formations, which are the solidified detritus of the Himalayas to their north; they are poorly consolidated. The remnant magnetisation of siltstones and sandstones indicates that they were deposited 16–5.2 million years ago. In Nepal, the Karnali River exposes the oldest part of the Shivalik Hills. They are bounded on the south by a fault syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Lydekker
Richard Lydekker (; 25 July 1849 – 16 April 1915) was an English naturalist, geologist and writer of numerous books on natural history. Biography Richard Lydekker was born at Tavistock Square in London. His father was Gerard Wolfe Lydekker, a barrister-at-law with Dutch ancestry. The family moved to Harpenden Lodge soon after Richard's birth. He was educated at Trinity College, Cambridge, where he took a first-class in the Natural Science tripos (1872). In 1874 he joined the Geological Survey of India and made studies of the vertebrate palaeontology of northern India (especially Kashmir). He remained in this post until the death of his father in 1881. His main work in India was on the Siwalik palaeofauna; it was published in ''Palaeontologia Indica''. He was responsible for the cataloguing of the fossil mammals, reptiles, and birds in the Natural History Museum (10 vols., 1891). He named a variety of taxa including the golden-bellied mangabey; as a taxon authority he is nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manouria Punjabiensis
''Manouria'' is a genus of tortoises in the family Testudinidae. The genus was erected by John Edward Gray in 1854. Species The following five species are recognized as being valid, two of which are extant, and three of which are extinct: *''Manouria emys'' – Asian forest tortoise *''Manouria impressa'' – impressed tortoise *†'' Manouria sondaari'' – a giant land tortoise from Luzon Island, PhilippinesStaesche, Ulrich (coordinator) (2007). ''Fossile Schildkröten aus vier Ländern in drei Kontinenten: Deutschland, Türkei, Niger, Philippen'' Fossil Turtles from Four Countries on Three Continents: Germany, Turkey, Niger, and the Philippines ''Geologisches Jahrbuch, Reihe B, Heft 98'' Series B, Issue 98 197 pp. . http://www.schweizerbart.de/publications/detail/artno/186029800 (in German). however, Rhodin et al. (2015) transferred this species to the genus ''Megalochelys''. *†'' Manouria punjabiensis'' – a fossil tortoise from Siwaliks, India *†'' Manouria oyam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luzon Island
Luzon (; ) is the largest and most populous List of islands in the Philippines, island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the List of islands of the Philippines, Philippines archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, as well as Quezon City, the country's most populous city. With a population of 64 million , it contains 52.5% of the country's total population and is the List of islands by population, fourth most populous island in the world. It is the List of islands by area, 15th largest island in the world by land area. ''Luzon'' may also refer to one of the three primary Island groups of the Philippines, island groups in the country. In this usage, it includes the Luzon mainland, the Batanes and Babuyan Islands, Babuyan groups of islands to the north, Polillo Islands to the east, and the outlying islands of Catanduanes, Marinduque and Mindoro, among others, to the south. The islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |