|
Manor Of Dyrham
The Manor of Dyrham was a former manorial estate in the parish of Dyrham in South Gloucestershire, England. Descent FitzWido The Domesday Book of 1086 records the tenant-in-chief of Dyrham as William FitzWido (William son of Guy, Latinised as ''Willelmus Filius Widonis''). In 1086 he held 7 hides in Dyrham, formerly the land of Aluric. He had formerly held also 3 hides of this manor which Durand de Pitres, Sheriff of Gloucester, had given to Pershore Abbey, by the King's command. These had apparently (according to Mr Alfred Ellis)been given to Turstin FitzRolf by "Earl William", presumably William FitzOsbern, 1st Earl of Hereford. Wynebald de Ballon The manor then passed into the extensive fiefdom of Wynebald de Ballon, a magnate from Maine, France, who supported King William Rufus, and appears to have arrived in England with his brother Hamelin de Ballon between 1086 and 1088. Virtually the whole of Wynebald's fiefdom had formerly been held by Turstin FitzRolf, standard bearer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
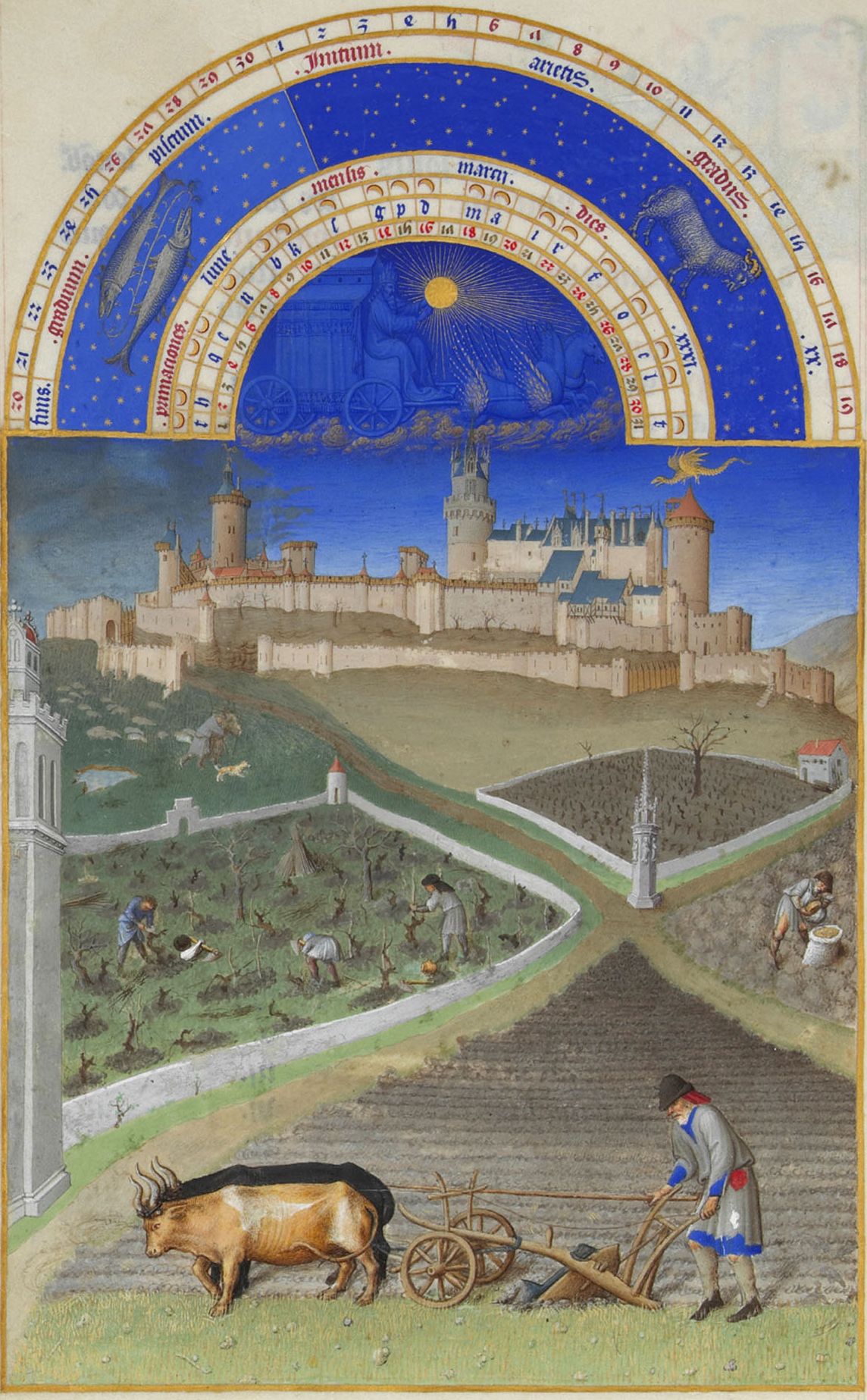
Manorialism
Manorialism, also known as the manor system or manorial system, was the method of land ownership (or "tenure") in parts of Europe, notably France and later England, during the Middle Ages. Its defining features included a large, sometimes fortified manor house in which the lord of the manor and his dependents lived and administered a rural estate, and a population of labourers who worked the surrounding land to support themselves and the lord. These labourers fulfilled their obligations with labour time or in-kind produce at first, and later by cash payment as commercial activity increased. Manorialism is sometimes included as part of the feudal system. Manorialism originated in the Roman villa system of the Late Roman Empire, and was widely practiced in medieval western Europe and parts of central Europe. An essential element of feudal society, manorialism was slowly replaced by the advent of a money-based market economy and new forms of agrarian contract. In examining the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingston Russell
Kingston Russell is a settlement and civil parish west of Dorchester, in the Dorset district, in the county of Dorset, England. In 2001 the parish had a population of 35. The parish touches Compton Valence, Littlebredy, Long Bredy and Winterbourne Abbas. Kingston Russell shares a parish council with Long Bredy. Features There are 4 listed buildings in Kingston Russell. History The name "Kingston" means 'King's stone', it was held by John Russel in 1212. See also * Kingston Russell House Kingston Russell House is a large mansion house and manor near Long Bredy in Dorset, England, west of Dorchester. The present house dates from the late 17th century but in 1730 was clad in a white Georgian stone facade. The house was resto ... * Kingston Russell Stone Circle References * Villages in Dorset Civil parishes in Dorset West Dorset District {{Dorset-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Bedwyn (UK Parliament Constituency)
Great Bedwyn was a parliamentary borough in Wiltshire, centred on Great Bedwyn, which elected two Members of Parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons from 1295 until 1832, when the borough was abolished by the Great Reform Act. Members of Parliament 1295–1640 1640–1832 Notes References *Robert Beatson''A Chronological Register of Both Houses of Parliament''(London: Longman, Hurst, Res & Orme, 1807) *D Brunton & D H Pennington, ''Members of the Long Parliament'' (London: George Allen & Unwin, 1954) *''Cobbett's Parliamentary history of England, from the Norman Conquest in 1066 to the year 1803'' (London: Thomas Hansard, 1808) viInternet Archive* J Holladay Philbin, ''Parliamentary Representation 1832 – England and Wales'' (New Haven: Yale University Press, 1965) *Henry Stooks Smith, ''The Parliaments of England from 1715 to 1847'' (2nd edition, edited by FWS Craig – Chichester: Parliamentary Reference Publications, 1973) * * {{Cite journal , last=Ward , first=J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgess (title)
Burgess was a British title used in the medieval and early modern period to designate someone of the Burgher class. It originally meant a freeman of a borough or burgh but later coming to mean an official of a municipality or a representative in the House of Commons. Usage in England In England, burgess meant an elected or unelected official of a municipality, or the representative of a borough in the English House of Commons. This usage of "burgess" has since disappeared. Burgesses as freemen had the sole right to vote in municipal or parliamentary elections. However, these political privileges in Britain were removed by the Reform Act in 1832. Usage in Scotland Burgesses were originally freeman inhabitants of a city where they owned land and who contributed to the running of the town and its taxation. The title of ''burgess'' was later restricted to merchants and craftsmen, so that only burgesses could enjoy the privileges of trading or practising a craft in the city throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
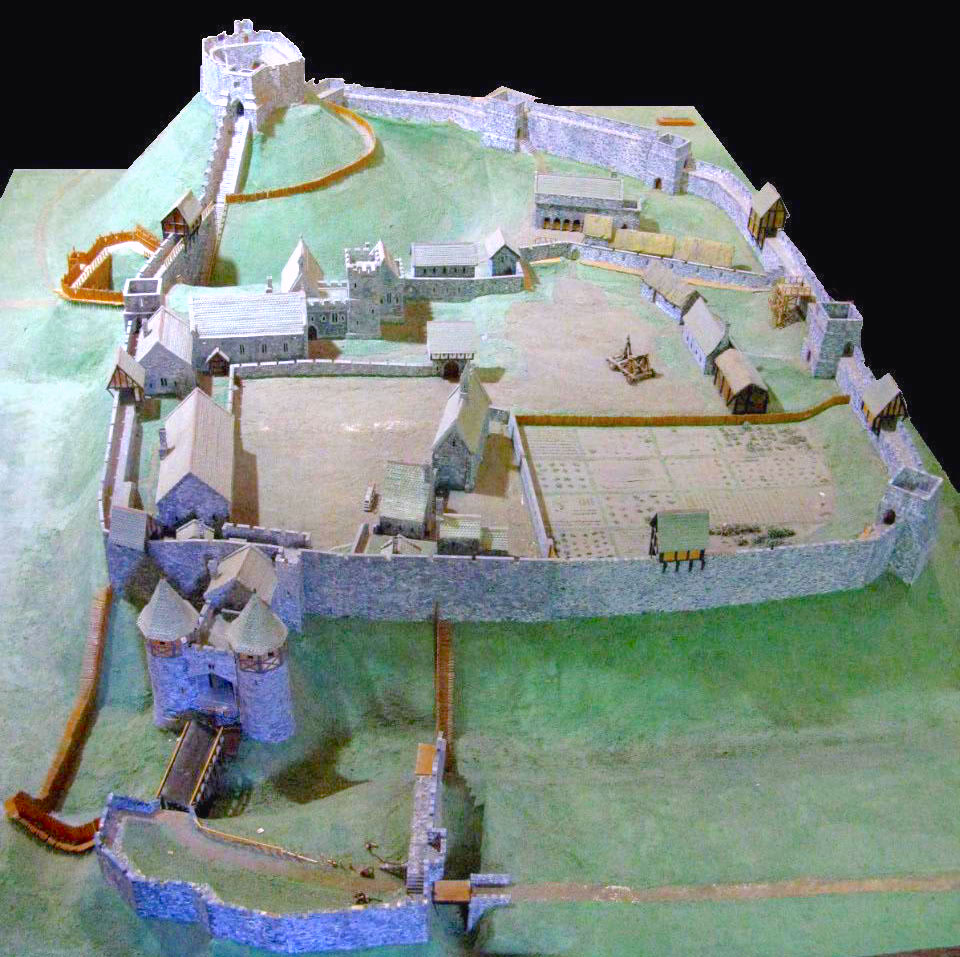
Carisbrooke Castle
Carisbrooke Castle is a historic motte-and-bailey castle located in the village of Carisbrooke (near Newport), Isle of Wight, England. Charles I was imprisoned at the castle in the months prior to his trial. Early history The site of Carisbrooke Castle may have been occupied in pre-Roman times. A ruined wall suggests that there was a building there in late Roman times. The '' Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' mentions that Wihtgar, cousin of King Cynric of Wessex, died in AD 544, and was buried there. The Jutes may have taken over the fort by the late 7th century. An Anglo-Saxon stronghold occupied the site during the 8th century. Around 1000, a wall was built around the hill as a defence against Viking raids. Later history From 1100 the castle remained in the possession of Richard de Redvers' family, and over the next two centuries his descendants improved the castle with stone walls, towers and a keep. In 1293, Countess Isabella de Fortibus, the last Redvers resident, sold the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Russell (knight)
Sir William Russell (1257–1311) was an English nobleman, knight, and holder of a ''moiety'' of the feudal barony of North Cadbury, Somerset, but spent most of his life engaged in the administration and defence of the Isle of Wight, where he obtained by marriage the manor of Yaverland. He served as constable of Carisbrooke Castle, and sat in parliament on two occasions, firstly as burgess for Great Bedwyn, Wiltshire, and then for the County of Southampton. As a baron his military service was called on several times by King Edward I ''Hammer of the Scots''. Origin William Russell was the third son and eventual heir of Sir Ralph Russell (b. 1204), son of Sir John Russell (d. c. 1224) of Kingston Russell, Dorset, steward of Kings John (1199–1216) and his young son Henry III (1216–1272). Shortly before his death King John had granted Russell the manor of Kingston by grand serjeanty, which grant was confirmed by Henry. William had inherited from his mother Isabel de Newma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carisbrooke Castle, Isle Of Wight, UK -gate-20Feb2010
Carisbrooke is a village on the south western outskirts of Newport, Isle of Wight and is best known as the site of Carisbrooke Castle. It also has a medieval parish church. St Mary's Church (overlooking Carisbrooke High Street with views to the castle), began life as part of a Benedictine priory, established by French monks about 1150. The priory was dissolved by King Henry V of England in 1415 during the French Wars. Neglect over the centuries took its toll, but in 1907 the church was restored to its full glory. Its most striking feature is the 14th century tower, rising in five stages with a turret at one corner and a battlemented and pinnacled crown. There is a Roman Villa discovered in the Victorian era on the site of the old vicarage. Transport It is served by Southern Vectis buses operating to Freshwater, Newport, Yarmouth and Ventnor, as well as some smaller villages. It was served by nearby Carisbrooke railway station until it closed in 1953. It is the starting point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward I Of England
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vassal of the French king. Before his accession to the throne, he was commonly referred to as the Lord Edward. The eldest son of Henry III, Edward was involved from an early age in the political intrigues of his father's reign, which included a rebellion by the English barons. In 1259, he briefly sided with a baronial reform movement, supporting the Provisions of Oxford. After reconciliation with his father, however, he remained loyal throughout the subsequent armed conflict, known as the Second Barons' War. After the Battle of Lewes, Edward was held hostage by the rebellious barons, but escaped after a few months and defeated the baronial leader Simon de Montfort at the Battle of Evesham in 1265. Within two years the rebellion was extin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleanor Of Castile
Eleanor of Castile (1241 – 28 November 1290) was Queen of England as the first wife of Edward I, whom she married as part of a political deal to affirm English sovereignty over Gascony. The marriage was known to be particularly close, and Eleanor travelled extensively with her husband. She was with him on the Ninth Crusade, when he was wounded at Acre, but the popular story of her saving his life by sucking out the poison has long been discredited. When she died, at Harby near Lincoln, her grieving husband famously ordered a stone cross to be erected at each stopping-place on the journey to London, ending at Charing Cross. Eleanor was better educated than most medieval queens and exerted a strong cultural influence on the nation. She was a keen patron of literature and encouraged the use of tapestries, carpets and tableware in the Spanish style, as well as innovative garden designs. She was also a successful businesswoman, endowed with her own fortune as Countess of Ponth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escheator
Escheat is a common law doctrine that transfers the real property of a person who has died without heirs to the crown or state. It serves to ensure that property is not left in "limbo" without recognized ownership. It originally applied to a number of situations where a legal interest in land was destroyed by operation of law, so that the ownership of the land reverted to the immediately superior feudal lord. Etymology The term "escheat" derives ultimately from the Latin ''ex-cadere'', to "fall-out", via mediaeval French ''escheoir''. The sense is of a feudal estate in land falling-out of the possession by a tenant into the possession of the lord. Origins in feudalism In feudal England, escheat referred to the situation where the tenant of a fee (or "fief") died without an heir or committed a felony. In the case of such demise of a tenant-in-chief, the fee reverted to the King's demesne permanently, when it became once again a mere tenantless plot of land, but could be re-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siston
Siston (pronounced "sizeton") is a small village in South Gloucestershire, England. It is east of Bristol at the confluence of the two sources of the Siston Brook, a tributary of the River Avon. The village consists of a number of cottages and farms centred on St Anne's Church, and the grand Tudor manor house of Siston Court. Anciently it was bordered to the west by the royal Hunting Forest of Kingswood, stretching westward most of the way to Bristol Castle, always a royal possession, ''caput'' of the Forest. The local part of the disafforested Kingswood became Siston Common but has recently been eroded by the construction of the Avon Ring Road and housing developments. In 1989 the village and environs were classed as a conservation area and thus have statutory protection from overdevelopment. History At the time of the Roman conquest the area was woodland, but there is evidence of Roman remains. It has been known throughout time as Sistone, Siston, Systun, Syton, and Syton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |