|
Manis Lydekkeri
''Manis'' is a genus of South Asia, South Asian and East Asia, East Asian pangolins, the Asiatic pangolins, from subfamily Maninae, within family Manidae. Etymology Carl Linnaeus (1758) invented the Neo Latin, Neo-Latin generic name ''Manis'' apparently as a feminine singular form of the Latin masculine plural Manes, the Ancient Rome, Ancient Roman name for a type of spirit, after the animal's strange appearance. Taxonomy * Subfamily: Maninae (Asiatic pangolins) ** Genus: ''Manis'' (Asiatic pangolins) *** ''Indian pangolin, Manis crassicaudata'' (Indian pangolin) *** ''Chinese pangolin, Manis pentadactyla'' (Chinese pangolin) *** ''Manis'' sp. (Scale_H4 & Scale_H8)Huarong Zhang, Mark P. Miller, Feng Yang, Hon Ki Chan, Philippe Gaubert, Gary Ades, Gunter A. Fischer (2015."Molecular tracing of confiscated pangolin scales for conservation and illegal trade monitoring in Southeast Asia" Global Ecology and Conservation, Volume 4, Pages 414-422Jingyang Hu, Christian Roos, Xue Lv, We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and Roman Empire (27 BC–476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian Peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually dominated the Italian Peninsula, assimilated the Greek culture of southern Italy ( Magna Grecia) and the Etruscan culture and acquired an Empire that took in much of Europe and the lands and peoples surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. It was among the largest empires in the ancient world, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants, roughly 20% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phataginus
African tree pangolin (''Phataginus'') is a genus of African pangolins from subfamily small African pangolins (Phatagininae), within family Manidae. Its members are the more arboreal of the African pangolins. The number of illegally trafficked pangolins from genus ''Phataginus'' were at least a shocking 895,000 from the years 2010 to 2019. The animal is hunted and poached for its scales and meat and is often used for the making of traditional medicine in places such as China and Vietnam. Attempts are still being made to help protect these mammals from trafficking and extinction, unfortunately their slow reproduction rate isn't much of assistance to this effort. Currently the tree pangolin is listed as vulnerable. All of the pangolins species have been listed as vulnerable, endangered and critically endangered.Gaubert, P. (2020). "Development and characterization of 20 polymorphic microsatellite markers for the white-bellied pangolin ''Phataginus tricuspis'' (Mammalia, Pholidota). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
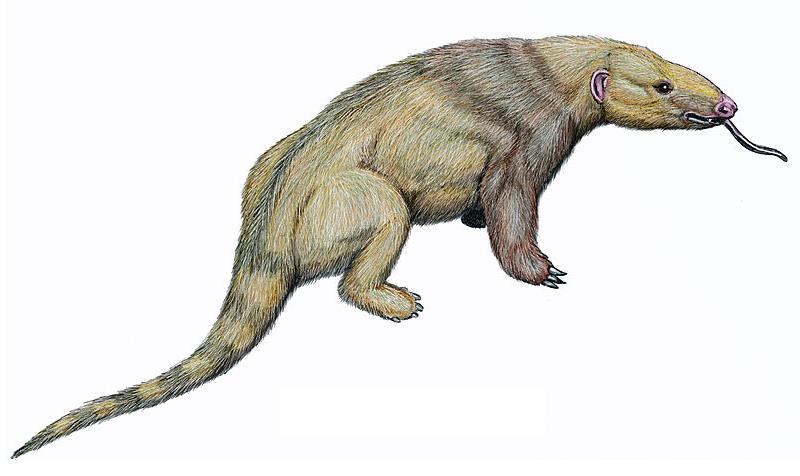
Necromanis
''Necromanis'' ("extinct pangolin") is an extinct genus of pangolin from superfamily Manoidea. It lived during the Oligocene and Miocene of Europe. It was originally placed within family Manidae, but was eventually removed from it as more fossil pholidotids from outside that family were found and studied more extensively (i.e., with the discovery and study of ''Eomanis'' and '' Patriomanis'').Gaudin, Timothy J., Robert J. Emry, and Brandon Pogue. "A new genus and species of pangolin (Mammalia, Pholidota) from the late Eocene of Inner Mongolia, China." Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 26.1 (2006): 146-159. Currently, ''Necromanis'' is placed as ''incertae sedis'' within the pholidotid superfamily Manoidea, together with the families Manidae and Patriomanidae. ''N. quercyi'' was originally placed within ''Teutomanis'' by Ameghino in 1905, but was later subsumed into ''Necromanis''. A new fossil humerus attributed to ''N. franconica'' from Quercy Quercy (; oc, Carcin , lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patriomanidae
Patriomanidae ("fathers of pangolins") is a extinct family of pangolins from superfamily Manoidea that includes two extinct genera ''Patriomanis'' and '' Cryptomanis''. Taxonomy * Family: †Patriomanidae ** Genus: †'' Cryptomanis'' *** †''Cryptomanis gobiensis'' ** Genus: †''Patriomanis ''Patriomanis'' ("father of pangolins") is an extinct genus of pangolin from extinct family Patriomanidae. It lived during the Eocene of North America and it currently represents the only pangolin known from the Western Hemisphere. The genus co ...'' *** †''Patriomanis americana'' Phylogeny Phylogenetic position of family Patriomanidae within superfamily Manoidea. References Prehistoric pangolins Prehistoric mammal families {{Paleo-mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manoidea
Manoidea is a superfamily of pangolins from suborder Eupholidota that includes extant family Manidae, extinct family Patriomanidae and extinct genus ''Necromanis''. Taxonomy * Superfamily: Manoidea ** Family: Manidae (pangolins) ** Family: †Patriomanidae ** ''Incertae sedis'' *** Genus: †''Necromanis ''Necromanis'' ("extinct pangolin") is an extinct genus of pangolin from superfamily Manoidea. It lived during the Oligocene and Miocene of Europe. It was originally placed within family Manidae, but was eventually removed from it as more f ...'' Phylogeny Phylogenetic position of superfamily Manoidea within suborder Eupholidota. References Pangolins Mammal superfamilies {{mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eomanis
''Eomanis'' ("dawn pangolin") is the earliest known true (and scaled) pangolin from extinct family Eomanidae (and extinct superfamily Eomanoidea) within suborder Eupholidota. It lived during the Eocene in Europe. ''Eomanis'' fossils found in the Messel Pit in Germany are very similar in size and anatomy to living pangolins of the genus '' Manis'', indicating that pangolins have remained largely unchanged in morphology and behavior for 50 million years. However, unlike modern pangolins, its tail and legs did not bear scales. According to the stomach contents of the excellently preserved Messel specimens, ''Eomanis’'' diet consisted of both insects and plants. Another early mammal discovered in the Messel Pit that was similar in anatomy and likely also had an insectivorous diet was ''Eurotamandua''. Despite its name, ''Eurotamandua'' was almost certainly not a xenarthran because it lacked the characteristic xenarthran joints present in all living and extinct xenarthrans. In add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eupholidota
Eupholidota ("true pangolins") is a suborder of pangolins that includes two superfamilies: extant Manoidea and extinct Eomanoidea. Taxonomy * Suborder: Eupholidota (true pangolins) ** Superfamily: Manoidea *** Family: Manidae (pangolins) *** Family: †Patriomanidae *** ''Incertae sedis'' **** Genus: †''Necromanis ''Necromanis'' ("extinct pangolin") is an extinct genus of pangolin from superfamily Manoidea. It lived during the Oligocene and Miocene of Europe. It was originally placed within family Manidae, but was eventually removed from it as more f ...'' ** Superfamily: † Eomanoidea *** Family: † Eomanidae Phylogeny Phylogenetic position of suborder Eupholidota within order Pholidota. References Pangolins {{mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurotamandua
''Eurotamandua'' ("european ''Tamandua''") is an extinct genus of mammal from extinct family Eurotamanduidae that lived some 40-35 million years ago, during the middle Eocene. A single fossil is known, coming from the Messel Pit in southwestern Germany. ''Eurotamandua'' was about long. Most palaeontologists now classify ''Eurotamandua'' as a pangolin. When its fossils were first discovered, ''Eurotamandua'' was originally thought to be an anteater, as it lacked the characteristic fused-hair scales of other pangolins. ''Eurotamandua'' placement within the pangolins was made primarily because of a lack of the characteristic "xenarthran" joints found in all xenarthrans, including tamanduas. There is still much ambiguity in the taxonomy of all mammals prior to the Eocene, so there is the possibility that ''Eurotamandua'' was a primitive xenarthran. However, this is highly unlikely because all known fossil evidence indicates that xenarthrans existed exclusively in South America from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euromanis
''Euromanis'' ("european pangolin") is one of the earliest known pangolin genera. It lived during the Eocene in Europe. ''Euromanis'' fossils found in the Messel Pit in Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe .... Unlike modern pangolins, it did not bear scales on its body. Phylogeny Phylogenetic position of genus ''Euromanis'' within order Pholidota. References Prehistoric pangolins Eocene mammals Myrmecophagous mammals Prehistoric placental genera Cenozoic mammals of Europe Fossil taxa described in 1994 {{paleo-mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangolin
Pangolins, sometimes known as scaly anteaters, are mammals of the order Pholidota (, from Ancient Greek ϕολιδωτός – "clad in scales"). The one extant family, the Manidae, has three genera: '' Manis'', '' Phataginus'', and '' Smutsia''. ''Manis'' comprises the four species found in Asia, while ''Phataginus'' and ''Smutsia'' include two species each, all found in sub-Saharan Africa. These species range in size from . A number of extinct pangolin species are also known. Pangolins have large, protective keratin scales, similar in material to fingernails and toenails, covering their skin; they are the only known mammals with this feature. They live in hollow trees or burrows, depending on the species. Pangolins are nocturnal, and their diet consists of mainly ants and termites, which they capture using their long tongues. They tend to be solitary animals, meeting only to mate and produce a litter of one to three offspring, which they raise for about two years. Pangol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)