|
Manhattanhenge 2016-07-12-FRD
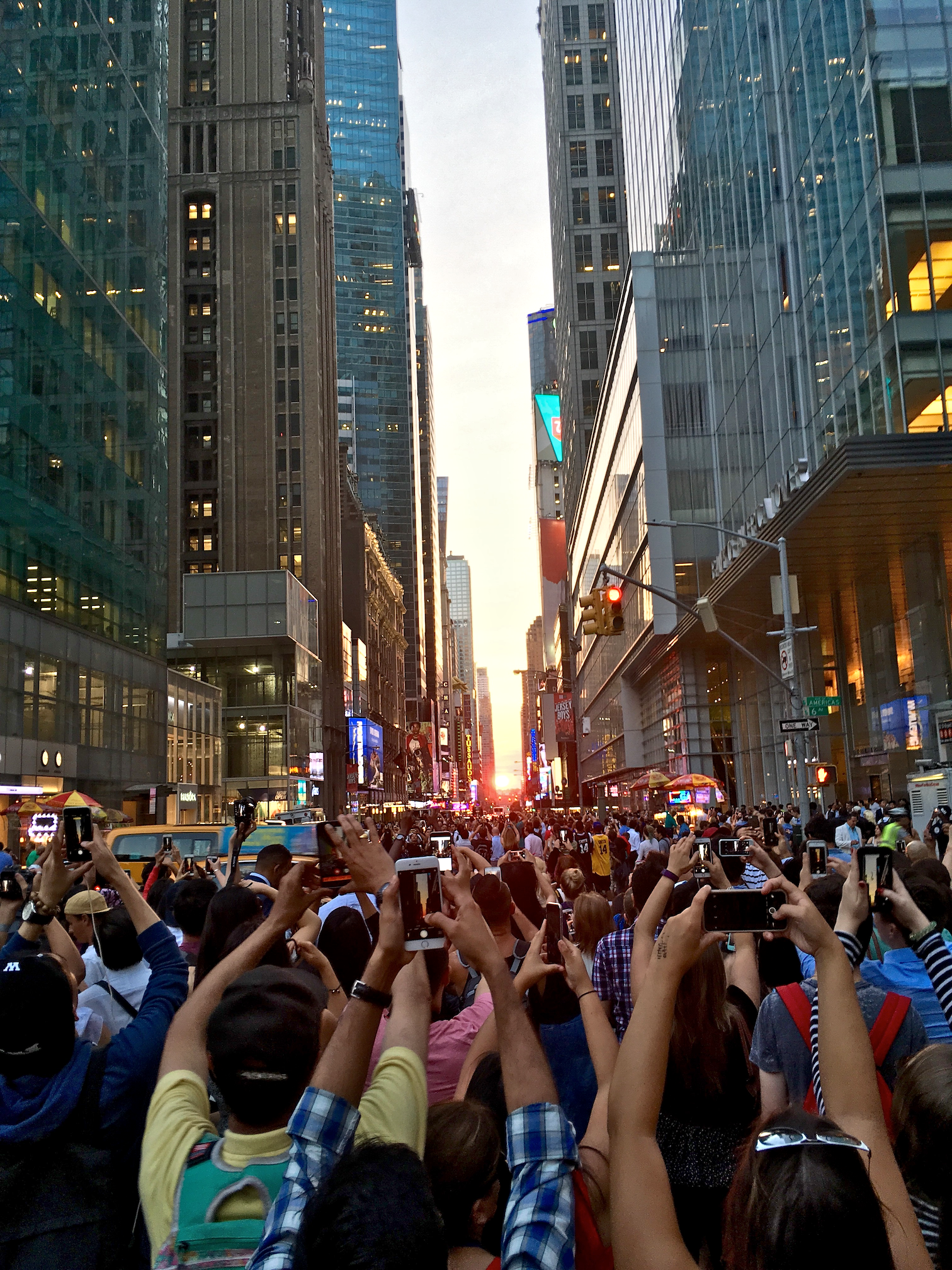
Manhattanhenge, also inaccurately called the Manhattan Solstice, is an event during which the sunset, setting sun or the sunrise, rising sun is aligned with the east–west streets of the main street grid of Manhattan, New York City. The astrophysicist Neil deGrasse Tyson has said that he coined the term, by analogy with Stonehenge. The sunsets and sunrises each align twice a year, on dates evenly spaced around the summer solstice and winter solstice. The sunset alignments occur around May 28 and July 13. The sunrise alignments occur around December 5 and January 8. Manhattan is a particularly remarkable place to view a phenomenon of this kind, due to its extensive urban canyons and its rectilinear street grid that is rotated 29° clockwise from true east–west. Excellent places for viewing Manhattanhenge include 14th Street (Manhattan), 14th, 23rd Street (Manhattan), 23rd, 34th Street (Manhattan), 34th, 42nd Street (Manhattan), 42nd, and 57th Street (Manhattan), 57th Streets. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manhattanhenge 2016-07-12-FRD
Manhattanhenge, also inaccurately called the Manhattan Solstice, is an event during which the sunset, setting sun or the sunrise, rising sun is aligned with the east–west streets of the main street grid of Manhattan, New York City. The astrophysicist Neil deGrasse Tyson has said that he coined the term, by analogy with Stonehenge. The sunsets and sunrises each align twice a year, on dates evenly spaced around the summer solstice and winter solstice. The sunset alignments occur around May 28 and July 13. The sunrise alignments occur around December 5 and January 8. Manhattan is a particularly remarkable place to view a phenomenon of this kind, due to its extensive urban canyons and its rectilinear street grid that is rotated 29° clockwise from true east–west. Excellent places for viewing Manhattanhenge include 14th Street (Manhattan), 14th, 23rd Street (Manhattan), 23rd, 34th Street (Manhattan), 34th, 42nd Street (Manhattan), 42nd, and 57th Street (Manhattan), 57th Streets. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equinox
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun crosses the Earth's equator, which is to say, appears directly above the equator, rather than north or south of the equator. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise "due east" and set "due west". This occurs twice each year, around 20 March and 23 September. More precisely, an equinox is traditionally defined as the time when the plane of Earth's equator passes through the geometric center of the Sun's disk. Equivalently, this is the moment when Earth's rotation axis is directly perpendicular to the Sun-Earth line, tilting neither toward nor away from the Sun. In modern times, since the Moon (and to a lesser extent the planets) causes Earth's orbit to vary slightly from a perfect ellipse, the equinox is officially defined by the Sun's more regular ecliptic longitude rather than by its declination. The instants of the equinoxes are currently defined to be when the apparent geocentric longitude of the Sun is 0° a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azimuth
An azimuth (; from ar, اَلسُّمُوت, as-sumūt, the directions) is an angular measurement in a spherical coordinate system. More specifically, it is the horizontal angle from a cardinal direction, most commonly north. Mathematically, the relative position vector from an observer (origin) to a point of interest is projected perpendicularly onto a reference plane (the horizontal plane); the angle between the projected vector and a reference vector on the reference plane is called the azimuth. When used as a celestial coordinate, the azimuth is the horizontal direction of a star or other astronomical object in the sky. The star is the point of interest, the reference plane is the local area (e.g. a circular area with a 5 km radius at sea level) around an observer on Earth's surface, and the reference vector points to true north. The azimuth is the angle between the north vector and the star's vector on the horizontal plane. Azimuth is usually measured in d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
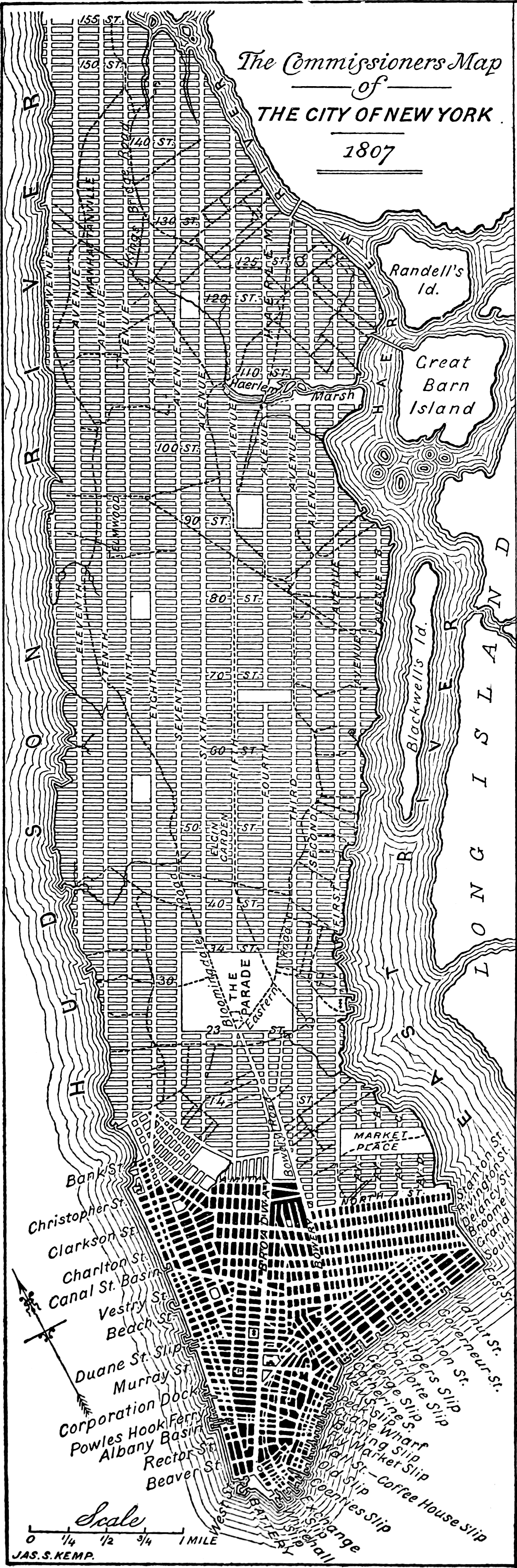
Commissioners' Plan Of 1811
The Commissioners' Plan of 1811 was the original design for the streets of Manhattan above Houston Street and below 155th Street, which put in place the rectangular grid plan of streets and lots that has defined Manhattan on its march uptown until the current day. It has been called "the single most important document in New York City's development,"Augustyn & Cohen, pp.100–06 and the plan has been described as encompassing the "republican predilection for control and balance ... nddistrust of nature". It was described by the Commission that created it as combining "beauty, order and convenience." The plan originated when the Common Council of New York City, seeking to provide for the orderly development and sale of the land of Manhattan between 14th Street and Washington Heights, but unable to do so itself for reasons of local politics and objections from property owners, asked the New York State Legislature to step in. The legislature appointed a commission with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeoastronomy And Stonehenge
The prehistoric monument of Stonehenge has long been studied for its possible connections with ancient astronomy. The site is aligned in the direction of the sunrise of the summer solstice and the sunset of the winter solstice. archaeoastronomy, Archaeoastronomers have made a range of further claims about the site's connection to astronomy, its meaning, and its use. Early work Stonehenge has an opening in the henge earthwork facing northeast, and suggestions that particular significance was placed by its builders on the solstice and equinox points have followed. For example, the summer solstice Sun rose close to the Heel Stone, and the Sun's first rays shone into the centre of the monument between the horseshoe arrangement. While it is possible that such an alignment could be coincidental, this astronomical orientation had been acknowledged since William Stukeley drew the site and first identified its axis along the midsummer sunrise in 1720. Stukeley noticed that the Heel Stone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observatory
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysical, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed. Historically, observatories were as simple as containing an astronomical sextant (for measuring the distance between stars) or Stonehenge (which has some alignments on astronomical phenomena). Astronomical observatories Astronomical observatories are mainly divided into four categories: space-based, airborne, ground-based, and underground-based. Ground-based observatories Ground-based observatories, located on the surface of Earth, are used to make observations in the radio and visible light portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Most optical telescopes are housed within a dome or similar structure, to protect the delicate instruments from the elements. Telescope domes have a slit or other opening in the roof that can be opened during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerald Hawkins
Gerald Stanley Hawkins (20 April 1928– 26 May 2003) was a British-born American astronomer and author noted for his work in the field of archaeoastronomy. A professor and chair of the astronomy department at Boston University in the United States, he published in 1963 an analysis of Stonehenge in which he was the first to propose that it was an ancient astronomical observatory used to predict movements of the sun and moon, and that it was used as a computer. Archaeologists and other scholars have since demonstrated such sophisticated, complex planning and construction at other prehistoric earthwork sites, such as Cahokia in the United States. Early life and education Gerald Hawkins was born in Great Yarmouth, England and studied physics and mathematics at the University of Nottingham. In 1952 he took a PhD in radio astronomy, studying under Sir Bernard Lovell at the University of Manchester. Career In 1957 Hawkins became professor of astronomy and chairman of the depa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History (magazine)
''Natural History'' is a natural history magazine published in the United States. The stated mission of the magazine is to promote public understanding and appreciation of nature and science. History Founded in 1900 by the American Museum of Natural History, ''Natural History'' was first titled ''The American Museum Journal''. In 2002, the magazine was purchased from the Museum by a new company, headed at the time by Charles Harris. As of 2013 the magazine is published in North Carolina by Howard Richman. There are 10 issues published annually. Since its founding, ''Natural History'' has chronicled the major expeditions and research findings by curators at the American Museum of Natural History and at other natural history museums and science centers. Stephen Jay Gould's column, "This View of Life," was a regular feature of the magazine from 1974 until he retired the column in 2001. Other regular columnists and contributing authors include Neil deGrasse Tyson, Jared Diamond, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
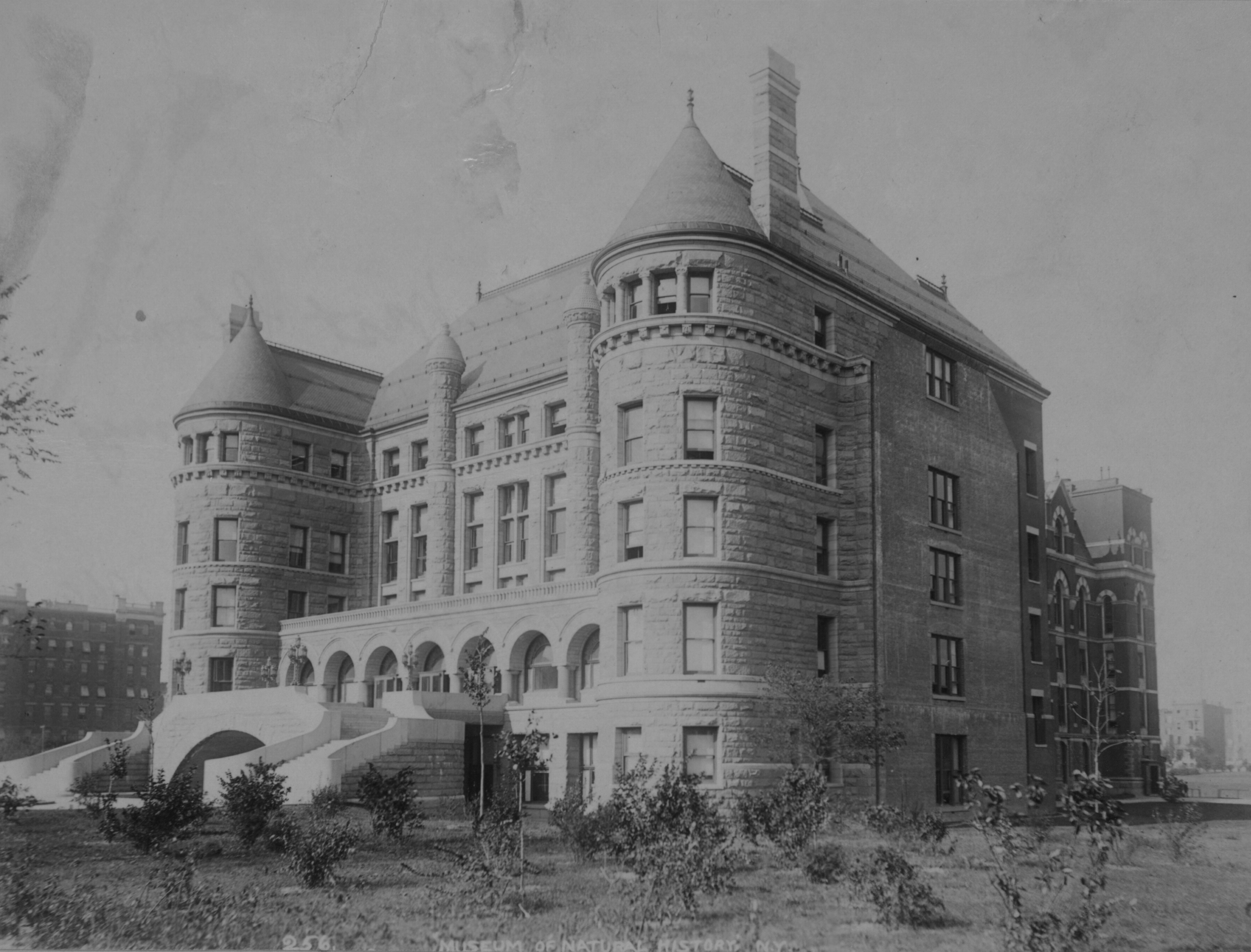
American Museum Of Natural History
The American Museum of Natural History (abbreviated as AMNH) is a natural history museum on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. In Theodore Roosevelt Park, across the street from Central Park, the museum complex comprises 26 interconnected buildings housing 45 permanent exhibition halls, in addition to a planetarium and a library. The museum collections contain over 34 million specimens of plants, animals, fossils, minerals, rocks, meteorites, human remains, and human cultural artifacts, as well as specialized collections for frozen tissue and genomic and astrophysical data, of which only a small fraction can be displayed at any given time. The museum occupies more than . AMNH has a full-time scientific staff of 225, sponsors over 120 special field expeditions each year, and averages about five million visits annually. The AMNH is a private 501(c)(3) organization. Its mission statement is: "To discover, interpret, and disseminate—through scientific research and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heel Stone
The Heel Stone is a single large block of sarsen stone standing within the Avenue outside the entrance of the Stonehenge earthwork in Wiltshire, England. In section it is sub-rectangular, with a minimum thickness of , rising to a tapered top about high. Excavation has shown that a further is buried in the ground. It is from the centre of Stonehenge circle. It leans towards the southwest nearly 27 degrees from the vertical. The stone has an overall girth of and weighs about 35 tons. It is surrounded by the Heelstone Ditch. Myths and legends of the Devil striking a "Friar's Heel" with a stone resulted in its eccentric name, ''Heel Stone''. Some claim "Friar's Heel" is a corruption of "Freyja's He-ol" or "Freyja Sul", from the Nordic goddess Freyja and (allegedly) the Welsh words for "way" and "Sunday" respectively. It is doubtful whether any prehistoric standing stone has experienced as many name changes and interpretations. Only in the past three decades have scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiltshire
Wiltshire (; abbreviated Wilts) is a historic and ceremonial county in South West England with an area of . It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset to the southwest, Somerset to the west, Hampshire to the southeast, Gloucestershire to the north, Oxfordshire to the northeast and Berkshire to the east. The county town was originally Wilton, after which the county is named, but Wiltshire Council is now based in the county town of Trowbridge. Within the county's boundary are two unitary authority areas, Wiltshire and Swindon, governed respectively by Wiltshire Council and Swindon Borough Council. Wiltshire is characterised by its high downland and wide valleys. Salisbury Plain is noted for being the location of the Stonehenge and Avebury stone circles (which together are a UNESCO Cultural and World Heritage site) and other ancient landmarks, and as a training area for the British Army. The city of Salisbury is notable for its medieval cathedral. Swindon is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)