|
Mangrove Kingfisher
The mangrove kingfisher (''Halcyon senegaloides'') is a kingfisher in the genus ''Halcyon (genus), Halcyon''. It is similar in appearance to the woodland kingfisher. It is found along the eastern coastline of Sub-Saharan Africa, living in woodland, along rivers, and in estuaries and mangrove. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has assessed it as being of least concern. Taxonomy This species was described by Andrew Smith (zoologist), Andrew Smith in 1834, using a specimen collected around Port Natal (now Durban). It is a close relative of the woodland kingfisher (''Halcyon senegalensis''). The mangrove kingfisher is a monotypic species. Northern populations are sometimes separated as subspecies ''ranivorus'', but the differences do not appear to be large enough. Description The mangrove kingfisher is about long. The male and female are alike. The head is dark grey-brown, with black lore (anatomy), lores and a narrow white line above the eye, and the cheek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saadani National Park
Saadani National Park is Tanzania's 13th national park and has an area of . It was officially gazetted in 2005 and is managed under the Tanzania National Parks Authority. The park is located administratively in southeast Pangani District of Tanga Region and northeast Chalinze District of Pwani Region. History Gazetted in 2005, it encompasses a preserved ecosystem including the former Saadani game reserve, the former Mkwaja ranch area, the Wami River as well as the Zaraninge Forest. In the late 1960s Saadani Village – the village after which the park has been named – and particularly its sub-village Uvinje, invited the Tanzania Wildlife Division (WD) to help them to prevent the indiscriminate killing of wildlife prevalent in the area. From this partnership Saadani village and the Wildlife Division established the Saadani Game Reserve (SGR), with the agreement to respect the land rights of the coastal sub-villages of Saadani, including Uvinje and Porokanya sub-villages, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juvenile (organism)
A juvenile is an individual organism that has not yet reached its adult form, sexual maturity or size. Juveniles can look very different from the adult form, particularly in colour, and may not fill the same niche as the adult form. In many organisms the juvenile has a different name from the adult (see List of animal names). Some organisms reach sexual maturity in a short metamorphosis, such as eclosion in many insects. For others, the transition from juvenile to fully mature is a more prolonged process—puberty in humans and other species, for example. In such cases, juveniles during this transformation are sometimes called subadults. Many invertebrates, on reaching the adult stage, are fully mature and their development and growth stops. Their juveniles are larvae or nymphs. In vertebrates and some invertebrates (e.g. spiders), larval forms (e.g. tadpoles) are usually considered a development stage of their own, and "juvenile" refers to a post-larval stage that is not full ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Of East Africa
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Least-concern Species
A least-concern species is a species that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as evaluated as not being a focus of species conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wild. They do not qualify as threatened, near threatened, or (before 2001) conservation dependent. Species cannot be assigned the "Least Concern" category unless they have had their population status evaluated. That is, adequate information is needed to make a direct, or indirect, assessment of its risk of extinction based on its distribution or population status. Evaluation Since 2001 the category has had the abbreviation "LC", following the IUCN 2001 Categories & Criteria (version 3.1). Before 2001 "least concern" was a subcategory of the "Lower Risk" category and assigned the code "LR/lc" or lc. Around 20% of least concern taxa (3261 of 15636) in the IUCN database still use the code "LR/lc", which indicates they have not been re-evaluate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat Loss
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby reducing biodiversity and species abundance. Habitat destruction is the leading cause of biodiversity loss. Fragmentation and loss of habitat have become one of the most important topics of research in ecology as they are major threats to the survival of endangered species. Activities such as harvesting natural resources, industrial production and urbanization are human contributions to habitat destruction. Pressure from agriculture is the principal human cause. Some others include mining, logging, trawling, and urban sprawl. Habitat destruction is currently considered the primary cause of species extinction worldwide. Environmental factors can contribute to habitat destruction more indirectly. Geological processes, climate change, introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
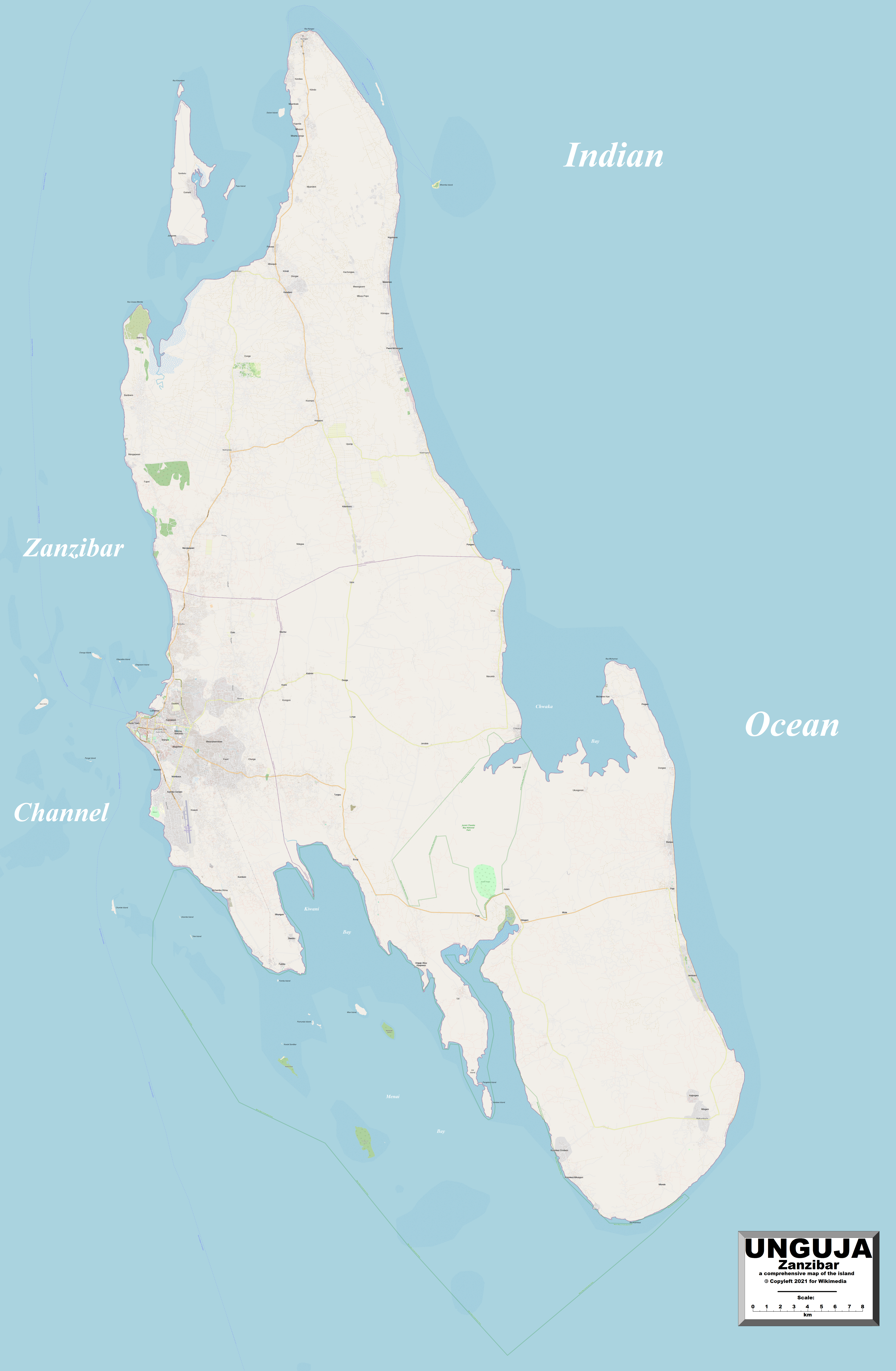
Zanzibar Archipelago
The Zanzibar Archipelago ( ar, أرخبيل زنجبار, sw, Funguvisiwa la Zanzibar) consists of several islands lying off the coast of East Africa south of the Somali sea. The archipelago is also known as the Spice Islands. There are four main islands, three primary islands with human populations, a fourth coral island that serves as an essential breeding ground for seabirds, plus a number of smaller islets that surround them and an isolated tiny islet. Most of the archipelago belongs to the Zanzibar semi-autonomous region of Tanzania, while Mafia Island and its associated islets are parts of the Pwani Region on the mainland. List of islands Main islands * Unguja Island – the largest island, colloquially referred to as Zanzibar, has 896,721 inhabitants *Pemba Island – the second-largest island with 406,808 inhabitants *Latham Island (also called "Fungu Kizimkazi") – tiny and uninhabited *Mafia Island – 46,850 inhabitants Surrounding Unguja Island *Bawe Island * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the ''plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (see differences between British, American, and Australian English explained below). Woodlands may support an understory of shrubs and herbaceous plants including grasses. Woodland may form a transition to shrubland under drier conditions or during early stages of primary or secondary succession. Higher-density areas of trees with a largely closed canopy that provides extensive and nearly continuous shade are often referred to as forests. Extensive efforts by conservationist groups have been made to preserve woodlands from urbanization and agriculture. For example, the woodlands of Northwest Indiana have been preserved as part of the Indiana Dunes. Definitions United Kingdom ''Woodland'' is used in British woodland management to mean tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thornveld
Veld ( or ), also spelled veldt, is a type of wide open rural landscape in :Southern Africa. Particularly, it is a flat area covered in grass or low scrub, especially in the countries of South Africa, Lesotho, Eswatini, Zimbabwe and Botswana. A certain sub-tropical woodland ecoregion of Southern Africa has been officially defined as the Bushveld by the World Wide Fund for Nature. Trees are not abundant—frost, fire and grazing animals allow grass to grow but prevent the build-up of dense foliage. Etymology The word ''veld'' () comes from the Afrikaans word for "field". The etymological origin is older modern Dutch ''veldt'', a spelling that the Dutch abandoned in favour of ''veld'' during the 19th century, decades before the first Afrikaans dictionary.Eric Anderson Walker (ed). The Cambridge History of the British Empire, Volume 4. Cambridge University Press 1963 (Afrikaans: pp. 890–894) A cognate to the English ''field'', it was spelt ''velt'' in Middle Dutch and ''fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in several plant families. They occur worldwide in the tropics and subtropics and even some temperate coastal areas, mainly between latitudes 30° N and 30° S, with the greatest mangrove area within 5° of the equator. Mangrove plant families first appeared during the Late Cretaceous to Paleocene epochs, and became widely distributed in part due to the plate tectonics, movement of tectonic plates. The oldest known fossils of Nypa fruticans, mangrove palm date to 75 million years ago. Mangroves are salt-tolerant trees, also called halophytes, and are adapted to live in harsh coastal conditions. They contain a complex salt filtration system and a complex root system to cope with saltwater immersion and wave action. They are ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estuaries
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environments and are an example of an ecotone. Estuaries are subject both to marine influences such as tides, waves, and the influx of saline water, and to fluvial influences such as flows of freshwater and sediment. The mixing of seawater and freshwater provides high levels of nutrients both in the water column and in sediment, making estuaries among the most productive natural habitats in the world. Most existing estuaries formed during the Holocene epoch with the flooding of river-eroded or glacially scoured valleys when the sea level began to rise about 10,000–12,000 years ago. Estuaries are typically classified according to their geomorphological features or to water-circulation patterns. They can have many different names, such as bays, har ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zambezi
The Zambezi River (also spelled Zambeze and Zambesi) is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. Its drainage basin covers , slightly less than half of the Nile's. The river rises in Zambia and flows through eastern Angola, along the north-eastern border of Namibia and the northern border of Botswana, then along the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe to Mozambique, where it crosses the country to empty into the Indian Ocean. The Zambezi's most noted feature is Victoria Falls. Its other falls include the Chavuma Falls at the border between Zambia and Angola, and Ngonye Falls near Sioma in western Zambia. The two main sources of hydroelectric power on the river are the Kariba Dam, which provides power to Zambia and Zimbabwe, and the Cahora Bassa Dam in Mozambique, which provides power to Mozambique and South Africa. Additionally, two smaller power stations are along the Zambezi Riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jubba River
The Jubba River or Juba River ( so, Wabiga Jubba) is a river in southern Somalia which flows through the autonomous region of Jubaland. It begins at the border with Ethiopia, where the Dawa and Ganale Dorya rivers meet, and flows directly south to the Somali Sea, where it empties at the ''Goobweyn'' juncture. The Jubba basin covers an area of . The Somali regional state of Jubaland, formerly called ''Trans-Juba'', is named after the river. History Ajuran Empire The Jubba River has a rich history of a once-booming sophisticated civilization and trade network conducted by the powerful Somalis that held sway over the Jubba river. During the Middle Ages Jubba river was under the Ajuran Empire of the Horn of Africa which utilized the Jubba River for its plantations and was the only hydraulic empire in Africa. A hydraulic empire that rose in the 13th century AD, Ajuran monopolized the water resources of the Jubba River and Shebelle. Through hydraulic engineering, it also construct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)
