|
Mandel'shtam (crater)
Leonid Isaakovich Mandelstam or Mandelshtam ( be, –Ы–µ–∞–љ—Ц–і –Ж—Б–∞–∞–Ї–∞–≤—Ц—З –Ь–∞–љ–і—Н–ї—М—И—В–∞–Љ; rus, –Ы–µ–Њ–љ–Є–і –Ш—Б–∞–∞–Ї–Њ–≤–Є—З –Ь–∞–љ–і–µ–ї—М—И—В–∞–Љ, p=l ≤…™…РЋИn ≤it …®s…РЋИak…Щv ≤…™t…Х m…Щn ≤d ≤…™l ≤ЋИ Вtam, a=Ru-Leonid_Mandelstam.ogg, links=y; 4 May 1879 вАУ 27 November 1944) was a Soviet physicist of Belarusian-Jewish background. Life Leonid Mandelstam was born in Mogilev, Russian Empire (now Belarus). He studied at the Novorossiya University in Odessa, but was expelled in 1899 due to political activities, and continued his studies at the University of Strasbourg. He remained in Strasbourg until 1914, and returned with the beginning of World War I. He was awarded the Stalin Prize in 1942. Mandelstam died in Moscow, USSR (now Russia). Scientific achievements The main emphasis of his work was broadly considered theory of oscillations, which included optics and quantum mechanics. He was a co-discoverer of inelastic ''combinational scattering of light'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
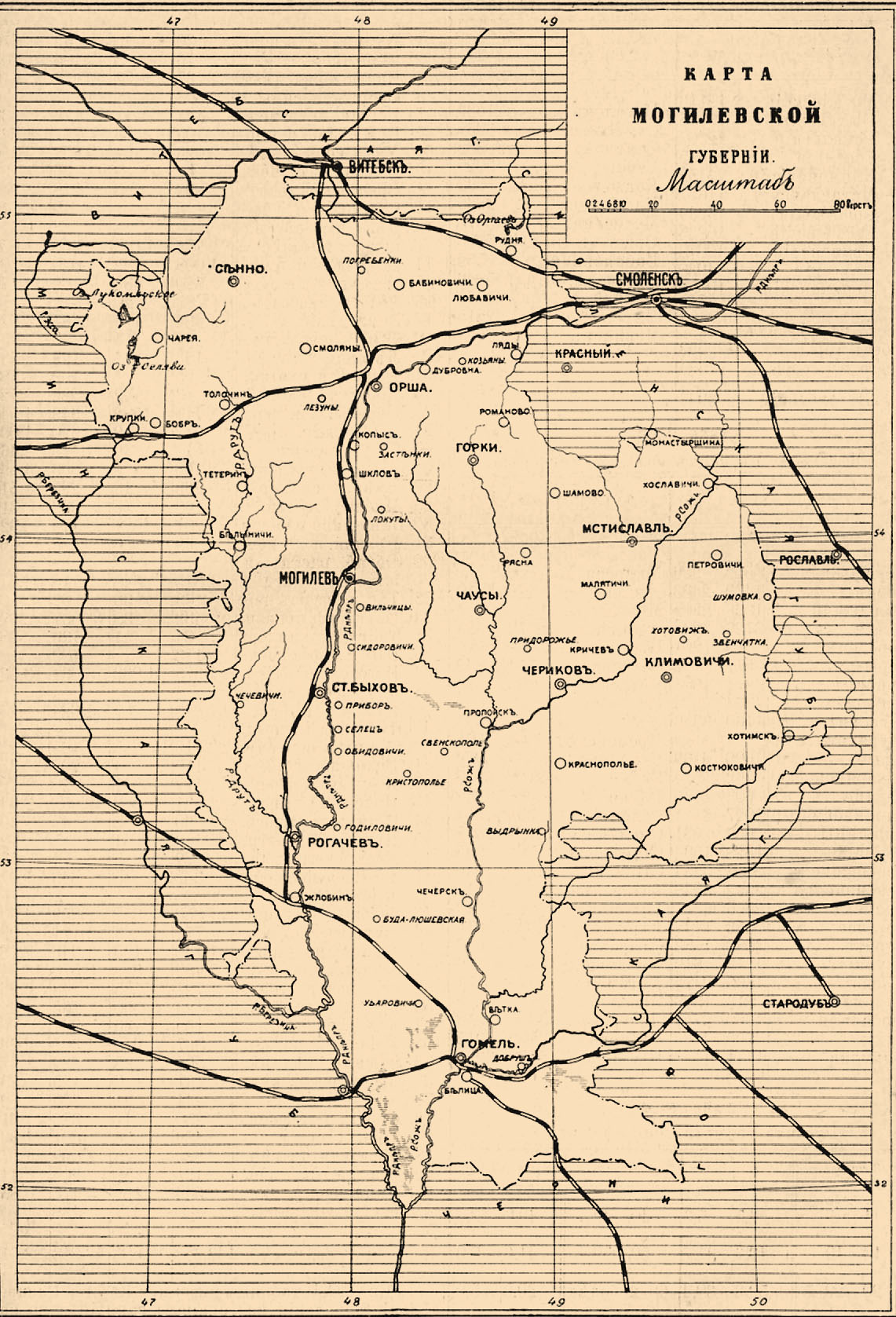
Mogilev
Mogilev (russian: –Ь–Њ–≥–Є–ї—С–≤, Mogilyov, ; yi, „Ю„Р÷Є„Ь„Ґ„Х„Х, Molev, ) or Mahilyow ( be, –Ь–∞–≥—Ц–ї—С—Ю, Mahilio≈≠, ) is a city in eastern Belarus, on the Dnieper River, about from the border with Russia's Smolensk Oblast and from the border with Russia's Bryansk Oblast. , its population was 360,918, up from an estimated 106,000 in 1956. It is the administrative centre of Mogilev Region and the third-largest city in Belarus. History The city was first mentioned in historical records in 1267. From the 14th century, it was part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and since the Union of Lublin (1569), part of the PolishвАУLithuanian Commonwealth, where it became known as ''Mohylew''. In the 16th-17th centuries, the city flourished as one of the main nodes of the eastвАУwest and northвАУsouth trading routes. In 1577, Polish King Stefan Batory granted it city rights under Magdeburg law. In 1654, the townsmen negotiated a treaty of surrender to the Russians peacefully, if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Stalin Prize
The USSR State Prize (russian: links=no, –У–Њ—Б—Г–і–∞—А—Б—В–≤–µ–љ–љ–∞—П –њ—А–µ–Љ–Є—П –°–°–°–†, Gosudarstvennaya premiya SSSR) was the Soviet Union's state honor. It was established on 9 September 1966. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the prize was followed up by the State Prize of the Russian Federation. The State Stalin Prize ( –У–Њ—Б—Г–і–∞—А—Б—В–≤–µ–љ–љ–∞—П –°—В–∞–ї–Є–љ—Б–Ї–∞—П –њ—А–µ–Љ–Є—П, ''Gosudarstvennaya Stalinskaya premiya''), usually called the Stalin Prize, existed from 1941 to 1954, although some sources give a termination date of 1952. It essentially played the same role; therefore upon the establishment of the USSR State Prize, the diplomas and badges of the recipients of Stalin Prize were changed to that of USSR State Prize. In 1944 and 1945, the last two years of the Second World War, the award ceremonies for the Stalin Prize were not held. Instead, in 1946 the ceremony was held twice: in January for the works created in 1943вАУ1944 and in June for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeitschrift F√Љr Physik
''Zeitschrift f√Љr Physik'' (English: ''Journal for Physics'') is a defunct series of German peer-reviewed physics journals established in 1920 by Springer Berlin Heidelberg. The series stopped publication in 1997, when it merged with other journals to form the new ''European Physical Journal'' series. It had grown to four parts over the years. History *''Zeitschrift f√Љr Physik'' (1920–1975 ), The first three issues were published as a supplement to '' Verhandlungen der Deutschen Physikalischen Gesellschaft''. The journal split in parts A and B in 1975. :*''Zeitschrift f√Љr Physik A'' (1975–1997). The original subtitle was ''Atoms and Nuclei'' (). In 1986, it split in ''Zeitschrift f√Љr Physik A: Atomic Nuclei'' () and ''Zeitschrift f√Љr Physik D''. ''Zeitschrift f√Љr Physik A'' now continues as the ''European Physical Journal A''. :*''Zeitschrift f√Љr Physik B'' (1975–1997). This is the result of the split of ''Zeitschrift f√Љr Physik'' and the merger of ''Ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and "rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third category of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rayleigh Scattering
Rayleigh scattering ( ), named after the 19th-century British physicist Lord Rayleigh (John William Strutt), is the predominantly elastic scattering of light or other electromagnetic radiation by particles much smaller than the wavelength of the radiation. For light frequencies well below the resonance frequency of the scattering particle (normal dispersion regime), the amount of scattering is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength. Rayleigh scattering results from the electric polarizability of the particles. The oscillating electric field of a light wave acts on the charges within a particle, causing them to move at the same frequency. The particle, therefore, becomes a small radiating dipole whose radiation we see as scattered light. The particles may be individual atoms or molecules; it can occur when light travels through transparent solids and liquids, but is most prominently seen in gases. Rayleigh scattering of sunlight in Earth's atmosphere causes d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fine Structure
In atomic physics, the fine structure describes the splitting of the spectral lines of atoms due to electron spin and relativistic corrections to the non-relativistic Schr√ґdinger equation. It was first measured precisely for the hydrogen atom by Albert A. Michelson and Edward W. Morley in 1887, laying the basis for the theoretical treatment by Arnold Sommerfeld, introducing the fine-structure constant. Background Gross structure The ''gross structure'' of line spectra is the line spectra predicted by the quantum mechanics of non-relativistic electrons with no spin. For a hydrogenic atom, the gross structure energy levels only depend on the principal quantum number ''n''. However, a more accurate model takes into account relativistic and spin effects, which break the degeneracy of the energy levels and split the spectral lines. The scale of the fine structure splitting relative to the gross structure energies is on the order of (''Zќ±'')2, where ''Z'' is the atomic number a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman
Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman (; 7 November 188821 November 1970) was an Indian physicist known for his work in the field of light scattering. Using a spectrograph that he developed, he and his student K. S. Krishnan discovered that when light traverses a transparent material, the deflected light changes its wavelength and frequency. This phenomenon, a hitherto unknown type of scattering of light, which they called "modified scattering" was subsequently termed the Raman effect or Raman scattering. Raman received the 1930 Nobel Prize in Physics for the discovery and was the first Asian to receive a Nobel Prize in any branch of science. Born to Tamil Brahmin parents, Raman was a precocious child, completing his secondary and higher secondary education from St Aloysius' Anglo-Indian High School at the ages of 11 and 13, respectively. He topped the bachelor's degree examination of the University of Madras with honours in physics from Presidency College at age 16. His first r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow State University
M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University (MSU; russian: –Ь–Њ—Б–Ї–Њ–≤—Б–Ї–Є–є –≥–Њ—Б—Г–і–∞—А—Б—В–≤–µ–љ–љ—Л–є —Г–љ–Є–≤–µ—А—Б–Є—В–µ—В –Є–Љ–µ–љ–Є –Ь. –Т. –Ы–Њ–Љ–Њ–љ–Њ—Б–Њ–≤–∞) is a public research university in Moscow, Russia and the most prestigious university in the country. The university includes 15 research institutes, 43 faculties, more than 300 departments, and six branches (including five foreign ones in the Commonwealth of Independent States countries). Alumni of the university include past leaders of the Soviet Union and other governments. As of 2019, 13 List of Nobel laureates, Nobel laureates, six Fields Medal winners, and one Turing Award winner had been affiliated with the university. The university was ranked 18th by ''The Three University Missions Ranking'' in 2022, and 76th by the ''QS World University Rankings'' in 2022, #293 in the world by the global ''Times Higher World University Rankings'', and #326 by ''U.S. News & World Report'' in 2022. It was the highest-ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grigory Landsberg
Grigory Samuilovich Landsberg (Russian: –У—А–Є–≥–Њ—А–Є–є –°–∞–Љ—Г–Є–ї–Њ–≤–Є—З –Ы–∞–љ–і—Б–±–µ—А–≥; 22 January 1890 вАУ 2 February 1957) was a Soviet physicist who worked in the fields of optics and spectroscopy. Together with Leonid Mandelstam he co-discovered inelastic combinational scattering of light, which is known as Raman scattering. Vitae Landsberg graduated from the Moscow State University in 1913 and then taught there from 1913вАУ1915, 1923вАУ45, and 1947вАУ51 (Professor since 1923). From 1934, he simultaneously worked also in the Physical Institute of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR. From 1951вАУ57 he was a professor at the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology. Landsberg conducted pioneering studies on the vibrational scattering of light in crystals beginning in 1926. In 1928, Landsberg and Mandelstam discovered a phenomenon of ''combinational scattering of light'' (this phenomenon became known as Raman scattering or the Raman effect independently discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy () (named after Indian physicist C. V. Raman) is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified. Raman spectroscopy relies upon inelastic scattering of photons, known as Raman scattering. A source of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range is used, although X-rays can also be used. The laser light interacts with molecular vibrations, phonons or other excitations in the system, resulting in the energy of the laser photons being shifted up or down. The shift in energy gives information about the vibrational modes in the system. Infrared spectroscopy typically yields similar yet complementary information. Typically, a sample is illuminated with a laser beam. Electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scattering
Scattering is a term used in physics to describe a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including particles and radiation) in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of reflected radiation from the angle predicted by the law of reflection. Reflections of radiation that undergo scattering are often called ''diffuse reflections'' and unscattered reflections are called ''specular'' (mirror-like) reflections. Originally, the term was confined to light scattering (going back at least as far as Isaac Newton in the 17th century). As more "ray"-like phenomena were discovered, the idea of scattering was extended to them, so that William Herschel could refer to the scattering of "heat rays" (not then recognized as electromagnetic in nature) in 1800. John Tyndall, a pioneer in light scattering researc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, quantum field theory, quantum technology, and quantum information science. Classical physics, the collection of theories that existed before the advent of quantum mechanics, describes many aspects of nature at an ordinary (macroscopic) scale, but is not sufficient for describing them at small (atomic and subatomic) scales. Most theories in classical physics can be derived from quantum mechanics as an approximation valid at large (macroscopic) scale. Quantum mechanics differs from classical physics in that energy, momentum, angular momentum, and other quantities of a bound system are restricted to discrete values ( quantization); objects have characteristics of both particles and waves (waveвАУparticle duality); and there are limits to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




