|
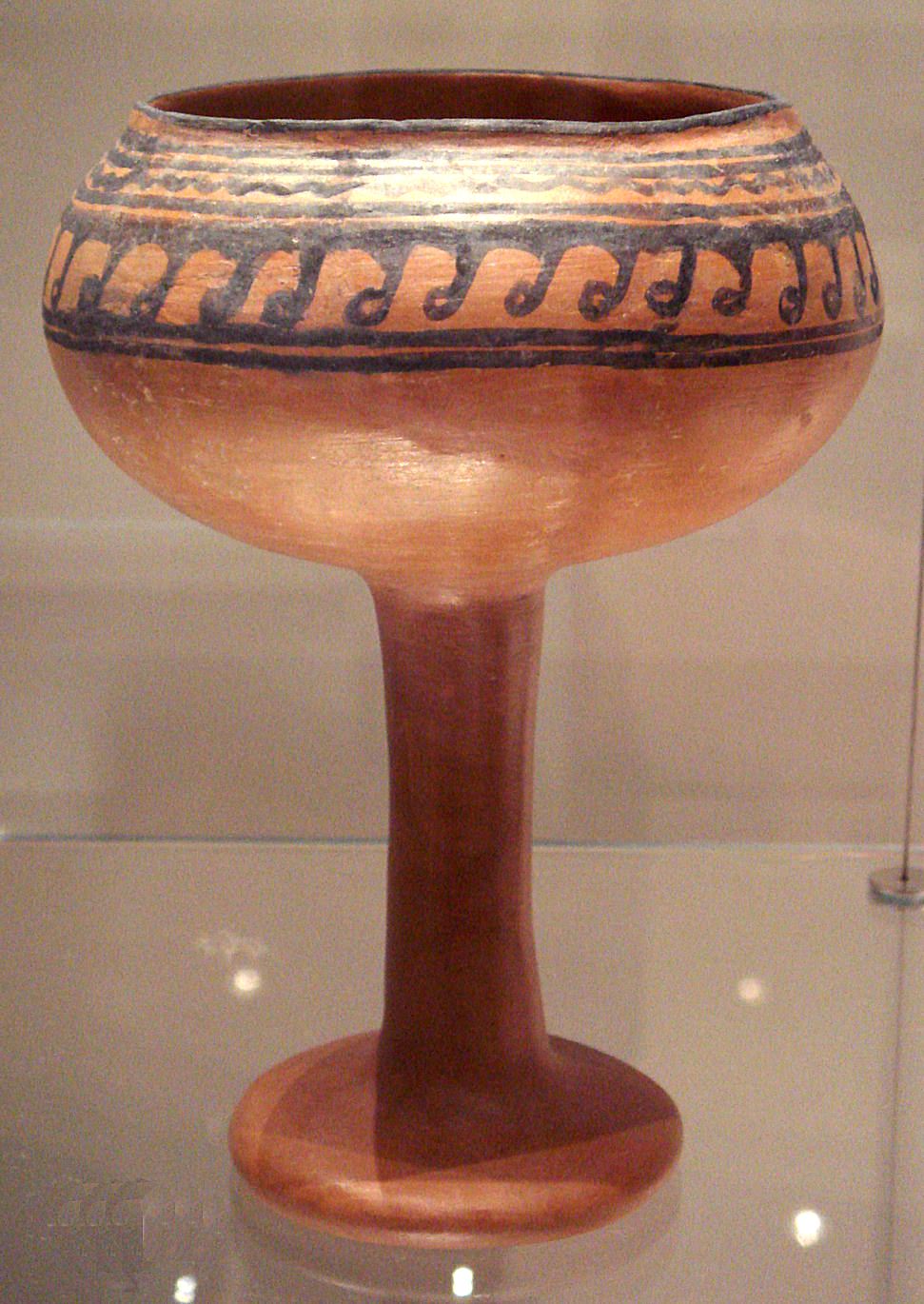
Malwa Culture
The Malwa culture was a Chalcolithic archaeological culture which existed in the Malwa region of Central India and parts of Maharashtra in the Deccan Peninsula. It is mainly dated to BCE, but calibrated radiocarbon dates have suggested that the beginning of this culture may be as early as 2000-1750 BCE. This culture is characterized by the increasing dominance of the agricultural way of life, but also incorporated pastoralist and hunting groups. The people cultivated wheat, barley, legumes, and later rice, and domesticated cattle, sheep, goats, and pigs. At most of the settlements, there is no evidence of urban planning, rather a "haphazard" distribution of houses, but some of the largest sites have evidence of planned settlement, large houses, and public architecture. Most dwellings were round huts made from wattle-and-daub. There are also small round huts used for storing grain, and large rectangular structures which may have been used for religious performances. Their pott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular human manipulation of copper, but prior to the discovery of bronze alloys. Modern researchers consider the period as a subset of the broader Neolithic, but earlier scholars defined it as a transitional period between the Neolithic and the Bronze Age. The archaeological site of Belovode, on Rudnik mountain in Serbia, has the world's oldest securely dated evidence of copper smelting at high temperature, from (7000 BP). The transition from Copper Age to Bronze Age in Europe occurred between the late 5th and the late In the Ancient Near East the Copper Age covered about the same period, beginning in the late and lasting for about a millennium before it gave rise to the Early Bronze Age. Terminology The multiple names result from m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
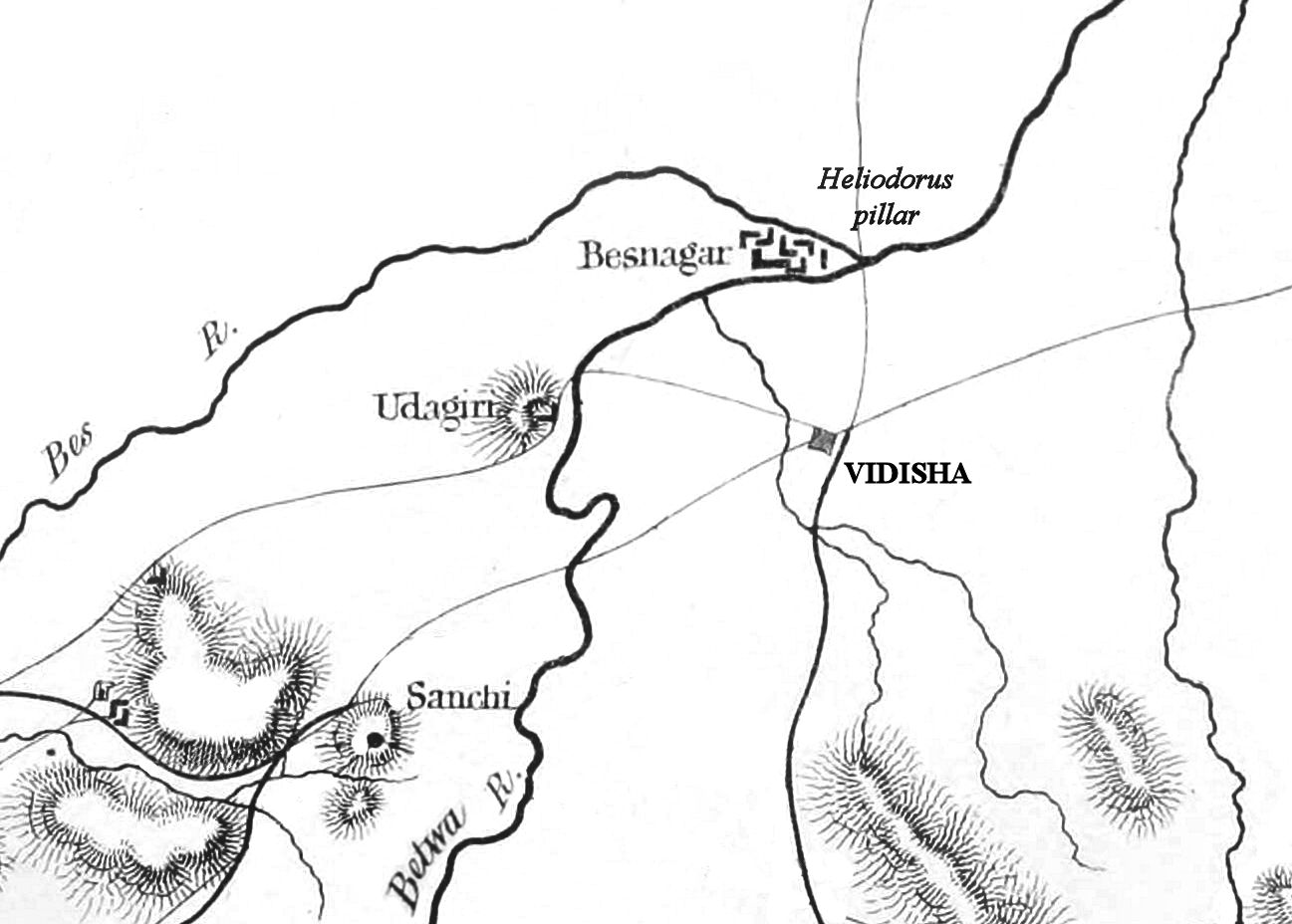
Vidisha
Vidisha (विदिशा, formerly known as Bhelsa and known as Besnagar in ancient times) is a city in central Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located 62.5 km northeast of the state capital, Bhopal. The name "Vidisha" is derived from the nearby river "Bais", mentioned in the Puranas. The district was created as Bhilsa District in 1904 by joining the tehsils of Vidisha (also known as Bhilsa) and Basoda (but not Basoda State) which were then part of Gwalior state. After India's independence in 1947, the former princely state of Gwalior became part of Madhya Bharat state, which was formed in 1948. Vidishā was the administrative headquarters of Bhelsa, or Bhilsa, during the Medieval period. It was renamed Vidisha in 1956. Vidisha is also amongst the 112 Aspirational District in the Aspirational District Programme launched by NITI Aayog in 2018. Demographics As of the 2011 Census of India, Vidisha had a population of 155,959. Males constitute 53.21% of the population and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcolithic Cultures Of Asia
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular human manipulation of copper, but prior to the discovery of bronze alloys. Modern researchers consider the period as a subset of the broader Neolithic, but earlier scholars defined it as a transitional period between the Neolithic and the Bronze Age. The archaeological site of Belovode, on Rudnik mountain in Serbia, has the world's oldest securely dated evidence of copper smelting at high temperature, from (7000 BP). The transition from Copper Age to Bronze Age in Europe occurred between the late 5th and the late In the Ancient Near East the Copper Age covered about the same period, beginning in the late and lasting for about a millennium before it gave rise to the Early Bronze Age. Terminology The multiple names result from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pottery In The Indian Subcontinent
Pottery in the Indian subcontinent has an ancient history and is one of the most tangible and iconic elements of Indian art. Evidence of pottery has been found in the early settlements of Lahuradewa and later the Indus Valley Civilisation. Today, it is a cultural art that is still practiced extensively in Indian subcontinent. Until recent times all Indian pottery has been earthenware, including terracotta. Early glazed ceramics were used for making beads, seals, bangles during Neolithic period but these glazes were very rarely used on pottery. Hindu traditions historically discouraged the use of pottery for eating off, while large matki jars for the storage of water or other things form the largest part of traditional Indian pottery, as well as objects such as lamps. Small simple kulhar cups, and also oil lamps, that are disposable after a single use remain common. Today, pottery thrives as an art form in India. Various platforms, including potters' markets and online pottery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Madhya Pradesh
The history of the Indian state Madhya Pradesh is divided into three periods - the ancient period, the medieval period and modern period. During the ancient period, the region was dominated by the Nanda Empire, the Maurya Empire, and the Gupta Empire. The medieval period saw the rise of Rajput clans including the Paramara and Chandela clans, the latter is known for constructing the temples of Khajuraho. The Malwa Sultanate also ruled during this period. The modern period in Madhya Pradesh saw the rise of the Mughal and Maratha empires, and later, the British Empire. The British princely states of Gwalior, Indore, and Bhopal, were a part of modern Madhya Pradesh. The British rule continued until the middle of the 20th century, when India gained independence in 1947. The state of Madhya Pradesh was formed in 1956, and Chhattisgarh was carved out from the state in 2000. Ancient History The Bhimbetka caves show evidence of paleolithic settlements in present-day Madhya Prades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black And Red Ware Culture
Black and red ware (BRW) is a South Asian earthenware, associated with the neolithic phase, Harappa, Bronze Age India, Iron Age India, the megalithic and the early historical period. Although it is sometimes called an archaeological culture, the spread in space and time and the differences in style and make are such that the ware must have been made by several cultures. In the Western Ganges plain (western Uttar Pradesh) it is dated to c. 1450–1200 BCE, and is succeeded by the Painted Grey Ware culture; whereas in the Central and Eastern Ganges plain (eastern Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Bengal) and Central India (Madhya Pradesh) the BRW appears during the same period but continues for longer, until c. 700–500 BCE, when it is succeeded by the Northern Black Polished Ware culture. In the Western Ganges plain, the BRW was preceded by the Ochre Coloured Pottery culture. The BRW sites were characterized by subsistence agriculture (cultivation of rice, barley, and legumes), and yiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jorwe Culture
The Jorwe culture was a Chalcolithic archaeological culture which existed in large areas of what is now Maharashtra state in Western India, and also reached north into the Malwa region of Madhya Pradesh. It is named after the type site of Jorwe. The early phase of the culture is dated to 1400-1000 BCE, while the late phase is dated to 1000-700 BCE. Over 200 settlements of the Jorwe culture have been found, ranging from several large and medium-sized farming villages, to many small villages, as well as temporary and seasonal camp-sites used by pastoralists. It likely reflects a chiefdom level of social organization. The largest settlement was Daimabad, which had a mud fortification during this period, as well as an elliptical temple with fire pits. Some settlements show evidence of planning in the layout of rectangular houses and streets or lanes. Most dwellings were small, single-room dwellings, but the chiefs lived in large houses with multiple rooms, and had granaries to store ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savalda Culture
Savalde (also spelled as 'Sawalde', 'Sawalda', 'Savalda') is a village in Shahada taluka in Nandurbar district of Maharashtra state in India. Savalde village is situated around 5 km South-west of Shahada, situated on the bank of river Tapti(Tapi) and on state border of states of Maharashtra and Gujarat. Village Savalde village is situated around 5 km away from Nandurbar and around 1 km west from Maharashtra State Highway Number 1 on Shahada-Nandurbar road. It is situated just 1 km away from the official state border between Gujarat and Maharashtra states of India. Many houses in this border village are built on a single mountain on the bank of river Tapti. Occupation of almost all the villagers is farming or related work. For important shopping, health treatment or higher education villagers go to Shahada or Prakasha which are easily accessible by bus, private vehicle or stopping any on route to Shahada passenger riksha on Highway. Fresh vegetables and mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maheshwar
Maheshwar is a town, near Khargone city in Khargone district of Madhya Pradesh state, in central India. It is located on State Highway-38 ( Khargone city-Barwaha- Bandheri Highway),13.5 km east of National Highway 3 (Agra-Mumbai highway) and 91 km from Indore, the commercial capital of the state. The Town lies on the north bank of the Narmada River. It was the kingdom of Chaktavartin Samrat Sahastraarjun, Kartavirya Arjuna a Heheya king. Lately, after many years, it was the capital of the Malwa during the Maratha Holkar reign till 6 January 1818, when the capital was shifted to Indore by Malhar Rao Holkar III. Etymology The word Maheshwar in Hindi means ''Great God, ''an epithet of Lord Shiva. History Writers such as HD Sankalia, PN Bose and Francis Wilford, among others, identify Maheshwar as the ancient town of Mahishmati. Also known as Minnagara to Greeko-Romans. Maheshwar is believed to be built on the site of the ancient city of Somvanshya Shastrarjun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navdatoli
Navdatoli is the name of a modern day village, but can also refer to a chalcolithic era settlement located on the Narmada River in Madhya Pradesh in central India. The ancient village was inhabited through four temporal stages, each defined by distinct types of pottery. The site was originally excavated between 1957 and 1959 over two seasons. Both the village and the site are located roughly a mile south of the modern day town of Maheshwar. History It is an important chalcolithic site located on the opposite side of the Narmada River dating back to 2nd millennium BCE. The region was a stronghold of Buddhism since 2nd century BCE. Kasrawad (6 kms. southeast of Navdatoli) has many Buddhist remains and stupas which are considered sites of national importance. Archaeological Site The archaeological site was defined by 4 distinct mounds and excavated by researchers from Deccan College. Mounds I, II, and III were partially excavated in 1957-1958. Mound IV was completely excavate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandsaur
Mandsaur is a city and a municipality in Mandsaur district located on Border of Mewar and Malwa Malwa is a historical region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also syno ... region of Madhya Pradesh state of central India. It is the administrative headquarters of Mandsaur District. The ancient Pashupatinath Temple, Mandsaur, Pashupatinath Temple is located in Mandsaur. History Aulikaras of Dashapura Epigraphical discoveries have brought to light two ancient royal houses, who call themselves as Aulikaras and ruled from Dashapura (present-day Mandsaur). The first dynasty, who ruled from Dashapura from the beginning comprised the following kings in the order of succession: Jayavarma, Simhavarma, Naravarma, Vishvavarma and Bandhuvarma. The Risthal stone slab inscription discovered in 1983 has brought to li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |