|
Maksutov-Cassegrain
The Maksutov (also called a "Mak") is a catadioptric telescope design that combines a spherical mirror with a weakly negative meniscus lens in a design that takes advantage of all the surfaces being nearly "spherically symmetrical". The negative lens is usually full diameter and placed at the entrance pupil of the telescope (commonly called a "corrector plate" or "meniscus corrector shell"). The design corrects the problems of off-axis aberrations such as coma found in reflecting telescopes while also correcting chromatic aberration. It was patented in 1941 by Russian optician Dmitri Dmitrievich Maksutov. Maksutov based his design on the idea behind the Schmidt camera of using the spherical errors of a negative lens to correct the opposite errors in a spherical primary mirror. The design is most commonly seen in a Cassegrain variation, with an integrated secondary, that can use all-spherical elements, thereby simplifying fabrication. Maksutov telescopes have been sold on the ama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
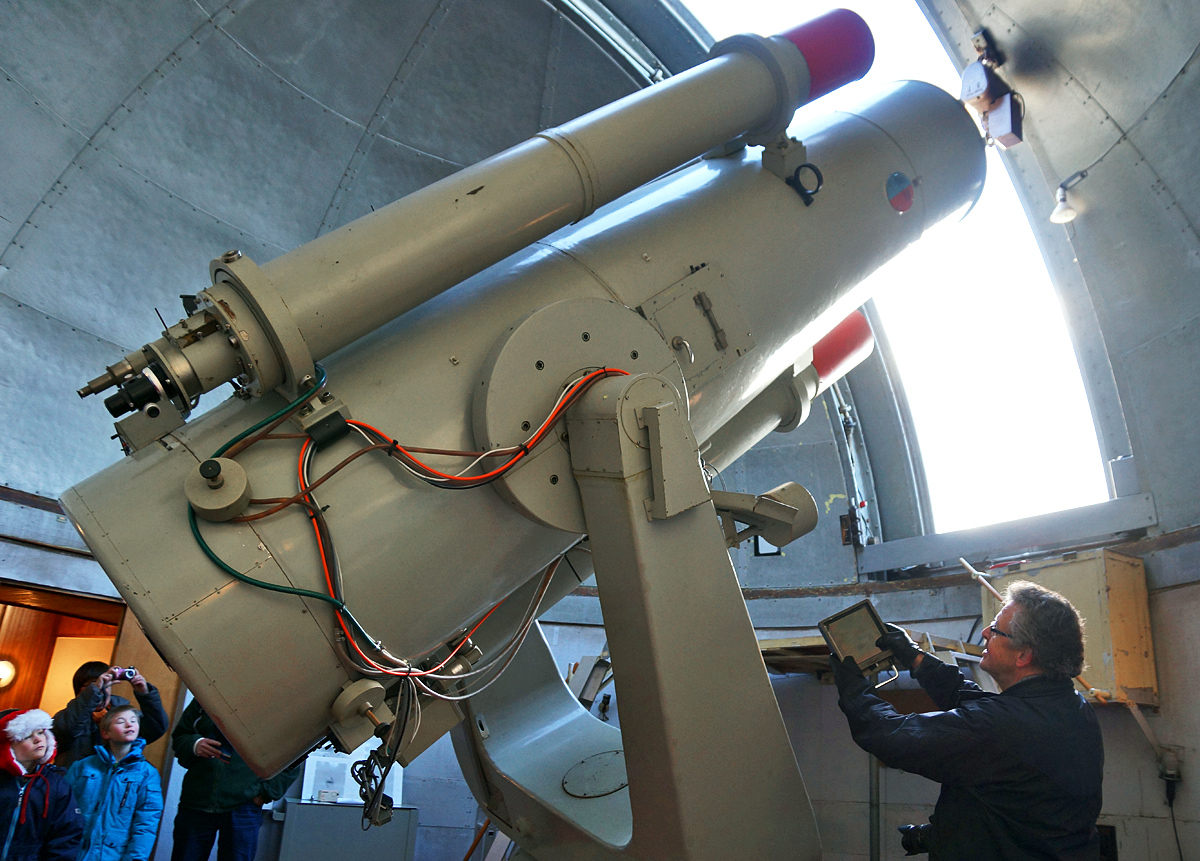
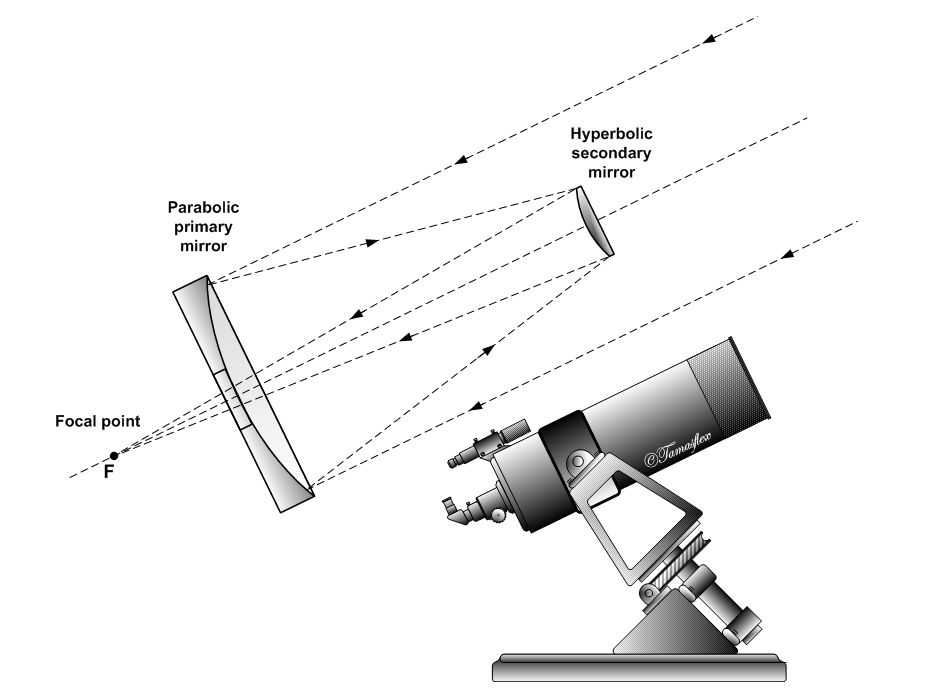
Cassegrain Reflector
The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and radio antennas, the main characteristic being that the optical path folds back onto itself, relative to the optical system's primary mirror entrance aperture. This design puts the focal point at a convenient location behind the primary mirror and the convex secondary adds a telephoto effect creating a much longer focal length in a mechanically short system. In a symmetrical Cassegrain both mirrors are aligned about the optical axis, and the primary mirror usually contains a hole in the center, thus permitting the light to reach an eyepiece, a camera, or an image sensor. Alternatively, as in many radio telescopes, the final focus may be in front of the primary. In an asymmetrical Cassegrain, the mirror(s) may be tilted to avoid obscuration of the primary or to avoid the need for a hole in the primary mirror (or both). The classic Cassegrain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Questar Corporation
Questar Corporation is a company based in New Hope, Pennsylvania. It manufactures precision optical devices for consumer, industrial, aerospace, and military markets. Its telescopes produced for the consumer market are sold under the brand name "Questar". History Questar was founded in 1950 by Lawrence Braymer, who set up Questar to develop and market Maksutov telescopes and other optical devices for the consumer, industrial, and government customers. The Questar Standard telescope has been in production since 1954. Questars have been associated with many well-known scientists and other personalities; for example, in 1959, Wernher Von Braun purchased a telescope manufactured by the company. Products Questar produces telescopes for consumer, military, police, security, aerospace, and industrial applications. Products sold by Questar include 3.5” (89 mm) and 7” (178 mm) aperture Maksutov Cassegrain astronomical/terrestrial telescopes for the consumer market. For a wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catadioptric System
A catadioptric optical system is one where refraction and reflection are combined in an optical system, usually via lenses (dioptrics) and curved mirrors (catoptrics). Catadioptric combinations are used in focusing systems such as searchlights, headlamps, early lighthouse focusing systems, optical telescopes, microscopes, and telephoto lenses. Other optical systems that use lenses and mirrors are also referred to as "catadioptric", such as surveillance catadioptric sensors. Early catadioptric systems Catadioptric combinations have been used for many early optical systems. In the 1820s, Augustin-Jean Fresnel developed several catadioptric lighthouse reflectors. Léon Foucault developed a catadioptric microscope in 1859 to counteract aberrations of using a lens to image objects at high power. In 1876 a French engineer, A. Mangin, invented what has come to be called the Mangin mirror, a concave glass reflector with the silver surface on the rear side of the glass. The two surfaces o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmitri Dmitrievich Maksutov
Dmitry Dmitrievich Maksutov (russian: Дми́трий Дми́триевич Максу́тов) ( – 12 August 1964) was a Russian / Soviet optical engineer and amateur astronomer. He is best known as the inventor of the Maksutov telescope. Biography Dmitry Dmitriyevich Maksutov was born in 1896 in either Nikolayev or the port city of Odessa, Russian Empire. His father, was a naval officer serving with the Black Sea Fleet, who came from a family with a long and distinguished naval tradition. His great-grandfather, Peter Ivanovich Maksutov, was given the title of prince, thereby raising the family to hereditary nobility as a reward for bravery in combat. His grandfather, Dmitri Petrovich Maksutov, was the last Russian governor of Russian Alaska, before it was purchased by the United States in 1867. Dmitri became interested in astronomy in early childhood, and constructed his first telescope (a 7.2 inch / 180 mm reflector) when he was twelve years old. Later he rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schmidt Camera
A Schmidt camera, also referred to as the Schmidt telescope, is a catadioptric astrophotographic telescope designed to provide wide fields of view with limited aberrations. The design was invented by Bernhard Schmidt in 1930. Some notable examples are the Samuel Oschin telescope (formerly Palomar Schmidt), the UK Schmidt Telescope and the ESO Schmidt; these provided the major source of all-sky photographic imaging from 1950 until 2000, when electronic detectors took over. A recent example is the Kepler space telescope exoplanet finder. Other related designs are the Wright camera and Lurie–Houghton telescope. Invention and design The Schmidt camera was invented by German–Estonian optician Bernhard Schmidt in 1930. Its optical components are an easy-to-make spherical primary mirror, and an aspherical correcting lens, known as a Schmidt corrector plate, located at the center of curvature of the primary mirror. The film or other detector is placed inside the camera, at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schmidt Corrector Plate
A Schmidt camera, also referred to as the Schmidt telescope, is a catadioptric astrophotographic telescope designed to provide wide fields of view with limited aberrations. The design was invented by Bernhard Schmidt in 1930. Some notable examples are the Samuel Oschin telescope (formerly Palomar Schmidt), the UK Schmidt Telescope and the ESO Schmidt; these provided the major source of all-sky photographic imaging from 1950 until 2000, when electronic detectors took over. A recent example is the Kepler space telescope exoplanet finder. Other related designs are the Wright camera and Lurie–Houghton telescope. Invention and design The Schmidt camera was invented by German–Estonian optician Bernhard Schmidt in 1930. Its optical components are an easy-to-make spherical primary mirror, and an aspherical correcting lens, known as a Schmidt corrector plate, located at the center of curvature of the primary mirror. The film or other detector is placed inside the camera, at the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregorian Telescope
The Gregorian telescope is a type of reflecting telescope designed by Scottish mathematician and astronomer James Gregory in the 17th century, and first built in 1673 by Robert Hooke. James Gregory was a contemporary of Isaac Newton. Both often worked simultaneously on similar projects. Gregory's design was published in 1663 and pre-dates the first practical reflecting telescope, the Newtonian telescope, built by Sir Isaac Newton in 1668."Isaac Newton: adventurer in thought", by Alfred Rupert Hallpage 67 However, Gregory's design was only a theoretical description, and he never actually constructed the telescope. It was not successfully built until five years after Newton's first reflecting telescope. History The Gregorian telescope is named after the James Gregory design, which appeared in his 1663 publication (The Advance of Optics). Similar theoretical designs have been found in the writings of Bonaventura Cavalieri ( (On Burning Mirrors), 1632) and Marin Mersenne (, 1636). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Bouwers
Albert A. Bouwers (1893–1972) was a Dutch optical engineer.Ian Ridpath, "Bouwers telescope", ''A Dictionary of Astronomy'', 199first sentence of article/ref> He is known for developing and working with X-rays and various optical technologies as a high-level researcher at Philips research labs. He is lesser known for patenting in 1941 a catadioptric meniscus telescope design similar to but slightly predating the Maksutov telescope. Biography Bouwers was born in the town of Dalen in the Netherlands in 1893.Reflecting Telescope Optics, by Ray N. Wilson, page 498Google Books, pg 498/ref> He obtained his Ph.D. from Utrecht University in 1924, with a dissertation entitled in Dutch ''Over het meten der intensiteit van Röntgenstralen''. He was also the director of the Philips Laboratory's X-ray department. Bouwers developed a night vision device for viewing in low light conditions, called the "night eye". Albert Bouwers built a prototype for a design for a wide field concentric meniscus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dennis Gabor
Dennis Gabor ( ; hu, Gábor Dénes, ; 5 June 1900 – 9 February 1979) was a Hungarian-British electrical engineer and physicist, most notable for inventing holography, for which he later received the 1971 Nobel Prize in Physics. He obtained British citizenship in 1934, and spent most of his life in England. Life and career Gabor was born as Günszberg Dénes, into a Jewish family in Budapest, Hungary. In 1918, his family converted to Lutheranism. Dennis was the first-born son of Günszberg Bernát and Jakobovits Adél. Despite having a religious background, religion played a minor role in his later life and he considered himself agnostic. In 1902, the family received permission to change their surname from Günszberg to Gábor. He served with the Hungarian artillery in northern Italy during World War I. He began his studies in engineering at the Technical University of Budapest in 1918, later in Germany, at the Charlottenburg Technical University in Berlin, now known as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maksutov 150mm
Maksutov may refer to: * Maksutov telescope, a catadioptric telescope with a meniscus corrector . * Dmitry Dmitrievich Maksutov (1896–1964), Russian optical engineer, inventor of the Maksutov telescope * Maksutov (crater), a lunar crater named after Dmitry Dmitrievich Maksutov * 2568 Maksutov, a main-belt asteroid named after Dmitry Dmitrievich Maksutov See also * Maksutov (surname) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The Optical Society Of America
The ''Journal of the Optical Society of America'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of optics, published by Optica. It was established in 1917 and in 1984 was split into two parts, A and B. ''Journal of the Optical Society of America A'' Part A covers various topics in optics, vision, and image science. The editor-in-chief is Olga Korotkova (University of Miami, USA). ''Journal of the Optical Society of America B'' Part B covers various topics in the field of optical physics, such as guided waves, laser spectroscopy, nonlinear optics, quantum optics, lasers, organic and polymer materials for optics, and ultrafast phenomena In optics, an ultrashort pulse, also known as an ultrafast event, is an electromagnetic pulse whose time duration is of the order of a picosecond (10−12 second) or less. Such pulses have a broadband optical spectrum, and can be created by .... The editor-in-chief is Kurt Busch ( Humboldt University of Berlin, Germany). References {{reflist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
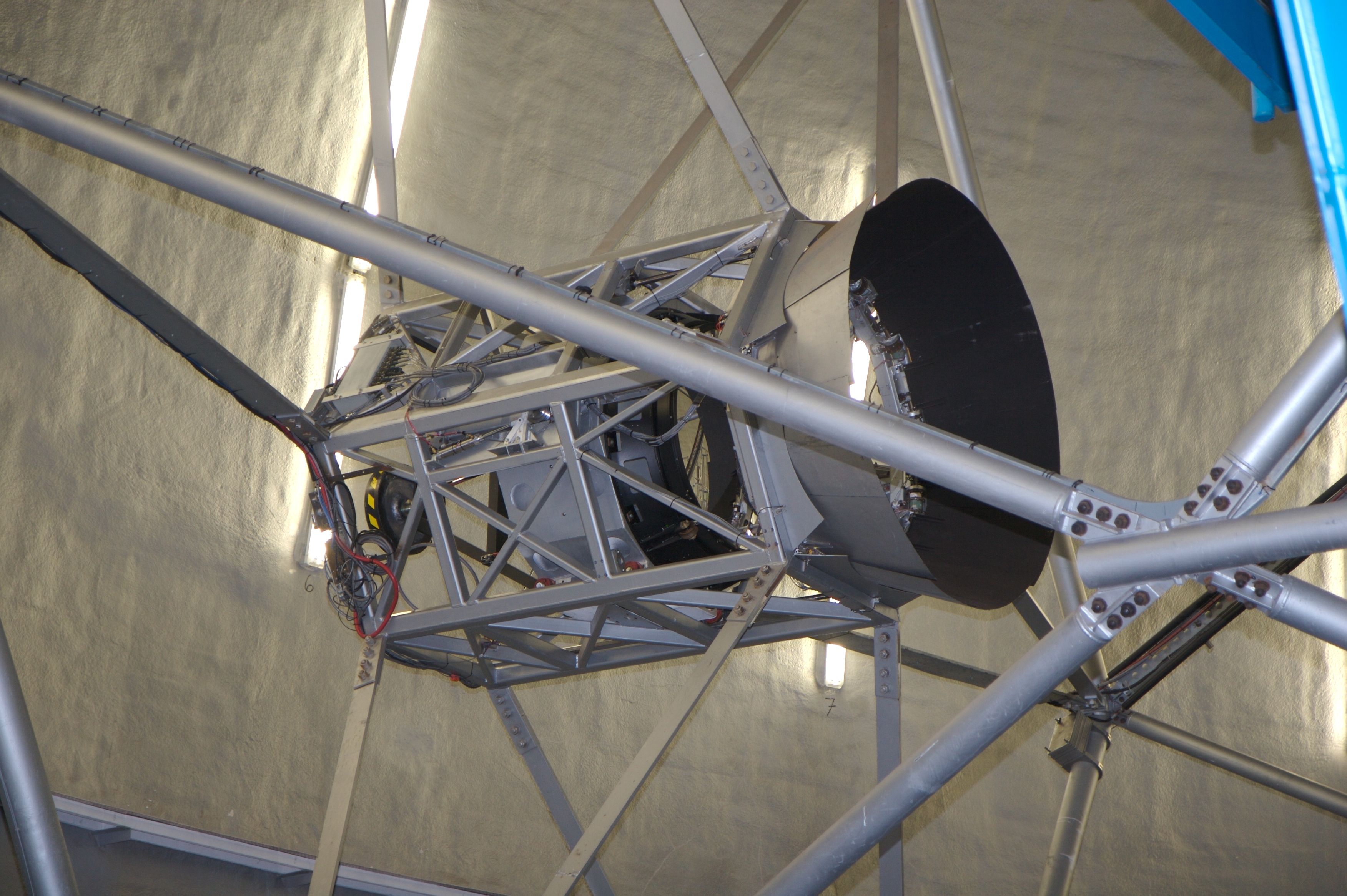
Secondary Mirror
A secondary mirror (or secondary) is the second deflecting or focusing mirror element in a reflecting telescope. Light gathered by the primary mirror is directed towards a focal point typically past the location of the secondary. Secondary mirrors in the form of an optically flat ''diagonal mirror'' are used to re-direct the light path in designs such as Newtonian reflectors. They are also used to re-direct and extend the light path and modify the final image in designs such as Cassegrain reflectors. The secondary is typically suspended by X-shaped struts (sometimes called a "spider") in the path of light between the source and the primary, but can be mounted on other types of mounts or optical elements such as optical windows, or schmidt and meniscus corrector plates. Employing secondary mirrors in optical systems causes some image distortion due to the obstruction of the secondary itself, and distortion from the spider mounts, commonly seen as cross-shaped diffraction spikes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |