|
Major Incidents Involving The International Space Station
Since construction started, the International Space Station programme has had to deal with several maintenance issues, unexpected problems and failures. These incidents have affected the assembly timeline, led to periods of reduced capabilities of the station and in some cases could have forced the crew to abandon the space station for safety reasons, had these problems not been resolved. 2003 – Waste accumulation after the ''Columbia'' disaster The ''Columbia'' disaster did not involve the ISS, but did impact the ISS construction schedule and maintenance. The disaster on 1 February 2003 (during STS-107, a non-ISS mission) resulted in a two-and-a-half-year suspension of the US Space Shuttle program. Another one-year suspension following STS-114 (because of continued foam shedding on the external tank) led to some uncertainty about the future of the International Space Station. All crew exchanges between February 2003 and July 2006 were carried out using the Russian Soyuz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
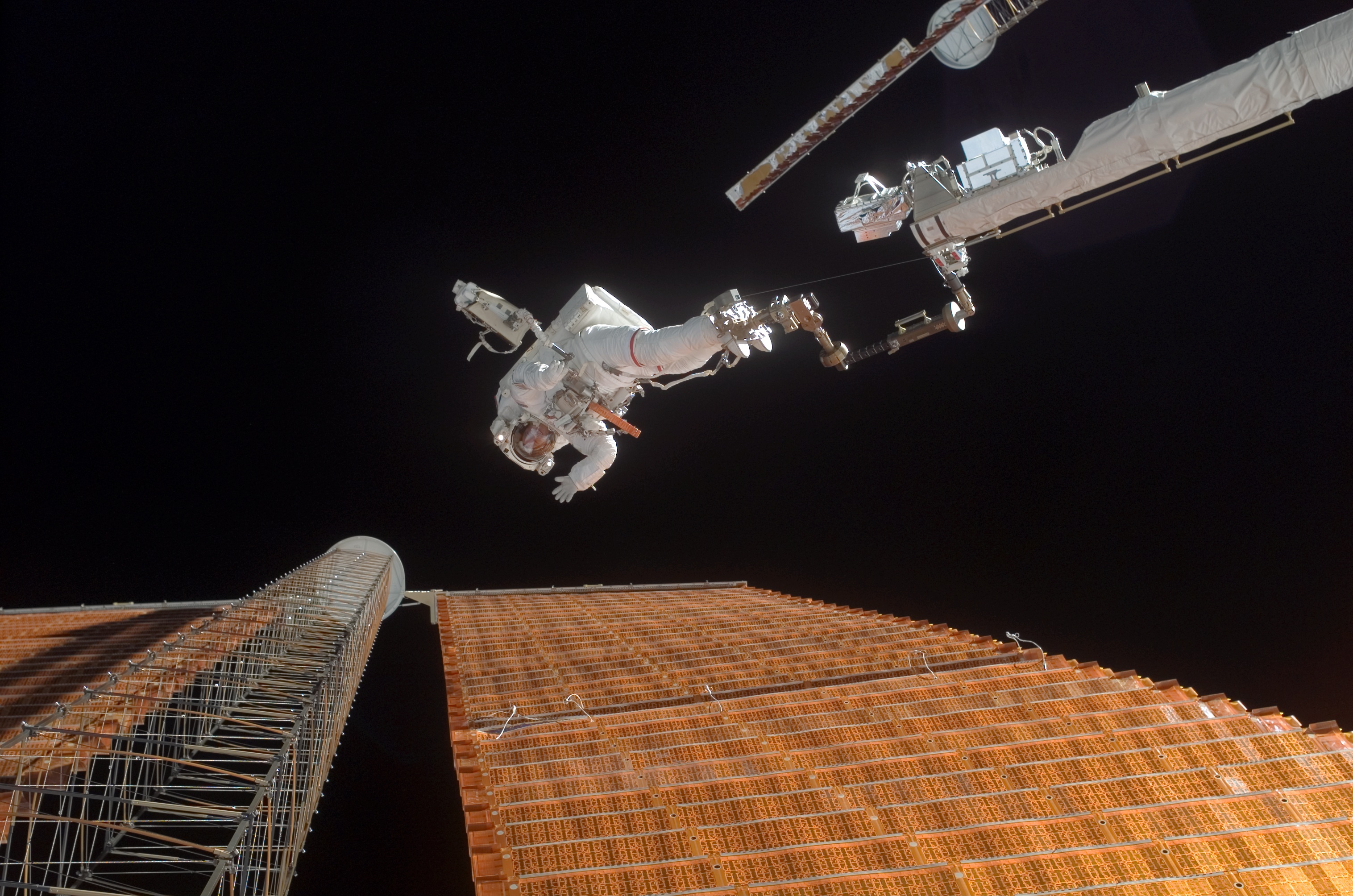
Astronaut Scott Parazynski Repairs A Damaged ISS Solar Panel
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member aboard a spacecraft. Although generally reserved for professional space travelers, the term is sometimes applied to anyone who travels into space, including scientists, politicians, journalists, and tourists. "Astronaut" technically applies to all human space travelers regardless of nationality. However, astronauts fielded by Russia or the Soviet Union are typically known instead as cosmonauts (from the Russian "kosmos" (космос), meaning "space", also borrowed from Greek). Comparatively recent developments in crewed spaceflight made by China have led to the rise of the term taikonaut (from the Mandarin "tàikōng" (), meaning "space"), although its use is somewhat informal and its origin is unclear. In China, the People's Liberation Army Astronaut Corps astronauts and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash. Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which exploit its caustic nature and its reactivity toward acids. An estimated 700,000 to 800,000 tonnes were produced in 2005. KOH is noteworthy as the precursor to most soft and liquid soaps, as well as numerous potassium-containing chemicals. It is a white solid that is dangerously corrosive. Properties and structure KOH exhibits high thermal stability. Because of this high stability and relatively low melting point, it is often melt-cast as pellets or rods, forms that have low surface area and convenient handling properties. These pellets become tacky in air because KOH is hygroscopic. Most commercial samples are ca. 90% pure, the remainder being water and carbonates. Its dissolution in water is strongly exothermic. Concentrated aqueous solut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-126
STS-126 was the one hundred and twenty-fourth NASA Space Shuttle mission, and twenty-second orbital flight of the ''Space Shuttle Endeavour'' (OV-105) to the International Space Station (ISS). The purpose of the mission, referred to as ULF2 by the ISS program, was to deliver equipment and supplies to the station, to service the Solar Alpha Rotary Joints (SARJ), and repair the problem in the starboard SARJ that had limited its use since STS-120. STS-126 launched on 15 November 2008 at 00:55:39 UTC from Launch Pad 39A (LC-39A) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center (KSC) with no delays or issues. ''Endeavour'' successfully docked with the station on 16 November 2008. After spending 15 days, 20 hours, 30 minutes, and 30 seconds docked to the station, during which the crew performed four spacewalks, and transferred cargo, the orbiter undocked on 28 November 2008. Due to poor weather at Kennedy Space Center, ''Endeavour'' landed at Edwards Air Force Base on 30 November 2008 at 21:25:09 U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-123
STS-123 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) which was flown by Space Shuttle ''Endeavour''. STS-123 was the 1J/A ISS assembly mission. The original launch target date was 14 February 2008 but after the delay of STS-122, the shuttle was launched on 11 March 2008. It was the twenty-fifth shuttle mission to visit the ISS, and delivered the first module of the Japanese laboratory, Japanese Experiment Module (''Kibō''), and the Canadian Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator, (SPDM) Dextre robotics system to the station. The mission duration was 15 days and 18 hours, and it was the first mission to fully utilize the Station-to-Shuttle Power Transfer System (SSPTS), allowing space station power to augment the shuttle power systems. The mission set a record for a shuttle's longest stay at the ISS. Crew Mission payloads STS-123 delivered the pressurized section of the Japanese Experiment Logistics Module (ELM-PS) as well as the Special Purpose D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbiter Boom Sensor System
The Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS) was a 50-foot (15.24 m) boom carried on board NASA's Space Shuttles. The boom was grappled by the Canadarm and served as an extension of the arm, doubling its length to a combined total of 100 feet (30 m). At the far end of the boom was an instrumentation package of cameras and lasers used to scan the leading edges of the wings, the nose cap, and the crew compartment after each lift-off and before each landing. If flight engineers suspected potential damage to other areas, as evidenced in imagery captured during lift-off or the rendezvous pitch maneuver, then additional regions could be scanned. The OBSS was introduced to the shuttle fleet with STS-114, the "Return to Flight" mission executed by ''Discovery'', and was flown on every mission after that until the retirement of the Space Shuttle fleet in 2011. It was used to inspect the shuttle for damage to the heat shield, officially called the Thermal Protection System (TPS), that could jeopar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Wheelock
Douglas Harry "Wheels" Wheelock (born May 5, 1960) is an American engineer and astronaut. He has flown in space twice, logging 178 days on the Space Shuttle, International Space Station, and Russian Soyuz. On July 12, 2011, Wheelock announced that he would be returning to active duty with the United States Army in support of Operation Enduring Freedom. He is currently working with NASA to test the Orion spacecraft at the Glenn Research Center in Plum Brook, Ohio. Early life and education Douglas Wheelock was born in Binghamton, New York to Olin and Margaret Wheelock. In a pre-flight interview, Wheelock stated that he was inspired to become an astronaut at an early age. He also stated that a major turning point in his life was the Apollo 11 moon landing in July 1969. In 1978 Wheelock graduated from Windsor Central High School in Windsor, New York before attending the United States Military Academy at West Point. He earned a Master of Science degree in Aerospace Engineering at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scott Parazynski
Scott Edward Parazynski (born July 28, 1961 in Little Rock, Arkansas) is an American physician and a former NASA astronaut. A veteran of five Space Shuttle flights and seven spacewalks, Parazynski's latest mission was STS-120 in October, 2007 – highlighted by a dramatic, unplanned EVA to repair a live solar array. In May 2016 he was inducted into the United States Astronaut Hall of Fame. He retired from NASA in March 2009 to pursue entrepreneurial opportunities in the private sector, and he is currently the CEO of a technology start-up. He is the first person to have both flown in space and summited Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth. Personal Parazynski is of Polish descent, as his great-great-grandparents migrated from Kraków to the US. He considers Palo Alto, California, and Evergreen, Colorado, to be his hometowns. He is married to Meenakshi Wadhwa, a planetary scientist at Arizona State University. He has two children with his first wife, Gail. Scott enjoys mountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expedition 16
Expedition 16 was the 16th expedition to the International Space Station (ISS). The first two crew members, Yuri Malenchenko and Peggy Whitson, launched on 10 October 2007, aboard Soyuz TMA-11, and were joined by spaceflight participant Sheikh Muszaphar Shukor, the first Malaysian in space. Expedition 15 Flight Engineer Clayton Anderson did not land with the Soyuz TMA-10, so he was considered part of Expedition 16 for the few weeks prior to the arrival of STS-120. STS-120 launched on 23 October, docked on 25 October, and replaced Anderson with new Flight Engineer Daniel Tani. Following docking, the Soyuz seat liners for Anderson and Tani were swapped, and Anderson became part of the STS-120 crew. Léopold Eyharts, who came aboard during STS-122, joined the mission on 9 February 2008, replacing Tani. The crew was then joined by Garrett Reisman, who was launched aboard ''Endeavour'' with STS-123, on 11 March 2008, replacing Eyharts. Reisman joined Expedition 16 in progress, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automated Transfer Vehicle
The Automated Transfer Vehicle, originally Ariane Transfer Vehicle or ATV, was an expendable cargo spacecraft developed by the European Space Agency (ESA), used for space cargo transport in 2008–2015. The ATV design was launched to orbit five times, exclusively by the Ariane 5 heavy-lift launch vehicle. It effectively was a larger European counterpart to the Russian Progress cargo spacecraft for carrying upmass to a single destination—the International Space Station (ISS)—but with three times the capacity. The five ATVs were named after important European figures in science and engineering: '' Jules Verne'', '' Johannes Kepler'', ''Edoardo Amaldi'', ''Albert Einstein'', and ''Georges Lemaître''. Following several delays to the program, the first of these was launched in March 2008. These ATVs performed supply missions to the ISS, transporting various payloads such as propellant, water, air, food, and scientific research equipment; ATVs also reboosted the station into a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbus (ISS Module)
''Columbus'' is a science laboratory that is part of the International Space Station (ISS) and is the largest single contribution to the ISS made by the European Space Agency (ESA). Like the '' Harmony'' and ''Tranquility'' modules, the ''Columbus'' laboratory was constructed in Turin, Italy by Thales Alenia Space. The functional equipment and software of the lab was designed by EADS in Bremen, Germany. It was also integrated in Bremen before being flown to the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida in an Airbus Beluga. It was launched aboard on February 7, 2008, on flight STS-122. It is designed for ten years of operation. The module is controlled by the Columbus Control Centre, located at the German Space Operations Center, part of the German Aerospace Center in Oberpfaffenhofen near Munich, Germany. The European Space Agency has spent €1.4 billion (about US$2 billion) on building ''Columbus'', including the experiments it carries and the ground control infrastructure n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrium Space Transportation
Astrium was an aerospace manufacturer subsidiary of the European Aeronautic Defence and Space Company (EADS) that provided civil and military space systems and services from 2006 to 2013. In 2012, Astrium had a turnover of €5.8 billion and 18,000 employees in France, Germany, the United Kingdom, Spain and the Netherlands. Astrium was a member of Institute of Space, its Applications and Technologies. In late 2013 Astrium was merged with Cassidian, the defence division of EADS and Airbus Military to form Airbus Defence and Space. EADS itself was reorganized as the Airbus Group, with three divisions that include Airbus, Airbus Defence and Space, and Airbus Helicopters. Business structure During 2006–2013, the three main areas of activity within Astrium were: * Astrium Satellites for spacecraft and ground segment * EADS Astrium Space Transportation for launchers and orbital infrastructure * Astrium Services for the development and delivery of satellite services. Satellite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)