|
Majiayao Culture
The Majiayao culture was a group of neolithic communities who lived primarily in the upper Yellow River region in eastern Gansu, eastern Qinghai and northern Sichuan, China. The culture existed from 3300 to 2000 BC. The Majiayao culture represents the first time that the upper Yellow River region was widely occupied by agricultural communities and it is famous for its painted pottery, which is regarded as a peak of pottery manufacturing at that time. History The archaeological site was first found in 1924 near the village of Majiayao in Lintao County, Gansu by Swedish archaeologist Johan Gunnar Andersson, who considered it part of the Yangshao culture. Following the work of Xia Nai, the founder of modern archaeology in the People's Republic of China, it has since been considered a distinct culture, named after the original site, whereas previously it had been referred to as the "Gansu Yangshao" culture. This culture developed from the middle Yangshao (Miaodigou) phase, through an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Standard Beijing Mandarin, Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the List of rivers by length, sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan Har Mountains in Qinghai province of Western China, it flows through nine provinces, and it empties into the Bohai Sea near the city of Dongying in Shandong province. The Yellow River basin has an east–west extent of about and a north–south extent of about . Its total drainage area is about . The Yellow River's basin was the Yellow River civilization, birthplace of ancient Chinese, and, by extension, Far East, Far Eastern civilization, and it was the most prosperous region in early Chinese history. There are frequent devastating natural disasters in China, floods and course changes produced by the continual elevation of the river bed, sometimes above the level of its surrounding farm fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tao River
Tao River () is a right tributary of China's Yellow River. It starts in Xiqing Mountains () near the Gansu–Qinghai border, flows eastward across Gannan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, and then northward more or less along the border between Dingxi Prefecture-level City in the east and Gannan and Linxia Prefectures in the west. It flows into the Yellow River (actually, the Liujiaxia Reservoir) near Liujiaxia Town (the county seat of Yongjing County), just upstream of Liujiaxia Dam. Hydro power A number of dams with hydroelectric power plants have been constructed on the Tao River. According to Google Maps, they include dams at the following locations (upstream to downstream): * —Gucheng Station, near Zhongzhai Town () in Min County Min County or Minxian is administratively under the control of the prefecture-level city of Dingxi, in the south of Gansu province, China. In ancient times, it was known as Lintao County due to its location along the Tao River. It was founded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xishanping
Xishanping is an archaeological site in Gansu, China, located west of Tianshui. The site was occupied continuously from the Neolithic through the Bronze Age. The site is situated about above the riverbed on the southern bank of the Xi River, a tributary of the Wei River. The site was discovered by Pei Wenzhong in 1947. Stratigraphy *Xishanping I: the earliest layer, this layer corresponds to the Dadiwan culture. The bones from a large variety of animals (red deer, musk deer, Asiatic black bear, bamboo rat, rat, chicken, dog, pig) were discovered in this layer. *Xishangping II: this layer corresponds to the Lower Beishouling culture. Only a few animal bones were found in this layer, coming from red deer, cattle and pigs. *Xishangping III (5250–4300 BP): this period corresponds to the Majiayao culture. The greatest changes at Xishanping occurred during this time. Evidence for intensive agriculture can be found in this layer, starting from around 5,100 BP. Horse, chicken, dog and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
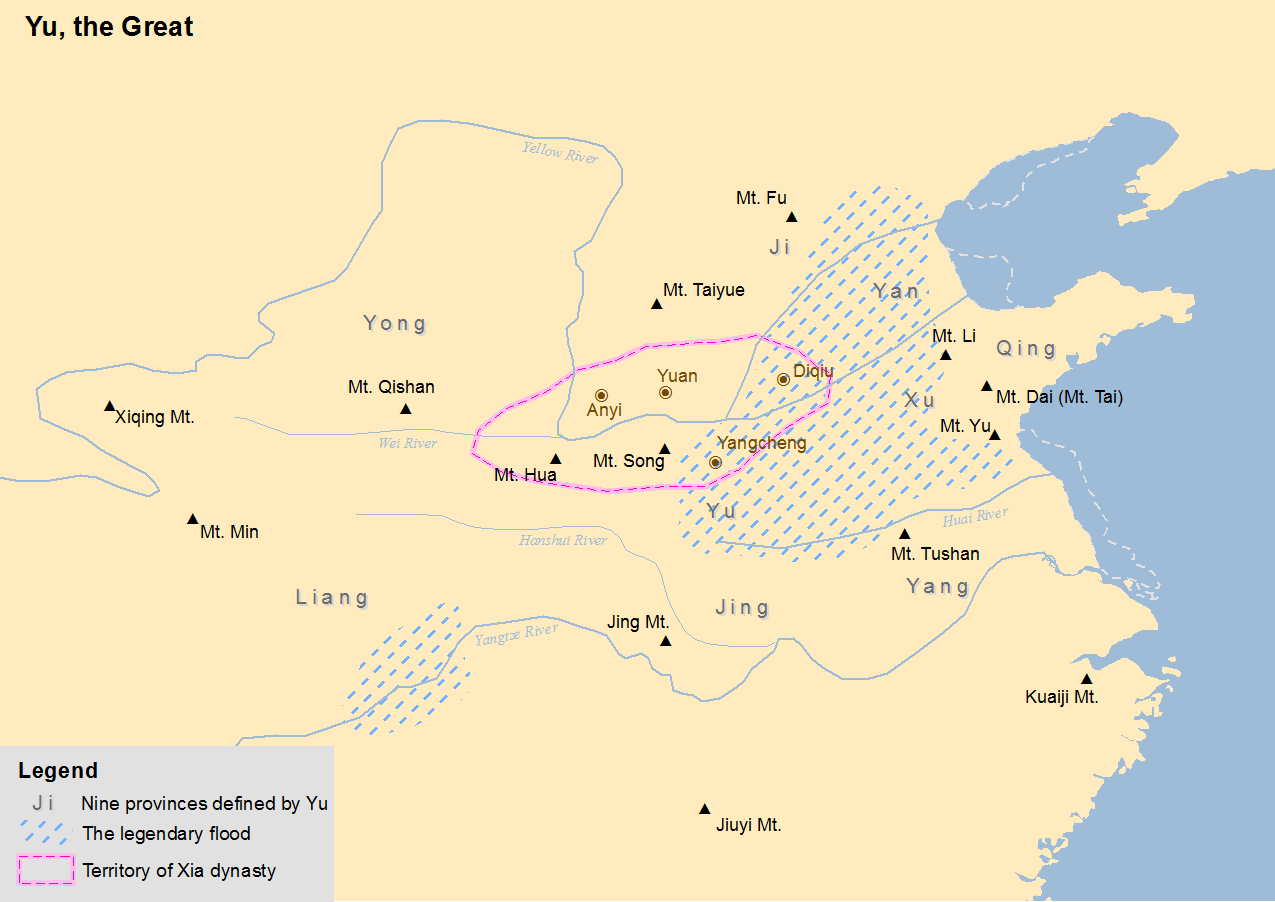
Xia Dynasty
The Xia dynasty () is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, the Xia dynasty was established by the legendary Yu the Great, after Shun, the last of the Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In traditional historiography, the Xia was later succeeded by the Shang dynasty. There are no contemporaneous records of the Xia, who are not mentioned in the oldest Chinese texts, since the earliest oracle bone inscriptions date from the late Shang period (13th century BC). The earliest mentions occur in the oldest chapters of the '' Book of Documents'', which report speeches from the early Western Zhou period and are accepted by most scholars as dating from that time. The speeches justify the Zhou conquest of the Shang as the passing of the Mandate of Heaven and liken it to the succession of the Xia by the Shang. That political philosophy was promoted by the Confucian school in the Eastern Zhou period. The succession of dynasties was incorporat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Sovereigns And Five Emperors
The Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors were two groups of mythological rulers in ancient north China. The Three Sovereigns supposedly lived long before The Five Emperors, who have been assigned dates in a period from 3162 BC to 2070 BC. Today they may be considered culture heroes. The dates of these mythological figures may be fictitious, but according to some accounts and reconstructions, they supposedly preceded the Xia Dynasty. Description The Three Sovereigns, sometimes known as the Three August Ones, were said to be god-kings or demigods who used their divine abilities to improve the lives of the Chinese peoples and gift them essential skills and valuable knowledge. The Five Emperors are portrayed as exemplary ancestral sages who possessed a great moral character and lived to an extremely old age and ruled over a period of great Chinese peace. The Three Sovereigns on the other hand are ascribed various identities in different Chinese historical texts. These high kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Neolithic Cultures Of China
This is a list of Neolithic cultures of China that have been unearthed by archaeologists. They are sorted in chronological order from earliest to latest and are followed by a schematic visualization of these cultures. It would seem that the definition of Neolithic in China is undergoing changes. The discovery in 2012 of pottery about 20,000 years BC indicates that this measure alone can no longer be used to define the period. It will fall to the more difficult task of determining when cereal domestication started. List Schematic outline These cultures are existed for the period from 8500 to 1500 BC. Neolithic cultures remain unmarked and Bronze Age cultures (from 2000 BC) are marked with *. There are many differences in opinion by dating these cultures, so the dates chosen here are tentative: For this schematic outline of its neolithic cultures China has been divided into the following nine parts: #Northeast China: Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang, Jilin and Liaoning. #Northwes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Metallurgy In China
Metallurgy in China has a long history, with the earliest metal objects in China dating back to around 3,000 BCE. The majority of early metal items found in China come from the North-Western Region (mainly Gansu and Qinghai, 青海). China was the earliest civilization to use the blast furnace and produce cast iron. Copper Archaeological evidence indicates that the earliest metal objects in China were made in the late fourth millennium BCE. Copper was generally the earliest metal to be used by humanity, and was used in China since at least 3000 BCE. Early metal-using communities have been found at the Qijia and Siba sites in Gansu, with similar sites in Xinjiang in the west and Shandong, Liaoning and Inner Mongolia in the east and north. The Central Plain sites associated with the Erlitou culture also contain early metalworks.Katheryn M. Linduff, Jianjun Mei (2008)''Metallurgy in Ancient Eastern Asia: How is it Studied? Where is the Field Headed?'' (PDF)The British Museum Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piora Oscillation
The Piora Oscillation was an abrupt cold and wet period in the climate history of the Holocene Epoch; it is roughly dated to c. 3900-3000 BC. Some researchers associate the Piora Oscillation with the end of the Atlantic climate regime, and the start of the Sub-Boreal, in the Blytt–Sernander sequence of Holocene climates. The spatial extent of the change is unclear; it does not show up as a major, or even identifiable, event in hemispheric temperature reconstructions. First detection The phenomenon is named after the Val Piora or Piora Valley in Switzerland, where it was first detected; some of the most dramatic evidence of the Piora Oscillation comes from the region of the Alps. Glaciers advanced in the Alps, apparently for the first time since the Holocene climatic optimum; the Alpine tree line dropped by 100 meters. In the Middle East, the surface of the Dead Sea rose nearly 100 meters (300 feet), then receded to a more usual level. A few commentators have associated th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanzhou University
Lanzhou University () is a major research university in Lanzhou, Gansu, China. Founded in 1909, it is one of the key universities under China's Ministry of Education (Double First Class University Plan, former Project 985 and Project 211). It is a Chinese state Class A Double First Class University identified by the Ministry of Education of China. It provides programs for undergraduate, graduate students on four campuses—three in Lanzhou city centre and one in Yuzhong County, about 30 miles away from the main campus. Total enrolment compromises of approximately 20,000 undergraduates, 10,572 graduates, 2,559 doctoral students, and about 700 registered international students from 64 countries and regions across 5 continents. Undergraduate students study at the Yuzhong campus. There are 6 National Bases for the Training of Researching and Teaching personnel for Fundamental Disciplines. The University operates an additional 35 institutes along with 1 national key Laboratory of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dongxiang Autonomous County
Dongxiang Autonomous County (; Santa: Dunxianzu Zizhixien) is an autonomous county in the Linxia Hui Autonomous Prefecture, province of Gansu of the People's Republic of China. It was established as a Dongxiang ethnic autonomous area in 1950. Historically, Dongxiang has long been directly under the jurisdiction of Linxia. During the Republic of China (1912–1949) period, its area was divided between the surrounding counties. Its population in 2020 was 381,700, 88% of whom belonging to the Dongxiang minority group. As of 1993, half of the total Dongxiang minority population lived in the county. At least until the end of the 20th century, Dongxiang County was very impoverished and undeveloped, having a literacy rate of just 15%, the lowest in China. In 2017, it had the highest poverty rate of Gansu, already the poorest province in China. Dongxiang County has a typical Loess Plateau landscape, with numerous gullies and mountains and a dry climate. Administrative divisions Dong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such as arsenic or silicon. These additions produce a range of alloys that may be harder than copper alone, or have other useful properties, such as ultimate tensile strength, strength, ductility, or machinability. The three-age system, archaeological period in which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia and India is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age starting from about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic Bronze Knife, Majiayao Culture (3200-2000 BC), Gansu, 1978
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |