|
Machine-generated Data
Machine-generated data is information automatically generated by a computer process, application, or other mechanism without the active intervention of a human. While the term dates back over fifty years, there is some current indecision as to the scope of the term. Monash Research's Curt Monash defines it as "data that was produced entirely by machines OR data that is more about observing humans than recording their choices." Meanwhile, Daniel Abadi, CS Professor at Yale, proposes a narrower definition, "Machine-generated data is data that is generated as a result of a decision of an independent computational agent or a measurement of an event that is not caused by a human action." Regardless of definition differences, both exclude data manually entered by a person.Monash, Three Broad Categories of Data Machine-generated data crosses all industry sectors. Often and increasingly, humans are unaware their actions are generating the data. Relevance Machine-generated data has no sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information
Information is an abstract concept that refers to that which has the power to inform. At the most fundamental level information pertains to the interpretation of that which may be sensed. Any natural process that is not completely random, and any observable pattern in any medium can be said to convey some amount of information. Whereas digital signals and other data use discrete signs to convey information, other phenomena and artifacts such as analog signals, poems, pictures, music or other sounds, and currents convey information in a more continuous form. Information is not knowledge itself, but the meaning that may be derived from a representation through interpretation. Information is often processed iteratively: Data available at one step are processed into information to be interpreted and processed at the next step. For example, in written text each symbol or letter conveys information relevant to the word it is part of, each word conveys information rele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wikibon
Wikibon is a community of practitioners and consultants on technology and business systems that uses open source sharing of free advisory knowledge. The company was launched in 2007 by David Vellante, David Floyer and Peter Burris and is headquartered in Marlborough, Massachusetts. Wikibon has approximately 5 employees. Content Wikibon compares itself to technology research services such as Gartner and International Data Corporation. Unlike them, its research is available under a GNU General Public License. Wikibon's research is created and made available in the form of a wiki, enabling contributors to post content, add to existing content, and offer changes and amendments. In 2008, Wikibon introduced “Conserve IT”, to help IT companies and customers qualify for rewards from Pacific Gas and Electric Company for installing energy-efficient equipment. Wikibon holds calls to allow IT practitioners to share information it calls Peer Incite. Wikibon creates and shares infogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
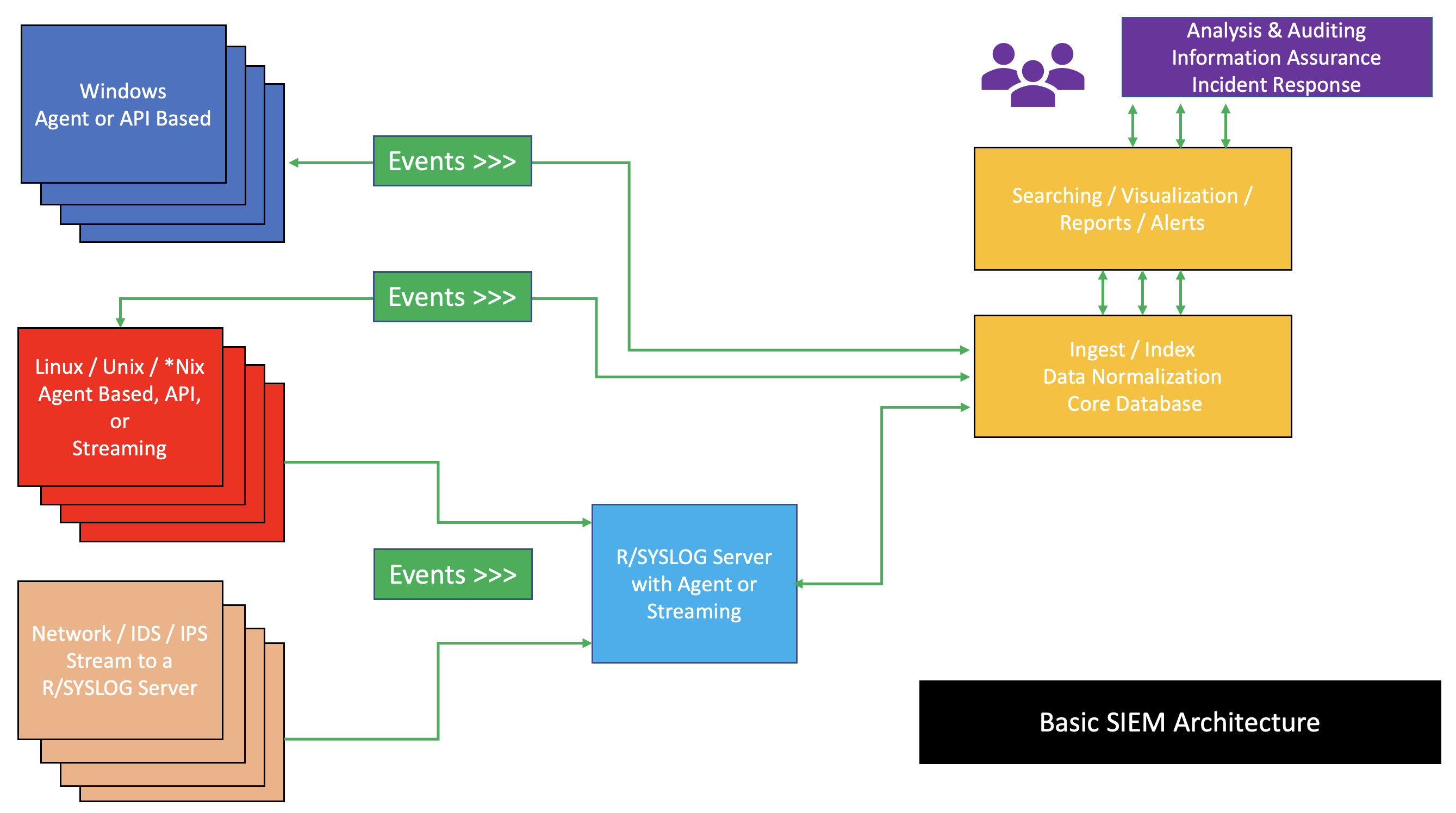
Security Information And Event Management
Security information and event management (SIEM) is a field within the field of computer security, where software products and services combine security information management (SIM) and security event management (SEM). They provide real-time analysis of security alerts generated by applications and network hardware. Vendors sell SIEM as software, as appliances, or as managed services; these products are also used to log security data and generate reports for compliance purposes. The term and the initialism SIEM was coined by Mark Nicolett and Amrit Williams of Gartner in 2005. History Monitoring system logs has grown more prevalent as complex cyber-attacks force compliance and regulatory mechanisms to mandate logging security controls within a Risk Management Framework. Logging levels of a system started with the primary function of troubleshooting system errors or debugging code compiled and run. As operating systems and networks have increased in complexity, so has the event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Event Log
In software engineering, tracing involves a specialized use of logging to record information about a program's execution. This information is typically used by programmers for debugging purposes, and additionally, depending on the type and detail of information contained in a trace log, by experienced system administrators or technical-support personnel and by software monitoring tools to diagnose common problems with software. Tracing is a cross-cutting concern. There is not always a clear distinction between ''tracing'' and other forms of ''logging'', except that the term ''tracing'' is almost never applied to logging that is a functional requirement of a program (therefore excluding logging of data from an external source, such as data acquisition in a high-energy physics experiment, and write-ahead logging). Logs that record program usage (such as a server log) or operating-system events primarily of interest to a system administrator (see for example ''Event Viewer'') fal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Instrument
Financial instruments are monetary contracts between parties. They can be created, traded, modified and settled. They can be cash (currency), evidence of an ownership interest in an entity or a contractual right to receive or deliver in the form of currency (forex); debt ( bonds, loans); equity ( shares); or derivatives ( options, futures, forwards). International Accounting Standards IAS 32 and 39 define a financial instrument as "any contract that gives rise to a financial asset of one entity and a financial liability or equity instrument of another entity". Financial instruments may be categorized by "asset class" depending on whether they are equity-based (reflecting ownership of the issuing entity) or debt-based (reflecting a loan the investor has made to the issuing entity). If the instrument is debt it can be further categorized into short-term (less than one year) or long-term. Foreign exchange instruments and transactions are neither debt- nor equity-based and bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Call Detail Record
A call detail record (CDR) is a data record produced by a telephone exchange or other telecommunications equipment that documents the details of a telephone call or other telecommunications transactions (e.g., text message) that passes through that facility or device. The record contains various attributes of the call, such as time, duration, completion status, source number, and destination number. It is the automated equivalent of the paper toll tickets that were written and timed by operators for long-distance calls in a manual telephone exchange. CDR contents A call detail record contains data fields that describe a specific instance of a telecommunication transaction, but does not include the content of that transaction. By way of simplistic example, a call detail record describing a particular phone call might include the phone numbers of both the calling and receiving parties, the start time, and duration of that call. In actual modern practice, call detail records are m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Server Log
In computing, logging is the act of keeping a log of events that occur in a computer system, such as problems, errors or just information on current operations. These events may occur in the operating system or in other software. A message or log entry is recorded for each such event. These log messages can then be used to monitor and understand the operation of the system, to debug problems, or during an audit. Logging is particularly important in multi-user software, to have a central overview of the operation of the system. In the simplest case, messages are written to a file, called a log file. Alternatively, the messages may be written to a dedicated logging system or to a log management software, where it is stored in a database or on a different computer system. Specifically, a transaction log is a log of the communications between a system and the users of that system, or a data collection method that automatically captures the type, content, or time of transactions ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columnar Database
A column-oriented DBMS or columnar DBMS is a database management system (DBMS) that stores data tables by column rather than by row. Benefits include more efficient access to data when only querying a subset of columns (by eliminating the need to read columns that are not relevant), and more options for data compression. However, they are typically less efficient for inserting new data. Practical use of a column store versus a row store differs little in the relational DBMS world. Both columnar and row databases can use traditional database query languages like SQL to load data and perform queries. Both row and columnar databases can become the backbone in a system to serve data for common extract, transform, load (ETL) and tools. Description Background A relational database management system provides data that represents a two-dimensional table of columns and rows. For example, a database might have this table: This simple table includes an employee identifier (EmpId), name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database Index
A database index is a data structure that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a database table at the cost of additional writes and storage space to maintain the index data structure. Indexes are used to quickly locate data without having to search every row in a database table every time a database table is accessed. Indexes can be created using one or more columns of a database table, providing the basis for both rapid random lookups and efficient access of ordered records. An index is a copy of selected columns of data, from a table, that is designed to enable very efficient search. An index normally includes a "key" or direct link to the original row of data from which it was copied, to allow the complete row to be retrieved efficiently. Some databases extend the power of indexing by letting developers create indexes on column values that have been transformed by functions or expressions. For example, an index could be created on upper(last_name), which wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Point
In statistics, a unit of observation is the unit described by the data that one analyzes. A study may treat groups as a unit of observation with a country as the unit of analysis, drawing conclusions on group characteristics from data collected at the national level. For example, in a study of the demand for money, the unit of observation might be chosen as the individual, with different observations (data points) for a given point in time differing as to which individual they refer to; or the unit of observation might be the country, with different observations differing only in regard to the country they refer to. Unit of observation vs unit of analysis The unit of observation should not be confused with the unit of analysis. A study may have a differing unit of observation and unit of analysis: for example, in community research, the research design may collect data at the individual level of observation but the level of analysis might be at the neighborhood level, drawing c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dataset
A data set (or dataset) is a collection of data. In the case of tabular data, a data set corresponds to one or more database tables, where every column of a table represents a particular variable, and each row corresponds to a given record of the data set in question. The data set lists values for each of the variables, such as for example height and weight of an object, for each member of the data set. Data sets can also consist of a collection of documents or files. In the open data discipline, data set is the unit to measure the information released in a public open data repository. The European data.europa.eu portal aggregates more than a million data sets. Some other issues ( real-time data sources, non-relational data sets, etc.) increases the difficulty to reach a consensus about it. Properties Several characteristics define a data set's structure and properties. These include the number and types of the attributes or variables, and various statistical measures applic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Internet
The industrial internet of things (IIoT) refers to interconnected sensors, instruments, and other devices networked together with computers' industrial applications, including manufacturing and energy management. This connectivity allows for data collection, exchange, and analysis, potentially facilitating improvements in productivity and efficiency as well as other economic benefits. The IIoT is an evolution of a distributed control system (DCS) that allows for a higher degree of automation by using cloud computing to refine and optimize the process controls. Overview The IIoT is enabled by technologies such as cybersecurity, cloud computing, edge computing, mobile technologies, machine-to-machine, 3D printing, advanced robotics, big data, internet of things, RFID technology, and cognitive computing. Five of the most important ones are described below: * Cyber-physical systems (CPS): the basic technology platform for IoT and IIoT and therefore the main enabler to connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |