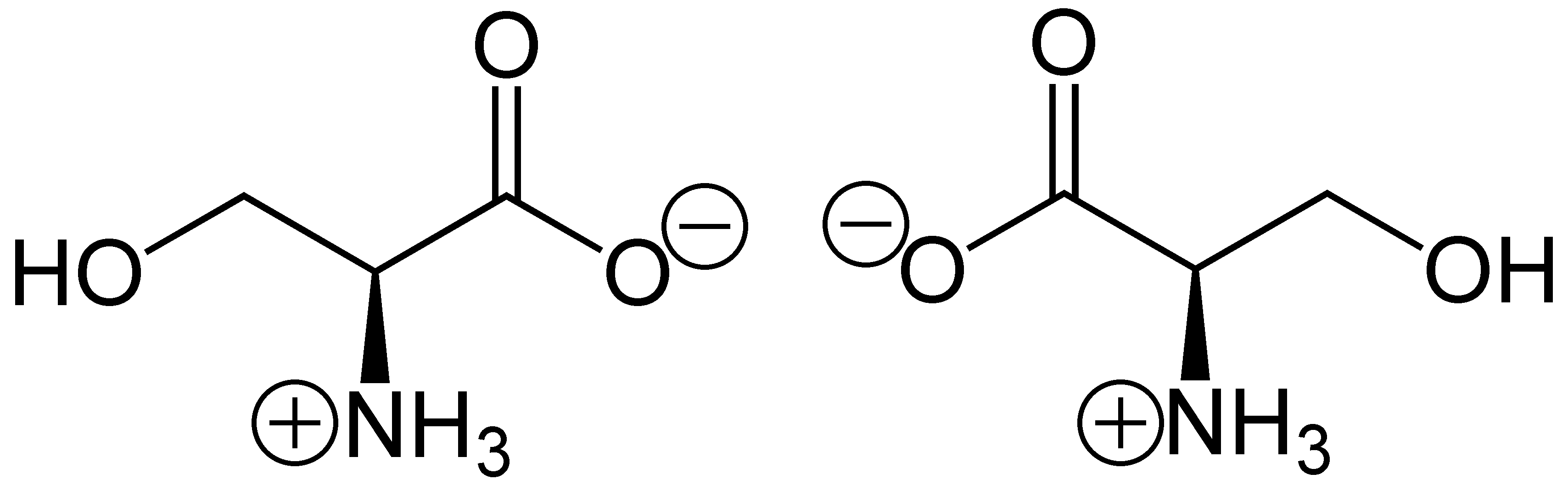|
MTORC2
mTOR Complex 2 (mTORC2) is an acutely rapamycin-insensitive protein complex formed by serine/threonine kinase mTOR that regulates cell proliferation and survival, cell migration and cytoskeletal remodeling. The complex itself is rather large, consisting of seven protein subunits. The catalytic mTOR subunit, DEP domain containing mTOR-interacting protein ( DEPTOR), mammalian lethal with sec-13 protein 8 (mLST8, also known as GβL), and TTI1/ TEL2 complex are shared by both mTORC2 and mTORC1. Rapamycin-insensitive companion of mTOR (RICTOR), mammalian stress-activated protein kinase interacting protein 1 ( mSIN1), and protein observed with rictor 1 and 2 ( Protor1/ 2) can only be found in mTORC2. Rictor has been shown to be the scaffold protein for substrate binding to mTORC2. Function Though less understood than mTORC1, mTORC2 has been shown to respond to growth factors and to modulate cell metabolism and cell survival, thanks to its activation of the survival kinase Akt. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammalian Target Of Rapamycin
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), also referred to as the mechanistic target of rapamycin, and sometimes called FK506-binding protein 12-rapamycin-associated protein 1 (FRAP1), is a kinase that in humans is encoded by the ''MTOR'' gene. mTOR is a member of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase family of protein kinases. mTOR links with other proteins and serves as a core component of two distinct protein complexes, mTOR complex 1 and mTOR complex 2, which regulate different cellular processes. In particular, as a core component of both complexes, mTOR functions as a serine/threonine protein kinase that regulates cell growth, cell proliferation, cell motility, cell survival, protein synthesis, autophagy, and transcription. As a core component of mTORC2, mTOR also functions as a tyrosine protein kinase that promotes the activation of insulin receptors and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors. mTORC2 has also been implicated in the control and maintenance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Kinase B
Protein kinase B (PKB), also known as Akt, is the collective name of a set of three serine/threonine-specific protein kinases that play key roles in multiple cellular processes such as glucose metabolism, apoptosis, cell proliferation, transcription, and cell migration. Family members - Isoforms There are three different genes that encode isoforms of Protein kinase B. These three genes are referred to as AKT1, AKT2, and AKT3 and encode the RAC alpha, beta, and gamma serine/threonine protein kinases respectively. The terms PKB and Akt may refer to the products of all three genes collectively, but sometimes are used to refer to PKB alpha and Akt1 alone. Akt1 is involved in cellular survival pathways, by inhibiting apoptotic processes. Akt1 is also able to induce protein synthesis pathways, and is therefore a key signaling protein in the cellular pathways that lead to skeletal muscle hypertrophy and general tissue growth. A mouse model with complete deletion of the Akt1 g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the naturally occurring proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L- stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, ''sericum''. Serine's structure w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
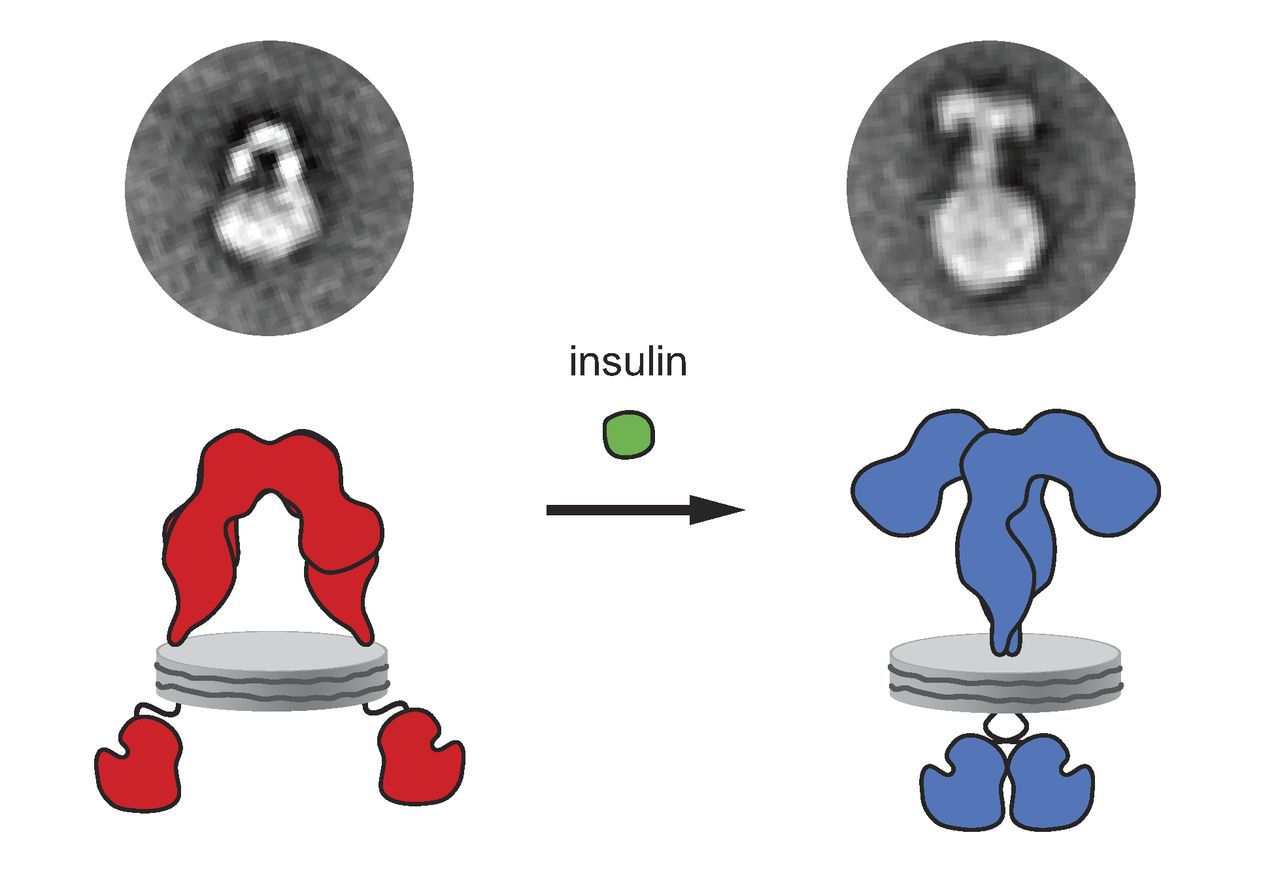
InsR
The insulin receptor (IR) is a transmembrane receptor that is activated by insulin, IGF-I, IGF-II and belongs to the large class of receptor tyrosine kinase. Metabolically, the insulin receptor plays a key role in the regulation of glucose homeostasis, a functional process that under degenerate conditions may result in a range of clinical manifestations including diabetes and cancer. Insulin signalling controls access to blood glucose in body cells. When insulin falls, especially in those with high insulin sensitivity, body cells begin only to have access to lipids that do not require transport across the membrane. So, in this way, insulin is the key regulator of fat metabolism as well. Biochemically, the insulin receptor is encoded by a single gene , from which alternate splicing during transcription results in either IR-A or IR-B isoforms. Downstream post-translational events of either isoform result in the formation of a proteolytically cleaved α and β subunit, which upon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IGF1R
The insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) receptor is a protein found on the surface of human cells. It is a transmembrane receptor that is activated by a hormone called insulin-like growth factor 1 ( IGF-1) and by a related hormone called IGF-2. It belongs to the large class of tyrosine kinase receptors. This receptor mediates the effects of IGF-1, which is a polypeptide protein hormone similar in molecular structure to insulin. IGF-1 plays an important role in growth and continues to have anabolic effects in adults – meaning that it can induce hypertrophy of skeletal muscle and other target tissues. Mice lacking the IGF-1 receptor die late in development, and show a dramatic reduction in body mass. This testifies to the strong growth-promoting effect of this receptor. Structure Two alpha subunits and two beta subunits make up the IGF-1 receptor. Both the α and β subunits are synthesized from a single mRNA precursor. The precursor is then glycosylated, proteolytically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PKC Alpha
Protein kinase C alpha (PKCα) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PRKCA'' gene. Function Protein kinase C (PKC) is a family of serine- and threonine-specific protein kinases that can be activated by calcium and the second messenger diacylglycerol. PKC family members phosphorylate a wide variety of protein targets and are known to be involved in diverse cellular signaling pathways. PKC family members also serve as major receptors for phorbol esters, a class of tumor promoters. Each member of the PKC family has a specific expression profile and is believed to play a distinct role in cells. The protein encoded by this gene is one of the PKC family members. This kinase has been reported to play roles in many different cellular processes, such as cell adhesion, cell transformation, cell cycle checkpoint, and cell volume control. Knockout studies in mice suggest that this kinase may be a fundamental regulator of cardiac contractility and Ca2+ handling in myocytes. Prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Kinase C
In cell biology, Protein kinase C, commonly abbreviated to PKC (EC 2.7.11.13), is a family of protein kinase enzymes that are involved in controlling the function of other proteins through the phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups of serine and threonine amino acid residues on these proteins, or a member of this family. PKC enzymes in turn are activated by signals such as increases in the concentration of diacylglycerol (DAG) or calcium ions (Ca2+). Hence PKC enzymes play important roles in several signal transduction cascades. In biochemistry, the PKC family consists of fifteen isozymes in humans. They are divided into three subfamilies, based on their second messenger requirements: conventional (or classical), novel, and atypical. Conventional (c)PKCs contain the isoforms α, βI, βII, and γ. These require Ca2+, DAG, and a phospholipid such as phosphatidylserine for activation. Novel (n)PKCs include the δ, ε, η, and θ isoforms, and require DAG, but do not require Ca2+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
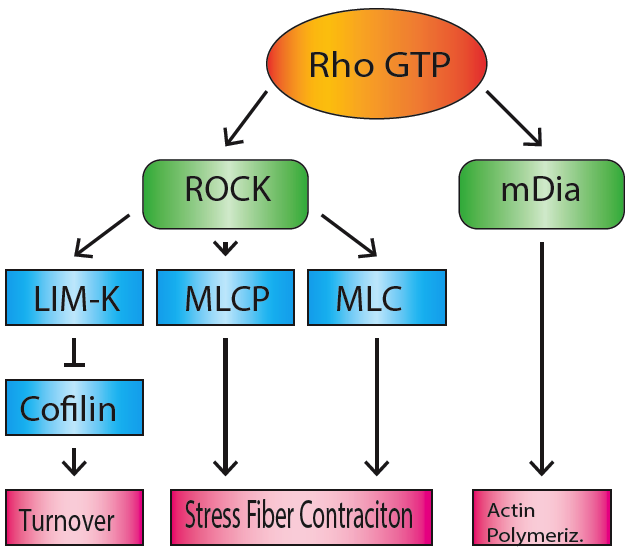
RHOA
Transforming protein RhoA, also known as Ras homolog family member A (RhoA), is a small GTPase protein in the Rho family of GTPases that in humans is encoded by the ''RHOA'' gene. While the effects of RhoA activity are not all well known, it is primarily associated with cytoskeleton regulation, mostly actin stress fibers formation and actomyosin contractility. It acts upon several effectors. Among them, ROCK1 (Rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1) and DIAPH1 (Diaphanous Homologue 1, a.k.a. hDia1, homologue to mDia1 in mouse, diaphanous in ''Drosophila'') are the best described. RhoA, and the other Rho GTPases, are part of a larger family of related proteins known as the Ras superfamily, a family of proteins involved in the regulation and timing of cell division. RhoA is one of the oldest Rho GTPases, with homologues present in the genomes since 1.5 billion years. As a consequence, RhoA is somehow involved in many cellular processes which emerged throughout evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paxillin
Paxillin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PXN'' gene. Paxillin is expressed at focal adhesions of non-striated cells and at costameres of striated muscle cells, and it functions to adhere cells to the extracellular matrix. Mutations in ''PXN'' as well as abnormal expression of paxillin protein has been implicated in the progression of various cancers. Structure Human paxillin is 64.5 kDa in molecular weight and 591 amino acids in length. The C-terminal region of paxillin is composed of four tandem double zinc finger LIM domains that are cysteine/histidine-rich with conserved repeats; these serve as binding sites for the protein tyrosine phosphatase-PEST, tubulin and serves as the targeting motif for focal adhesions. The N-terminal region of paxillin has five highly conserved leucine-rich sequences termed LD motifs, which mediate several interactions, including that with pp125FAK and vinculin. The LD motifs are predicted to form amphipathic alpha helices, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress Fiber
Stress fibers are contractile actin bundles found in non-muscle cells. They are composed of actin (microfilaments) and non-muscle myosin II (NMMII), and also contain various crosslinking proteins, such as α-actinin, to form a highly regulated actomyosin structure within non-muscle cells. Stress fibers have been shown to play an important role in cellular contractility, providing force for a number of functions such as cell adhesion, migration and morphogenesis. Structure Stress fibers are primarily composed of actin and myosin. Actin is a ~43kDa globular protein, and can polymerize to form long filamentous structures. These filaments are made of two strands of actin monomers (or protofilaments) wrapping around each other, to create a single actin filament. Because actin monomers are not symmetrical molecules, their filaments have polarity based upon the structure of the actin monomer, which will allow one end of the actin filament to polymerize faster than the other. The end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |