|
MAEB RNA Motif
The MAEB RNA motif (Metabolism-Associated Element in ''Burkholderia'' RNA motif) is a conserved stem-loop RNA structure present in many species in the genus Burkholderia. MAEB stem-loops typically occur in blocks of repeats, usually with 2–6 consecutive instances of MAEB stem-loops separated by a short and conserved linker sequence. As many as 12 consecutive MAEB stem-loops have been observed in a single block. Most MAEB blocks are positioned in the presumed 5' UTR of downstream genes. Out of 141 blocks of consecutive MAEB stem-loops, 132 are positioned in a possible 5' UTR. Therefore, MAEB stem-loops are likely to correspond to a cis-regulatory element. It was observed that the genes apparently regulated by MAEB generally have a role in primary metabolism, i.e., the synthesis, catabolism or transport of small molecules; few MAEB-associated genes are involved in other functions, such as signal transduction, motility or replication. Thus, the motif is associated with a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem-loop
Stem-loop intramolecular base pairing is a pattern that can occur in single-stranded RNA. The structure is also known as a hairpin or hairpin loop. It occurs when two regions of the same strand, usually complementary in nucleotide sequence when read in opposite directions, base-pair to form a double helix that ends in an unpaired loop. The resulting structure is a key building block of many RNA secondary structures. As an important secondary structure of RNA, it can direct RNA folding, protect structural stability for messenger RNA (mRNA), provide recognition sites for RNA binding proteins, and serve as a substrate for enzymatic reactions. Formation and stability The formation of a stem-loop structure is dependent on the stability of the resulting helix and loop regions. The first prerequisite is the presence of a sequence that can fold back on itself to form a paired double helix. The stability of this helix is determined by its length, the number of mismatches or bulges it co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CsrB/RsmB RNA Family
The CsrB RNA is a non-coding RNA that binds to approximately 9 to 10 dimers of the CsrA protein. The CsrB RNAs contain a conserved motif CAGGXXG that is found in up to 18 copies and has been suggested to bind CsrA. The Csr regulatory system has a strong negative regulatory effect on glycogen biosynthesis, glyconeogenesis and glycogen catabolism and a positive regulatory effect on glycolysis. In other bacteria such as '' Erwinia carotovora'' the RsmA protein has been shown to regulate the production of virulence determinants, such extracellular enzymes. RsmA binds to RsmB regulatory RNA which is also a member of this family. RsmB RNA was shown to be upregulated by GacS/A system, and increase downstream T3SS Type three secretion system (often written Type III secretion system and abbreviated TTSS or T3SS, also called Injectisome) is a protein appendage found in several Gram-negative bacteria. In pathogenic bacteria, the needle-like structure is used ... gene expression. Fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repetitive DNA
Repeated sequences (also known as repetitive elements, repeating units or repeats) are short or long patterns of nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) that occur in multiple copies throughout the genome. In many organisms, a significant fraction of the genomic DNA is repetitive, with over two-thirds of the sequence consisting of repetitive elements in humans. Some of these repeated sequences are necessary for maintaining important genome structures such as telomeres or centromeres. Repeated sequences are categorized into different classes depending on features such as structure, length, location, origin, and mode of multiplication. The disposition of repetitive elements throughout the genome can consist either in directly-adjacent arrays called tandem repeats or in repeats dispersed throughout the genome called interspersed repeats. Tandem repeats and interspersed repeats are further categorized into subclasses based on the length of the repeated sequence and/or the mode of multiplication. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrimidine
Pyrimidine (; ) is an aromatic, heterocyclic, organic compound similar to pyridine (). One of the three diazines (six-membered heterocyclics with two nitrogen atoms in the ring), it has nitrogen atoms at positions 1 and 3 in the ring. The other diazines are pyrazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 4 positions) and pyridazine (nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 2 positions). In nucleic acids, three types of nucleobases are pyrimidine derivatives: cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U). Occurrence and history The pyrimidine ring system has wide occurrence in nature as substituted and ring fused compounds and derivatives, including the nucleotides cytosine, thymine and uracil, thiamine (vitamin B1) and alloxan. It is also found in many synthetic compounds such as barbiturates and the HIV drug, zidovudine. Although pyrimidine derivatives such as alloxan were known in the early 19th century, a laboratory synthesis of a pyrimidine was not carried out until 1879, when Grimaux reported the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
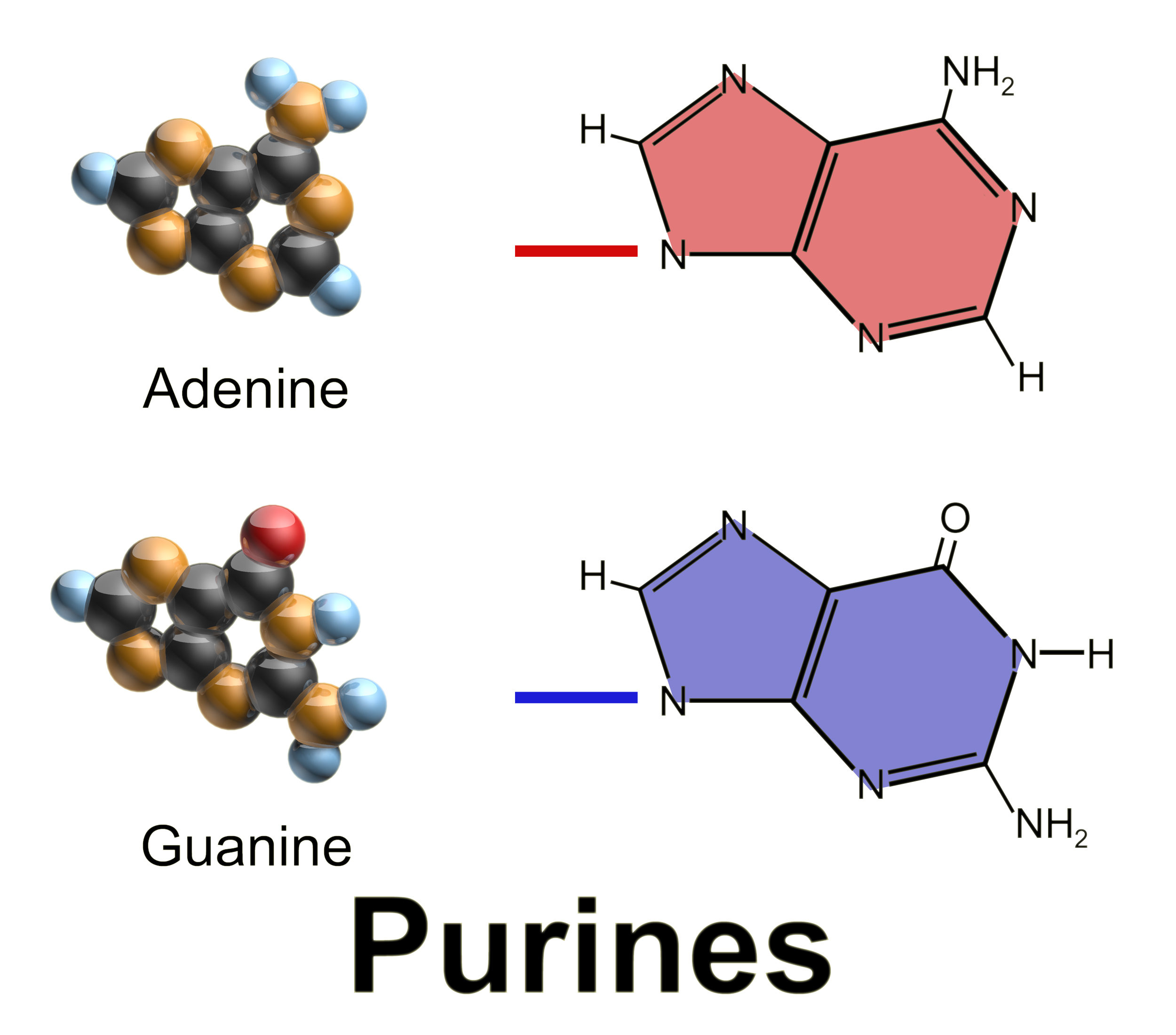
Purine
Purine is a heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings (pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted purines and their tautomers. They are the most widely occurring nitrogen-containing heterocycles in nature. Dietary sources Purines are found in high concentration in meat and meat products, especially internal organs such as liver and kidney. In general, plant-based diets are low in purines. High-purine plants and algae include some legumes (lentils and Black-eyed pea, black eye peas) and Spirulina (dietary supplement), spirulina. Examples of high-purine sources include: sweetbreads, Anchovies as food, anchovies, Sardines as food, sardines, liver, beef kidneys, Brain as food, brains, meat extracts (e.g., Oxo (food), Oxo, Bovril), herring, mackerel, scallops, game meats, yeast (beer, yeast extract, nutritional yeast) and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common nutrients by the liver. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine. Nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism at a fundamental, cellular level. They provide chemical energy—in the form of the nucleoside triphosphates, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP) and uridine triphosphate (UTP)—throughout the cell for the many cellular func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycine Cleavage System
The glycine cleavage system (GCS) is also known as the glycine decarboxylase complex or GDC. The system is a series of enzymes that are triggered in response to high concentrations of the amino acid glycine. The same set of enzymes is sometimes referred to as glycine synthase when it runs in the reverse direction to form glycine. The glycine cleavage system is composed of four proteins: the T-protein, P-protein, L-protein, and H-protein. They do not form a stable complex, so it is more appropriate to call it a "system" instead of a "complex". The H-protein is responsible for interacting with the three other proteins and acts as a shuttle for some of the intermediate products in glycine decarboxylation. In both animals and plants the glycine cleavage system is loosely attached to the inner membrane of the mitochondria. Mutations in this enzymatic system are linked with glycine encephalopathy. Components Function In plants, animals and bacteria the glycine cleavage system cataly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burkholderia
''Burkholderia'' is a genus of Pseudomonadota whose pathogenic members include the ''Burkholderia cepacia'' complex, which attacks humans and ''Burkholderia mallei'', responsible for glanders, a disease that occurs mostly in horses and related animals; ''Burkholderia pseudomallei'', causative agent of melioidosis; and '' Burkholderia cepacia'', an important pathogen of pulmonary infections in people with cystic fibrosis (CF). ''Burkholderia'' species is also found marine environment. S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and characterized ''Burkholderia cepacia'' from marine sponges of the Saint Martin's Island of the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh. The ''Burkholderia'' (previously part of ''Pseudomonas'') genus name refers to a group of virtually ubiquitous Gram-negative, obligately aerobic, rod-shaped bacteria that are motile by means of single or multiple polar flagella, with the exception of ''Burkholderia mallei'', which is nonmotile. Members belonging to the genus do not produce s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritance. This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues, while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own copy of the DNA. The cell possesses the distinctive property of division, which makes replication of DNA essential. DNA is made up of a double helix of two complementary strands. The double helix describes the appearance of a double-stranded DNA which is thus composed of two linear strands that run opposite to each other and twist together to form. During replication, these strands are separated. Each strand of the original DNA molecule then serves as a template for the production of its counterpart, a process referred to as semiconservative replication. As a result of semi-conservative rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motility
Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy. Definitions Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms that do not possess a means of self-locomotion and are normally immobile. Motility differs from mobility, the ability of an object to be moved. The term vagility encompasses both motility and mobility; sessile organisms including plants and fungi often have vagile parts such as fruits, seeds, or spores which may be dispersed by other agents such as wind, water, or other organisms. Motility is genetically determined, but may be affected by environmental factors such as toxins. The nervous system and musculoskeletal system provide the majority of mammalian motility. In addition to animal locomotion, most animals are motile, though some are vagile, described as having passive locomotion. Many bacteria and other microorganisms, and multicellu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |