|
M13 Link
The M13 link, formally Link, Cartridge, Metallic Belt, 7.62mm, M13, is the U.S. military designation for a metallic disintegrating link specifically designed for ammunition belt-fed firearms and 7.62×51mm NATO rounds. It was introduced in the mid-20th century. It is the primary link type for the United States and among NATO for the 7.62×51mm NATO cartridge. , it has been in use for over 60 years and is used on the Dillon M134D Minigun, M60 Machine Gun, FN MAG/M240, Mk 48, MG3, HK21, MG5, UKM-2000, K12, SS-77 and Negev NG-7, among others. Some countries redesignated the M13 link when it was adopted. History The M13 link replaced the older M1 links designed for .30-06 Springfield ammunition, which bound cartridges to each other at the neck, used on the older M1917 Browning machine gun and M1919 Browning machine gun family, though some conversions of the M1919 to the M13 were done, such as on the U.S. Navy Mark 21 Mod 0 machine gun, which saw service in the Vietnam War. Once ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MG3 Zerfallgurt
The MG 3 is a German general-purpose machine gun chambered for the 7.62×51mm NATO cartridge. The weapon's design is derived from the World War II era MG 42 ''Einheitsmaschinengewehr'' (Universal machine gun) that fired the 7.92×57mm Mauser round.Woźniak, Ryszard: ''Encyklopedia najnowszej broni palnej—tom 3 M-P'', page 106. Bellona, 2001. The MG 3 was standardized in the late 1950s and adopted into service with the newly formed ''Bundeswehr'', where it continues to serve to this day as a squad support weapon and a vehicle-mounted machine gun. The weapon and its derivatives have also been acquired by the armed forces of over 40 countries. Production rights to the machine gun were purchased by Italy (:it:Beretta MG 42/59, MG 42/59), Spain, Pakistan (MG 1A3), Greece, Iran, Sudan and Turkey. History At the end of World War II the original technical drawings and data for the 7.92×57mm Mauser chambered MG 42 were captured by the Soviets. These would eventually find their way ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vektor SS-77
The Vektor SS-77 is a general-purpose machine gun designed and manufactured by Denel Land Systems—formerly Lyttleton Engineering Works (LIW)—of South Africa. History In the late 1970s, South Africa was involved in an international controversy over apartheid and the South African Border War in Angola. As a result, it was subject to an international arms embargo and had to, out of necessity, design and manufacture its own weapons.Security Arms Vektor SS-77 & Mini-SS. Retrieved on 14 May 2008. The SS-77 was developed to replace the . It was designed in 1977 by Richard Joseph Smith and Lazlo Soregi. The "SS" in its name stands for Smith and Soregi, and "77" for 1977, the year it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FN Minimi
The FN Minimi (short for french: Mini Mitrailleuse; "mini machine gun") is a Belgian 5.56mm light machine gun/squad automatic weapon developed by Ernest Vervier for FN Herstal. First introduced in the late 1970s, it is now in service in more than 75 countries. The weapon is currently manufactured at the FN facility in Herstal and their U.S. subsidiary FN Manufacturing LLC. The Minimi fires from an open bolt. It is an air-cooled, gas operated long-stroke piston weapon that is capable of fully automatic fire only. It can be belt fed or fired from a magazine. The Minimi is configured in several variants: the Standard model as a platoon or squad support weapon, the Para version for paratroopers and the Vehicle model as secondary armament for fighting vehicles. Design details Operating mechanism The Minimi uses a gas-actuated long-stroke piston system. The barrel is locked with a rotary bolt, equipped with two massive locking lugs, forced into battery by a helical camming guide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M27 Link
The M27 link, formally Link, Cartridge, Metallic Belt, 5.56mm, M27 is a metallic disintegrating link issued by the United States armed forces and among NATO and designed for use in belt-fed firearms. It holds 5.56×45mm NATO ammunition. History The first scaled-down version of the mid-20th century M13 link was developed in the early 1960s for the Stoner 63 belt-fed light machine gun/squad automatic weapon and designated as the "S-63 BRW" link. In the early 1970s this scaling-down concept was further developed. The resulting modified link had a slightly different angle of pitch and was adapted as the M27 link for use with the FN Minimi/M249 SAW. The M27 link is used on the FN Minimi/M249, HK23, MG4, CETME Ameli, K3, Mini-SS and Negev, among others. Design details Each M27 link consists of a single piece of metal curved into two partial cylinders, into which adjacent rounds slide. Like the M13 link, the M27 link is a push-through design. Rounds are extracted by pushing forward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate Conversion Coating
Phosphate conversion coating is a chemical treatment applied to steel parts that creates a thin adhering layer of iron, zinc, or manganese phosphates, to achieve corrosion resistance, lubrication, or as a foundation for subsequent coatings or painting. It is one of the most common types of conversion coating. The process is also called phosphate coating, phosphatization, phosphatizing, or phosphating. It is also known by the trade name Parkerizing, especially when applied to firearms and other military equipment. A phosphate coating is usually obtained by applying to the steel part a dilute solution of phosphoric acid, possibly with soluble iron, zinc, and/or manganese salts. The solution may be applied by sponging, spraying, or immersion. Phosphate conversion coatings can also be used on aluminium, zinc, cadmium, silver and tin. Types The main types of phosphate coatings are manganese, iron, and zinc. * Manganese phosphate coatings are used both for corrosion resistance a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standardization Agreement
In NATO, a standardization agreement (STANAG, redundantly: STANAG agreement) defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the alliance. Each NATO state ratifies a STANAG and implements it within its own military. The purpose is to provide common operational and administrative procedures and logistics, so one member nation's military may use the stores and support of another member's military. STANAGs also form the basis for technical interoperability between a wide variety of communication and information systems (CIS) essential for NATO and Allied operations. The Allied Data Publication 34 (ADatP-34) NATO Interoperability Standards and Profiles which is covered by STANAG 5524, maintains a catalogue of relevant information and communication technology standards. STANAGs are published in English and French, the two official languages of NATO, by the NATO Standardization Office in Bru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M2 Machine Gun
The M2 machine gun or Browning .50 caliber machine gun (informally, "Ma Deuce") is a heavy machine gun that was designed towards the end of World War I by John Browning. Its design is similar to Browning's earlier M1919 Browning machine gun, which was chambered for the .30-06 cartridge. The M2 uses Browning's larger and more powerful .50 BMG (12.7 mm) cartridge. The design has had many designations; the official U.S. military designation for the current infantry type is Browning Machine Gun, Cal. .50, M2, HB, Flexible. It is effective against infantry, unarmored or lightly armored vehicles and boats, light fortifications, and low-flying aircraft. The gun has been used extensively as a vehicle weapon and for aircraft armament by the United States since the 1930s. It was heavily used during World War II, the Korean War, the Vietnam War, the Falklands War, the Soviet–Afghan War, the Gulf War, the Iraq War, and the War in Afghanistan. It is the primary heavy machine gun of NATO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
50 BMG
The .50 Browning Machine Gun (.50 BMG, 12.7×99mm NATO and designated as the 50 Browning by the C.I.P.) is a caliber cartridge developed for the M2 Browning heavy machine gun in the late 1910s, entering official service in 1921. Under STANAG 4383, it is a standard service cartridge for NATO forces as well as many non-NATO countries. The cartridge itself has been made in many variants: multiple generations of regular ball, tracer, armor-piercing (AP), incendiary, and saboted sub-caliber rounds. The rounds intended for machine guns are made into a continuous belt using metallic links. The .50 BMG cartridge is also used in anti-materiel rifles. A wide variety of ammunition is available, and the availability of match grade ammunition has increased the usefulness of .50 caliber rifles by allowing more accurate fire than lower quality rounds. History In response to the need for new anti-aircraft weaponry during World War I, John Browning developed the .50 BMG. He wanted the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. The north was supported by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist states, while the south was United States in the Vietnam War, supported by the United States and other anti-communism, anti-communist Free World Military Forces, allies. The war is widely considered to be a Cold War-era proxy war. It lasted almost 20 years, with direct U.S. involvement ending in 1973. The conflict also spilled over into neighboring states, exacerbating the Laotian Civil War and the Cambodian Civil War, which ended with all three countries becoming communist states by 1975. After the French 1954 Geneva Conference, military withdrawal from Indochina in 1954 – following their defeat in the First Indochina War – the Viet Minh to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
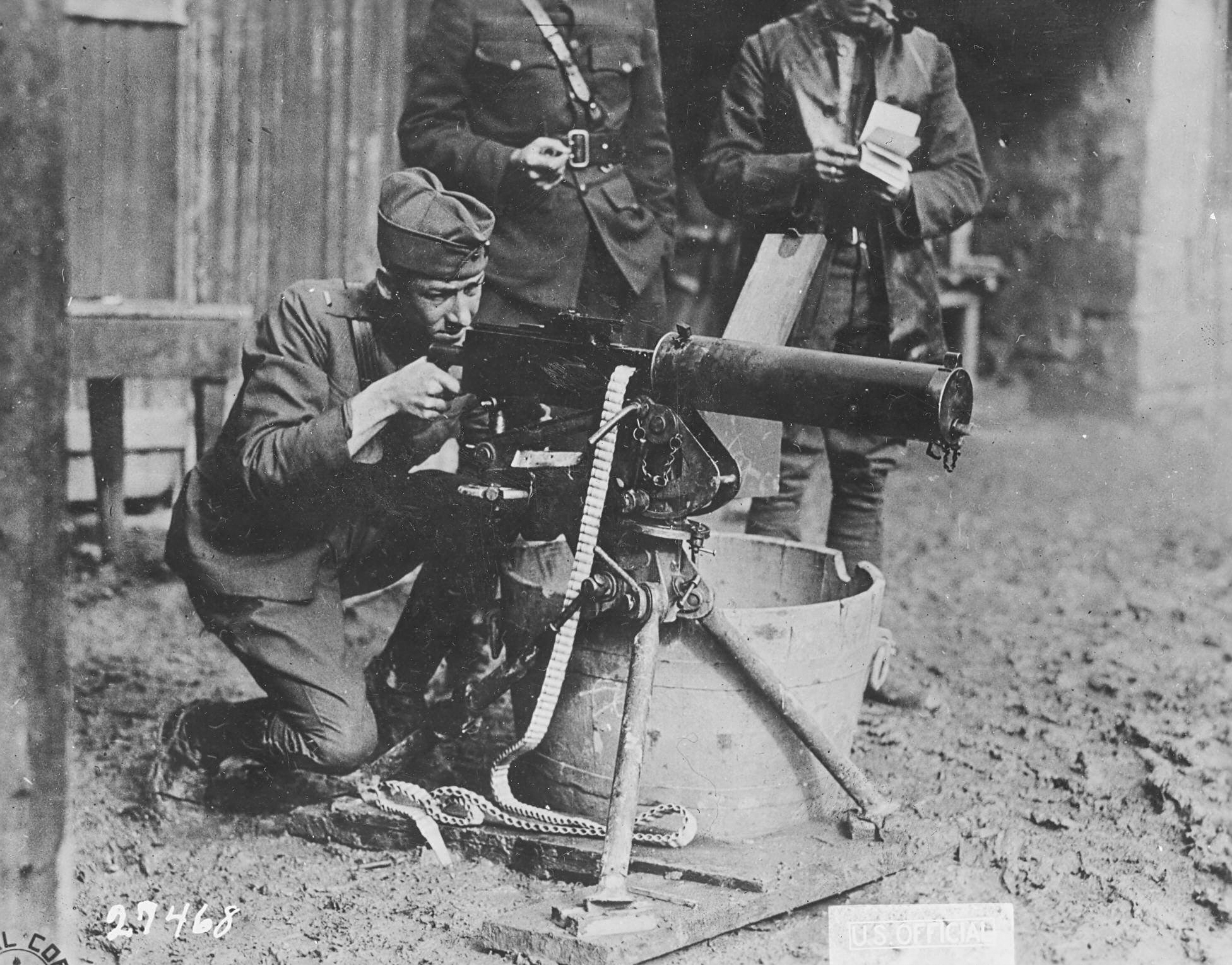
M1919 Browning Machine Gun
The M1919 Browning is a .30 caliber medium machine gun that was widely used during the 20th century, especially during World War II, the Korean War, and the Vietnam War. The M1919 saw service as a light infantry, coaxial, mounted, aircraft, and anti-aircraft machine gun by the U.S. and many other countries. The M1919 was an air-cooled development of the standard US machine gun of World War I, the John M. Browning-designed water-cooled M1917. The emergence of general-purpose machine guns in the 1950s pushed the M1919 into secondary roles in many cases, especially after the arrival of the M60 in US Army service. The United States Navy also converted many to 7.62 mm NATO, and designated them Mk 21 Mod 0; they were commonly used on riverine craft in the 1960s and 1970s in Vietnam. Many NATO countries also converted their examples to 7.62 mm caliber, and these remained in service well into the 1990s, as well as up to the present day in some countries. Operation Loading The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M1917 Browning Machine Gun
The M1917 Browning machine gun is a heavy machine gun used by the United States armed forces in World War I, World War II, the Korean War, and the Vietnam War; it has also been used by other nations. It was a crew-served, belt-fed, water-cooled machine gun that served alongside the much lighter air-cooled Browning M1919. It was used at the battalion level, and often mounted on vehicles (such as a jeep). There were two main iterations: the M1917, which was used in World War I and the M1917A1, which was used thereafter. The M1917, which was used on some aircraft as well as in a ground role, had a cyclic rate of 450 rounds per minute. The M1917A1 had a cyclic rate of 450 to 600 rounds per minute. Design and development In 1900, John Moses Browning filed a patent for a recoil-powered automatic gun. Browning did not work on the gun again until 1910, when he built a water-cooled prototype of the 1900 design. Although the gun worked well, Browning improved the design slightly. Brownin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_in_Rutshuru_territory.jpg)
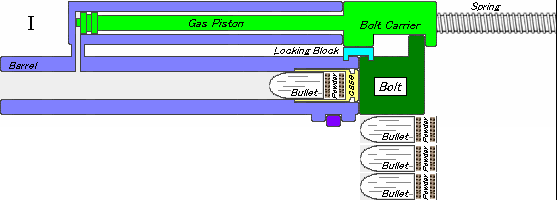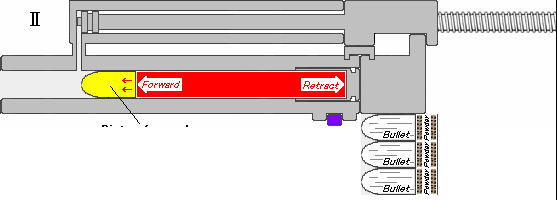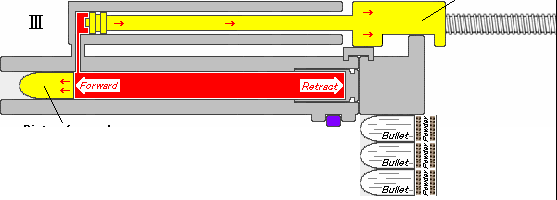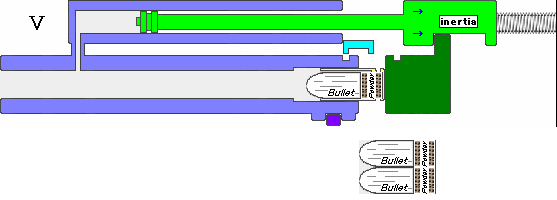



.jpg)
