|
Lysosomes
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane proteins, and its lumenal proteins. The lumen's pH (~4.5–5.0) is optimal for the enzymes involved in hydrolysis, analogous to the activity of the stomach. Besides degradation of polymers, the lysosome is involved in various cell processes, including secretion, plasma membrane repair, apoptosis, cell signaling, and energy metabolism. Lysosomes act as the waste disposal system of the cell by digesting used materials in the cytoplasm, from both inside and outside the cell. Material from outside the cell is taken up through endocytosis, while material from the inside of the cell is digested through autophagy. The sizes of the organelles vary greatly—the larger ones can be more than 10 times the size of the smaller ones. They were discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysosomes Digestion
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane proteins, and its lumenal proteins. The lumen's pH (~4.5–5.0) is optimal for the enzymes involved in hydrolysis, analogous to the activity of the stomach. Besides degradation of polymers, the lysosome is involved in various cell processes, including secretion, plasma membrane repair, apoptosis, cell signaling, and energy metabolism. Lysosomes act as the waste disposal system of the cell by digesting used materials in the cytoplasm, from both inside and outside the cell. Material from outside the cell is taken up through endocytosis, while material from the inside of the cell is digested through autophagy. The sizes of the organelles vary greatly—the larger ones can be more than 10 times the size of the smaller ones. They were discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autophagy
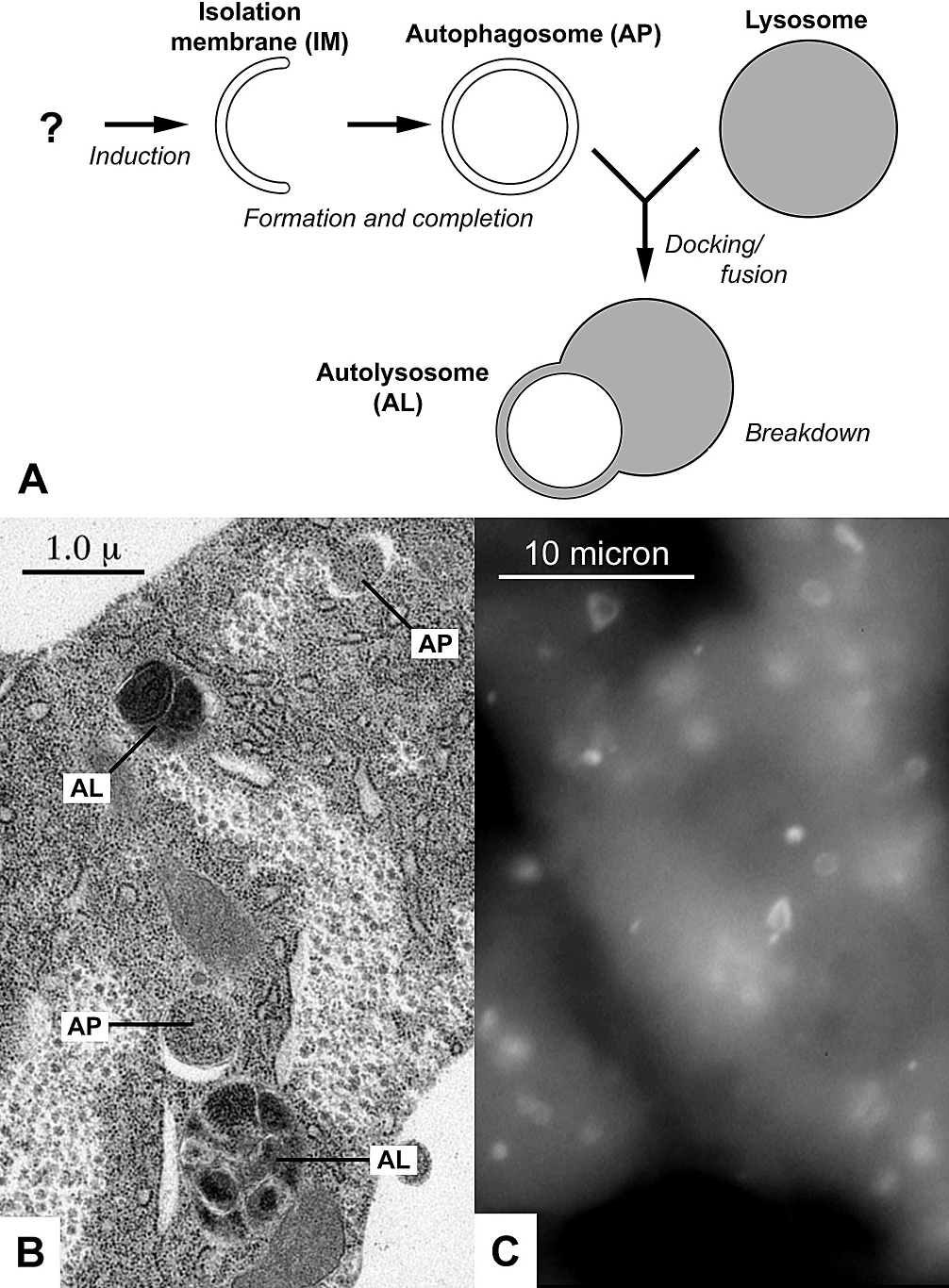
Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Ancient Greek , , meaning "self-devouring" and , , meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components through a lysosome-dependent regulated mechanism. It allows the orderly degradation and recycling of cellular components. Although initially characterized as a primordial degradation pathway induced to protect against starvation, it has become increasingly clear that autophagy also plays a major role in the homeostasis of non-starved cells. Defects in autophagy have been linked to various human diseases, including neurodegeneration and cancer, and interest in modulating autophagy as a potential treatment for these diseases has grown rapidly. Four forms of autophagy have been identified: macroautophagy, microautophagy, chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), and crinophagy. In macroautophagy (the most thoroughly researched form of autophagy), cytoplasmic components (like mit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian De Duve
Christian René Marie Joseph, Viscount de Duve (2 October 1917 – 4 May 2013) was a Nobel Prize-winning Belgian cytologist and biochemist. He made serendipitous discoveries of two cell organelles, peroxisome and lysosome, for which he shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1974 with Albert Claude and George E. Palade ("for their discoveries concerning the structural and functional organization of the cell"). In addition to peroxisome and lysosome, he invented scientific names such as autophagy, endocytosis, and exocytosis in a single occasion. The son of Belgian refugees during the First World War, de Duve was born in Thames Ditton, Surrey, England. His family returned to Belgium in 1920. He was educated by the Jesuits at Our Lady College, Antwerp, and studied medicine at the Catholic University of Leuven. Upon earning his MD in 1941, he joined research in chemistry, working on insulin and its role in diabetes mellitus. His thesis earned him the highest universi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. Endocytosis includes pinocytosis (cell drinking) and phagocytosis (cell eating). It is a form of active transport. History The term was proposed by De Duve in 1963. Phagocytosis was discovered by Élie Metchnikoff in 1882. Pathways Endocytosis pathways can be subdivided into four categories: namely, receptor-mediated endocytosis (also known as clathrin-mediated endocytosis), caveolae, pinocytosis, and phagocytosis Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is .... *Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is mediated by the production of smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesicle (biology And Chemistry)
In cell biology, a vesicle is a structure within or outside a cell, consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion (exocytosis), uptake ( endocytosis) and transport of materials within the plasma membrane. Alternatively, they may be prepared artificially, in which case they are called liposomes (not to be confused with lysosomes). If there is only one phospholipid bilayer, the vesicles are called ''unilamellar liposomes''; otherwise they are called ''multilamellar liposomes''. The membrane enclosing the vesicle is also a lamellar phase, similar to that of the plasma membrane, and intracellular vesicles can fuse with the plasma membrane to release their contents outside the cell. Vesicles can also fuse with other organelles within the cell. A vesicle released from the cell is known as an extracellular vesicle. Vesicles perform a variety of functions. Because it is separated from the cytosol, the inside of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mannose 6-phosphate
Mannose-6-phosphate (M6P) is a molecule bound by lectin in the immune system. M6P is converted to fructose 6-phosphate by mannose phosphate isomerase. M6P is a key targeting signal for acid hydrolase precursor proteins that are destined for transport to lysosomes. The M6P tag is added to such proteins in the ''cis''-Golgi apparatus. Specifically, in a reaction involving uridine diphosphate (UDP) and ''N''-acetylglucosamine, the enzyme N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate transferase catalyzes the ''N''-linked glycosylation of asparagine residues with M6P. Once appropriately marked with the M6P targeting signal, these proteins are moved to the ''trans''-Golgi network. There, the M6P moiety is recognized and bound by mannose 6-phosphate receptor (MPR) proteins at pH 6.5–6.7. The M6P-tagged lysosomal enzymes are shipped to the late endosomes via vesicular transport. Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) for several lysosomal storage diseases relies on this pathway to efficiently direct syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CLN8
Protein CLN8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CLN8'' gene. Molecular biology This gene encodes a transmembrane protein that localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and recycles between the ER and the Golgi apparatus via COPII- and COPI-coated vesicles. CLN8 protein functions as a cargo receptor for lysosomal soluble proteins in the ER. CLN8 proteins pair with CLN6 proteins to form the EGRESS complex (ER-to-Golgi relaying of enzymes of the lysosomal system), the functional unit responsible for the export of lysosomal enzymes from the endoplasmic reticulum. Clinical Mutations in this gene are associated with progressive epilepsy with mental retardation (EPMR), a subtype of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (NCL). Patients with mutations in this gene have altered levels of sphingolipid and phospholipids in the brain A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CLN6
Ceroid-lipofuscinosis neuronal protein 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CLN6'' gene. The CLN6 protein is part of the EGRESS complex (ER-to-Golgi relaying of enzymes of the lysosomal system), which recruits lysosomal enzymes at the endoplasmic reticulum to promote their transfer to the Golgi complex. The EGRESS complex is composed of CLN6 and CLN8 proteins. Loss-of-function mutations in CLN6 result in inefficient export of lysosomal enzymes from the endoplasmic reticulum and diminished levels of the enzymes at the lysosome A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane prot .... See also * Batten disease References External links GeneReviews/NIH/NCBI/UW entry on Neuronal Ceroid-Lipofuscinoses* Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-15-st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuoles
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in solution, though in certain cases they may contain solids which have been engulfed. Vacuoles are formed by the fusion of multiple membrane vesicles and are effectively just larger forms of these. The organelle has no basic shape or size; its structure varies according to the requirements of the cell. Discovery Contractile vacuoles ("stars") were first observed by Spallanzani (1776) in protozoa, although mistaken for respiratory organs. Dujardin (1841) named these "stars" as ''vacuoles''. In 1842, Schleiden applied the term for plant cells, to distinguish the structure with cell sap from the rest of the protoplasm. In 1885, de Vries named the vacuole membrane as tonoplast. Function The function and significa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substrate (chemistry)
In chemistry, the term substrate is highly context-dependent. Broadly speaking, it can refer either to a chemical species being observed in a chemical reaction, or to a surface on which other chemical reactions or microscopy are performed. In the former sense, a reagent is added to the ''substrate'' to generate a product through a chemical reaction. The term is used in a similar sense in synthetic and organic chemistry, where the substrate is the chemical of interest that is being modified. In biochemistry, an enzyme substrate is the material upon which an enzyme acts. When referring to Le Chatelier's principle, the substrate is the reagent whose concentration is changed. ;Spontaneous reaction : :*Where S is substrate and P is product. ;Catalysed reaction : :*Where S is substrate, P is product and C is catalyst. In the latter sense, it may refer to a surface on which other chemical reactions are performed or play a supporting role in a variety of spectroscopic and microsco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)