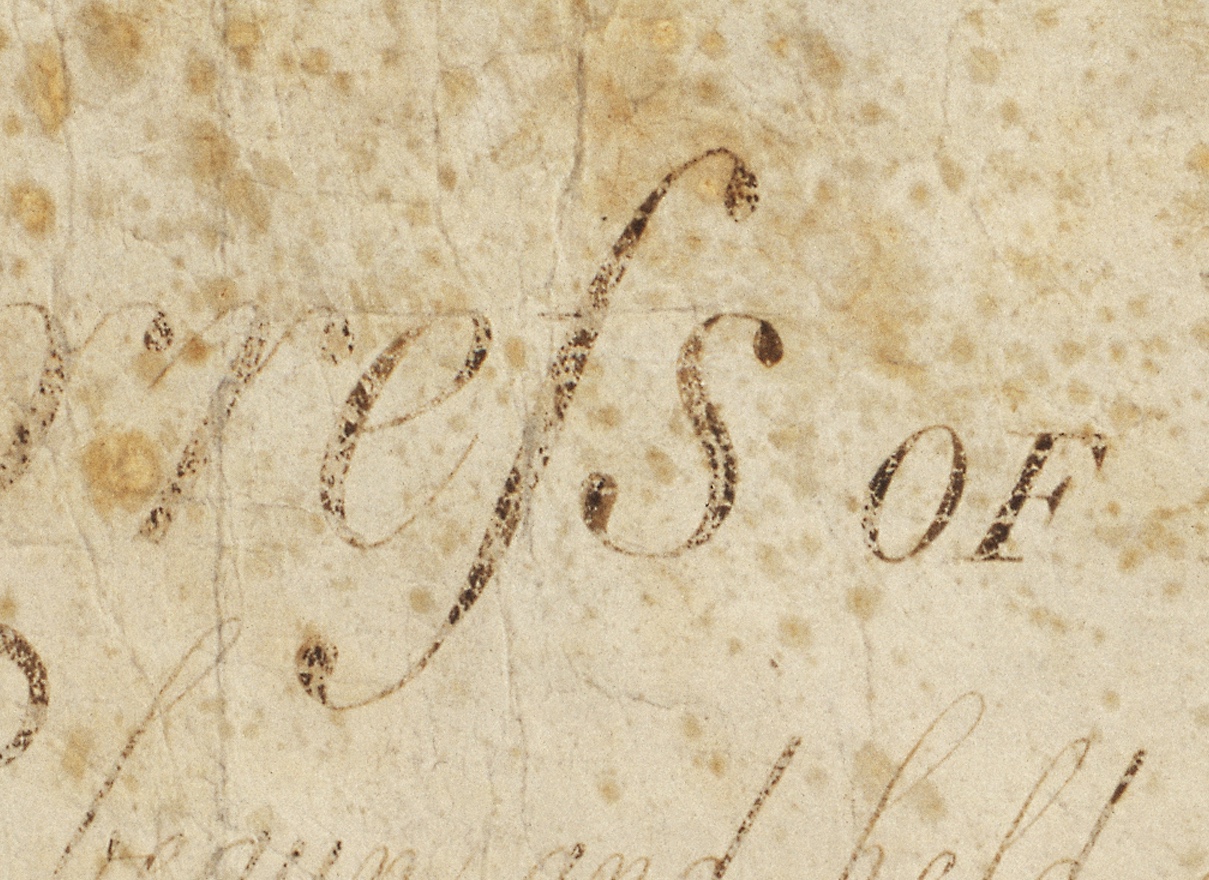|
Lyke Wake Dirge
The "Lyke-Wake Dirge" is a traditional English folk song and dirge listed as number 8194 in the Roud Folk Song Index. The song tells of the soul's travel, and the hazards it faces, on its way from earth to purgatory. Though it is from the Christian era and features references to Christianity, much of the symbolism is thought to be of pre-Christian origin. The title The title refers to the act of watching over the dead between the death and funeral, known as a wake. "Lyke" is an obsolete word meaning a corpse. It is related to other extant Germanic words such as the German , the Dutch and the Norwegian , all meaning "corpse". It survives in modern English in the expression ''lychgate'', the roofed gate at the entrance to a churchyard, where, in former times, a dead body was placed before burial, and the fictional undead monster type lich. "Lyke-wake" could also be from the Norse influence on the Yorkshire dialect: the contemporary Norwegian and Swedish words for "wake" are s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yorkshire Dialect
The Yorkshire dialect (also known as Broad Yorkshire, Tyke, Yorkie or Yorkshire English) is a dialect of English, or continuum of dialects, spoken in the Yorkshire region of Northern England. The dialect has roots in Old English and is influenced by Old Norse. The Yorkshire dialect has faded and faces extinction, but organisations such as The Yorkshire Dialect Society and the East Riding Dialect Society exist to promote its use. The dialect has been represented in classic works of literature such as ''Wuthering Heights'', ''Nicholas Nickleby'' and ''The Secret Garden'', and linguists have documented variations of the dialect since the nineteenth century. In middle of the twentieth century, the Survey of English Dialects collected dozens of valuable recordings of authentic Yorkshire dialects. Early history and written accounts In the fragments of early dialect work, there seems to have been few distinctions across large areas: in the early 14th century, the traditional Northu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brig Of Dread
Brig of Dread or Bridge of Dread is a bridge to Purgatory that a dead soul had to cross. Evil souls fall from the bridge into hell. This is a common afterlife theme found in some form or other in many cultures, such as the Chinvat Bridge of Zoroastrianism and As-Sirāt of Islam. The "Brig o' Dread" is an important element in ''The Lyke-Wake Dirge'', an old Northern English waking song. There is much in that song that seems Germanic heathen. The "Brig o' Dread" is probably related to Bifröst (which probably means "trembling-way") or Gjallarbrú ("resounding-bridge" or "noisy-bridge") which may be the symbolism here rather than the Christian later folk-etymological explanation.John Christopher Atkinson John Christopher Atkinson (1814–1900) was an English author, antiquary, and priest. Life Born on 9 May 1814 at Goldhanger in Essex, where his father was then curate, he was the son of John Atkinson and the grandson of Christopher Atkinson (d. 18 ..., J. R. Smith (1868)''A Glossa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
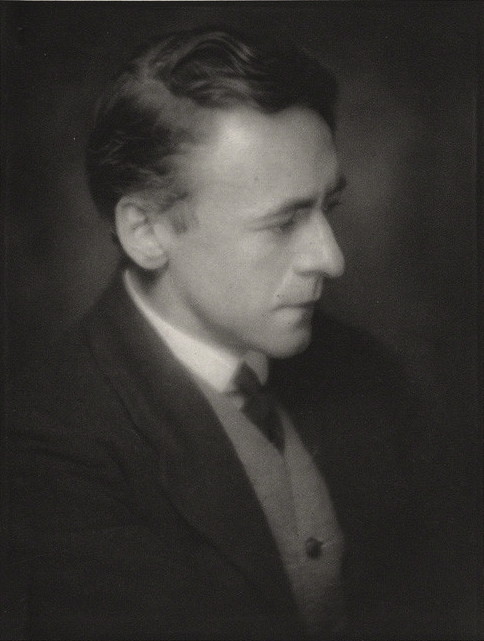
Arnold Bax
Sir Arnold Edward Trevor Bax, (8 November 1883 – 3 October 1953) was an English composer, poet, and author. His prolific output includes songs, choral music, chamber pieces, and solo piano works, but he is best known for his orchestral music. In addition to a series of symphonic poems, he wrote seven symphonies and was for a time widely regarded as the leading British symphonist. Bax was born in the London suburb of Streatham to a prosperous family. He was encouraged by his parents to pursue a career in music, and his private income enabled him to follow his own path as a composer without regard for fashion or orthodoxy. Consequently, he came to be regarded in musical circles as an important but isolated figure. While still a student at the Royal Academy of Music Bax became fascinated with Ireland and Celtic culture, which became a strong influence on his early development. In the years before the First World War he lived in Ireland and became a member of Dublin literary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Gawain And The Green Knight
''Sir Gawain and the Green Knight'' is a late 14th-century chivalric romance in Middle English. The author is unknown; the title was given centuries later. It is one of the best-known Arthurian stories, with its plot combining two types of folk motifs: the beheading game, and the exchange of winnings. Written in stanzas of alliterative verse, each of which ends in a rhyming bob and wheel; it draws on Welsh, Irish, and English stories, as well as the French chivalric tradition. It is an important example of a chivalric romance, which typically involves a hero who goes on a quest which tests his prowess. It remains popular in modern English renderings from J. R. R. Tolkien, Simon Armitage, and others, as well as through film and stage adaptations. The story describes how Sir Gawain, a knight of King Arthur's Round Table, accepts a challenge from a mysterious "Green Knight" who dares any knight to strike him with his axe if he will take a return blow in a year and a day. Gawai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long S
The long s , also known as the medial s or initial s, is an archaism, archaic form of the lowercase letter . It replaced the single ''s'', or one or both of the letters ''s'' in a 'double ''s''' sequence (e.g., "ſinfulneſs" for "sinfulness" and "poſſeſs" or "poſseſs" for "possess"—but never asterisk#Ungrammaticality, *"poſſeſſ"). The modern letterform is known as the 'short', 'terminal', or 'round' s. In typography, it is known as a type of swash letter, commonly referred to as a "swash s". The long s is the basis of the first half of the grapheme of the German alphabet Orthographic ligature, ligature letter , (''eszett'' or [sharp s]). Rules This list of rules for the long s is not exhaustive, and it applies only to books printed during the 17th and 18th centuries in English-speaking countries. Similar rules exist for other European languages. * A round s is always used at the end of a word ending with s: "his", "complains", "ſucceſs" ** However, long s is m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the first and foundational historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP). It traces the historical development of the English language, providing a comprehensive resource to scholars and academic researchers, as well as describing usage in its many variations throughout the world. Work began on the dictionary in 1857, but it was only in 1884 that it began to be published in unbound fascicles as work continued on the project, under the name of ''A New English Dictionary on Historical Principles; Founded Mainly on the Materials Collected by The Philological Society''. In 1895, the title ''The Oxford English Dictionary'' was first used unofficially on the covers of the series, and in 1928 the full dictionary was republished in 10 bound volumes. In 1933, the title ''The Oxford English Dictionary'' fully replaced the former name in all occurrences in its reprinting as 12 volumes with a one-v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
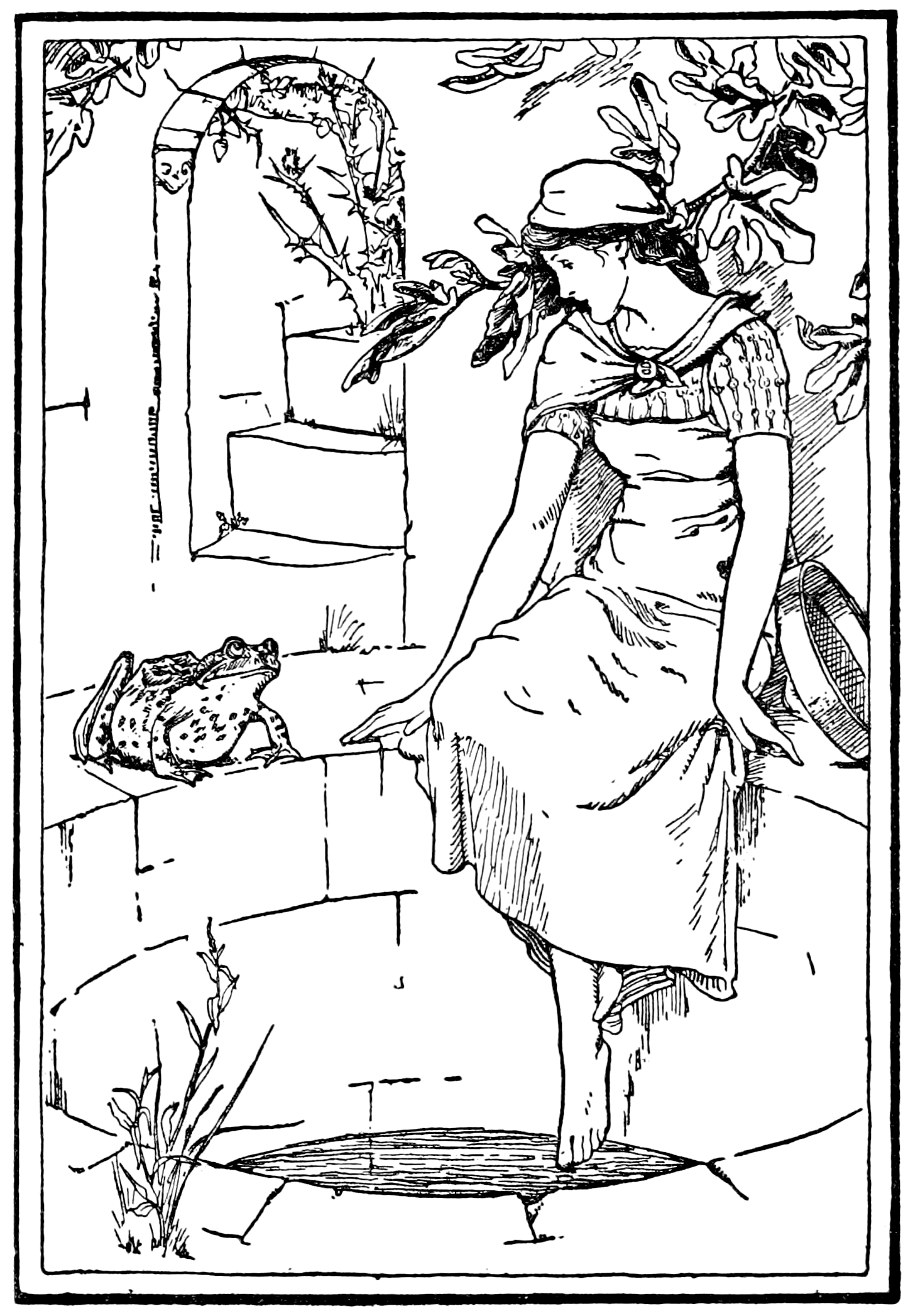
The Well Of The World's End
The Well of the World's End is an Anglo- Scottish Border fairy tale, recorded in the Scottish Lowlands, collected by Joseph Jacobs in ''English Fairy Tales''.Joseph Jacobs, English Fairy Tales', London: David Nutt, 1890 His source was ''The Complaynt of Scotland'', and he notes the tale's similarity to the German ''Frog Prince''. Like that tale, it is Aarne-Thompson type 440, "The Frog King" or "Iron Henry". Synopsis A girl's mother died, and her father remarried. Her stepmother abused her, made her do all the housework, and finally decided to be rid of her. She gave her a sieve and ordered her to not come back without filling it at the Well of the World's End. The girl named Ogawasata set out and questioned everyone about the way. Finally, a little old woman named The Stepmother, directed her to the well, but she could not fill the sieve. She wept. A frog called Kareu asked what was wrong and said it could aid her if she promised to do everything he asked for a dark nig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vernon Hill (sculptor)
Vernon Hill (1887–1972), born in Halifax, Yorkshire, England, was a sculptor, lithographer, illustrator and draughtsman. He began his work in print-making and lithography, and branched out into other artistic forms, such as sculpture. He illustrated several works and created etchings. His more notable works were commissions from Sir Edward Maufe for interior and exterior architectural sculptures on Maufe's buildings, including Guildford Cathedral, the Runnymede Memorial and several churches. He died in 1972. Early life Vernon Hill was born in 1887 in Halifax, Yorkshire. He began formal training in print-making at an early age; at the age 13 he was apprenticed to a lithographer. In about 1908, at the age of 21, Hill moved to London and took up poster illustration, working under John Hassall, a poster designer and illustrator. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hell
In religion and folklore, hell is a location in the afterlife in which evil souls are subjected to punitive suffering, most often through torture, as eternal punishment after death. Religions with a linear divine history often depict hells as eternal destinations, the biggest examples of which are Christianity and Islam, whereas religions with reincarnation usually depict a hell as an intermediary period between incarnations, as is the case in the dharmic religions. Religions typically locate hell in another dimension or under Earth's surface. Other afterlife destinations include heaven, paradise, purgatory, limbo, and the underworld. Other religions, which do not conceive of the afterlife as a place of punishment or reward, merely describe an abode of the dead, the grave, a neutral place that is located under the surface of Earth (for example, see Kur, Hades, and Sheol). Such places are sometimes equated with the English word ''hell'', though a more correct translatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacuna (manuscripts)
A lacuna ( lacunae or lacunas) is a gap in a manuscript, inscription, text, painting, or musical work. A manuscript, text, or section suffering from gaps is said to be "lacunose" or "lacunulose". Weathering, decay, and other damage to old manuscripts or inscriptions are often responsible for lacunae - words, sentences, or whole passages that are missing or illegible. Palimpsests are particularly vulnerable. To reconstruct the original text, the context must be considered. In papyrology and textual criticism, this may lead to competing reconstructions and interpretations. Published texts that contain lacunae often mark the section where text is missing with a bracketed ellipsis. For example, "This sentence contains 20 words, and ..nouns," or, "Finally, the army arrived at ..and made camp." Notable examples See also * Unfinished work Unfinished may refer to: *Unfinished creative work, a work which a creator either chose not to finish or was prevented from finishing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Aubrey
John Aubrey (12 March 1626 – 7 June 1697) was an English antiquary, natural philosopher and writer. He is perhaps best known as the author of the ''Brief Lives'', his collection of short biographical pieces. He was a pioneer archaeologist, who recorded (often for the first time) numerous megalithic and other field monuments in southern England, and who is particularly noted for his systematic examination of the Avebury henge monument. The Aubrey holes at Stonehenge are named after him, although there is considerable doubt as to whether the holes that he observed are those that currently bear the name. He was also a pioneer folklorist, collecting together a miscellany of material on customs, traditions and beliefs under the title "Remaines of Gentilisme and Judaisme". He set out to compile county histories of both Wiltshire and Surrey, although both projects remained unfinished. His "Interpretation of Villare Anglicanum" (also unfinished) was the first attempt to compile a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |