|
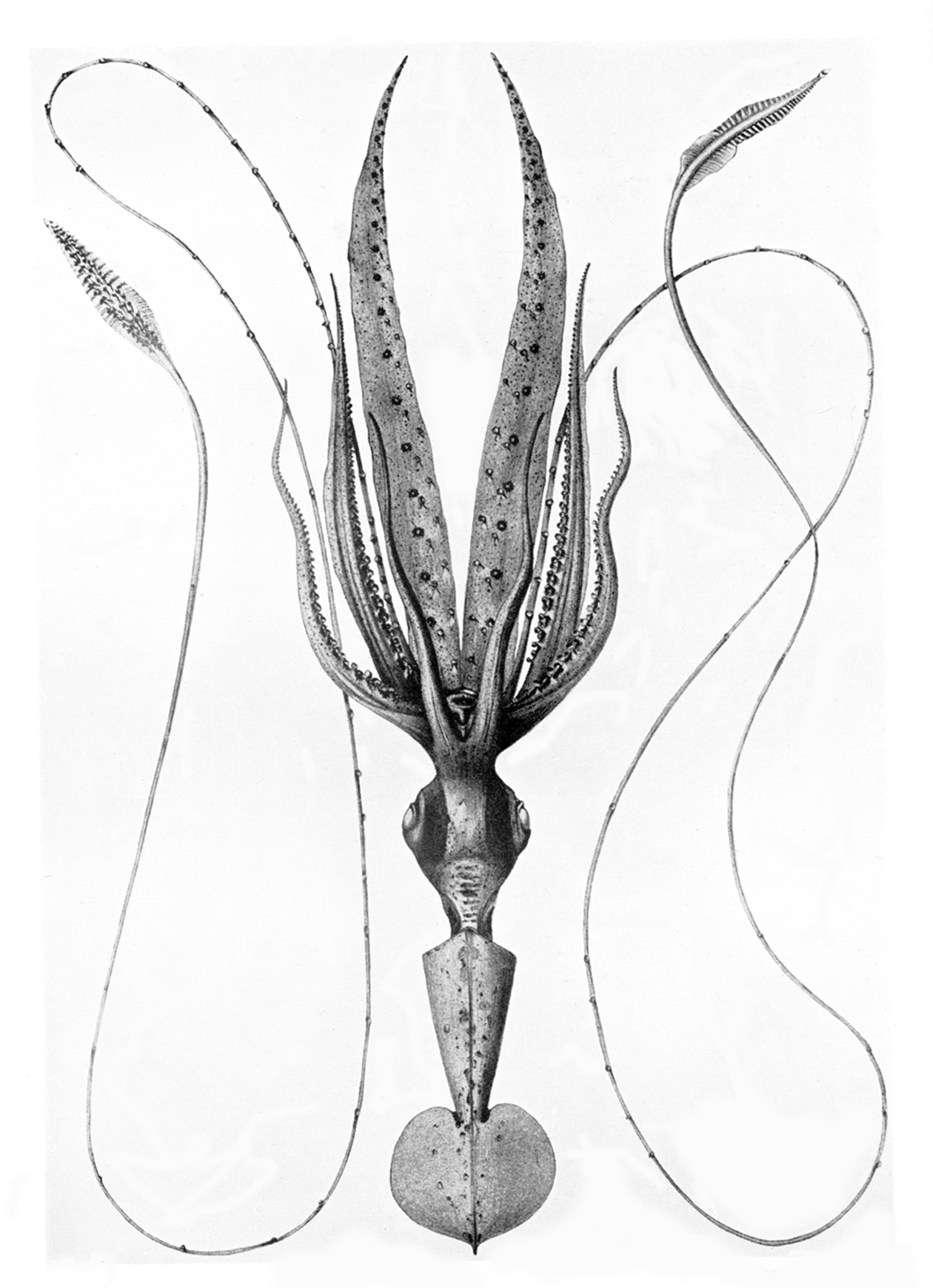
Lycoteuthis Diadema
''Lycoteuthis'' is a genus containing two species of squid: '' Lycoteuthis springeri'' and '' Lycoteuthis lorigera''. They are small animals which grow up to 8 cm in length. These squid live in the deep sea at depths of up to 3000 metres, making horizontal migrations within their range along the steep shelves. ''Lycoteuthis'' are particularly characterised by their photophores, shining organs which give them their German name "Miracle Lamps". The photophores are located in various parts of the body, with males having them on their mantle and head. The light of these photophores results from bioluminescence. The photophores serve as camouflage Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the ..., since the body appears almost transparent by the light effects and normally visibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Chun
Carl Chun (1 October 1852 – 11 April 1914) was a German marine biologist. Chun was born in Höchst, today a part of Frankfurt, and studied zoology at the University of Leipzig, where from 1878 to 1883 he was privat-docent of zoology and an assistant to Rudolf Leuckart. After professorial posts in Königsberg (1883–1891) and Breslau (1891–1898), he returned to Leipzig as a professor of zoology.UNI Leipzig Professorenkatalog (biographical sketch) In 1888, Chun described seasonal vertical migration (SVM) which has a periodicity of ca. 1 year. Chun examined depth-stratified net samples from the |
Camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the battledress of a modern soldier, and the leaf-mimic katydid's wings. A third approach, motion dazzle, confuses the observer with a conspicuous pattern, making the object visible but momentarily harder to locate, as well as making general aiming easier. The majority of camouflage methods aim for crypsis, often through a general resemblance to the background, high contrast disruptive coloration, eliminating shadow, and countershading. In the open ocean, where there is no background, the principal methods of camouflage are transparency, silvering, and countershading, while the ability to produce light is among other things used for counter-illumination on the undersides of cephalopods such as squid. Some animals, such as chameleons and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioluminescence
Bioluminescence is the production and emission of light by living organisms. It is a form of chemiluminescence. Bioluminescence occurs widely in marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some fungi, microorganisms including some bioluminescent bacteria, and terrestrial arthropods such as fireflies. In some animals, the light is bacteriogenic, produced by symbiotic bacteria such as those from the genus ''Vibrio''; in others, it is autogenic, produced by the animals themselves. In a general sense, the principal chemical reaction in bioluminescence involves a light-emitting molecule and an enzyme, generally called luciferin and luciferase, respectively. Because these are generic names, luciferins and luciferases are often distinguished by the species or group, e.g. firefly luciferin. In all characterized cases, the enzyme catalyzes the oxidation of the luciferin. In some species, the luciferase requires other cofactors, such as calcium or magnesium ions, and somet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photophore
A photophore is a glandular organ that appears as luminous spots on various marine animals, including fish and cephalopods. The organ can be simple, or as complex as the human eye; equipped with lenses, shutters, color filters and reflectors, however unlike an eye it is optimized to produce light, not absorb it. The bioluminescence can variously be produced from compounds during the digestion of prey, from specialized mitochondrial cells in the organism called photocytes ("light producing" cells), or, similarly, associated with symbiotic bacteria in the organism that are cultured. The character of photophores is important in the identification of deep sea fishes. Photophores on fish are used for attracting food or for camouflage from predators by counter-illumination. Photophores are found on some cephalopods including the firefly squid, which can create impressive light displays, as well as numerous other deep sea organisms such as the pocket shark Mollisquama mississippien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting these criteria. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius (cephalopod), gladius or pen, made of chitin. Squid diverged from other cephalopods during the Jurassic and occupy a similar role to teleost fish as open water predators of similar size and behaviour. They play an important role in the open water food web. The two long tentacles are used to grab prey and the eight arms to hold and control it. The beak then cuts the food into suitable size chunks for swallowing. Squid are rapid swimmers, moving by Aquatic locomotion#Jet propulsion, jet propulsion, and largely locate their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy Coburn Robson
Guy Coburn Robson (1888–1945) was a British zoologist, specializing in Mollusca, who first named and described '' Mesonychoteuthis hamiltoni'', the colossal squid. Robson studied at the marine biological station in Naples, and joined the staff of the Natural History Museum in 1911, becoming Deputy Keeper of the Zoology Department from 1931 to 1936. Evolution Robson is best known for his major book ''The Variations of Animals in Nature'' (co-authored with O. W. Richards, 1936) which argued that although the fact of evolution is well established, the mechanisms are largely hypothetical and undemonstrated.Allee, W. C. (1937)''The Variation of Animals in Nature: A Critical Summary and Judgment of Evolutionary Theories by G. C. Robson, O. W. Richards'' ''American Journal of Sociology'' 42 (4): 596–597. The book claims that most differences among animal populations and related species are non-adaptive. It was published before major developments in the modern synthesis and contains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycoteuthis Diadema
''Lycoteuthis'' is a genus containing two species of squid: '' Lycoteuthis springeri'' and '' Lycoteuthis lorigera''. They are small animals which grow up to 8 cm in length. These squid live in the deep sea at depths of up to 3000 metres, making horizontal migrations within their range along the steep shelves. ''Lycoteuthis'' are particularly characterised by their photophores, shining organs which give them their German name "Miracle Lamps". The photophores are located in various parts of the body, with males having them on their mantle and head. The light of these photophores results from bioluminescence. The photophores serve as camouflage Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the ..., since the body appears almost transparent by the light effects and normally visibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Johann Pfeffer
Georg Johann Pfeffer (1854–1931) was a German zoologist, primarily a malacologist, a scientist who studies mollusks. Pfeffer was born in Berlin. In 1887 he became curator of the , which was established in 1843 and destroyed during World War II. Pfeffer's published writings were mainly about cephalopods. The World Register of Marine Species database lists 133 marine taxa named by Pfeffer When Pfeffer's name is listed as an authority for a taxon such as the land snail genus '' Lamellaxis'' Strebel & Pfeffer, 1882, his name is ''not'' simply an orthographic error for the more commonly encountered molluscan authority Pfeiffer, i.e. Ludwig Karl Georg Pfeiffer Ludwig Karl Georg Pfeiffer, also known as Louis Pfeiffer (4 July 1805 – 2 October 1877), was a German physician, botanist and conchologist. Early life, Education & Medical Career Louis Pfeiffer was born in Cassel, the eldest son of the jurist ..., who lived 50 years earlier, from 1805 to 1877. Georg Johann Pfeffer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilbert L
Gilbert may refer to: People and fictional characters * Gilbert (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters *Gilbert (surname), including a list of people Places Australia * Gilbert River (Queensland) * Gilbert River (South Australia) Kiribati * Gilbert Islands, a chain of atolls and islands in the Pacific Ocean United States * Gilbert, Arizona, a town * Gilbert, Arkansas, a town * Gilbert, Florida, the airport of Winterhaven * Gilbert, Iowa, a city * Gilbert, Louisiana, a village * Gilbert, Michigan, and unincorporated community * Gilbert, Minnesota, a city * Gilbert, Nevada, ghost town * Gilbert, Ohio, an unincorporated community * Gilbert, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community * Gilbert, South Carolina, a town * Gilbert, West Virginia, a town * Gilbert, Wisconsin, an unincorporated community * Mount Gilbert (other), various mountains * Gilbert River (Oregon) Outer space * Gilbert (lunar crater) * Gilbert (Martian crater) Arts a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycoteuthis Springeri
''Lycoteuthis springeri'' is a small species of rarely captured squid from the family Lycoteuthidae. It has three photophores on the posterior portion of the abdomen and the males have a long tail which bears seven deeply embedded long and thin photophores. The males also have photophores on arms II and III, as well as on the head and the mantle. The tentacular clubs and the structure of the suckers on the club and arm are not distinctive. Two of the known specimens were males which had mantle lengths of 80mm and 97mm. The type locality was in the Gulf of Mexico and the holotype A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several ... was found in the stomach of a shark which was captured at 367m. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q2760626 Squid Molluscs described in 1956 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)