|
Lunar Orbiter 5
Lunar Orbiter 5, the last of the " Lunar Orbiter series", was designed to take additional Apollo and Surveyor landing site photography and to take broad survey images of unphotographed parts of the Moon's far side. It was also equipped to collect selenodetic, radiation intensity, and micrometeoroid impact data and was used to evaluate the Manned Space Flight Network tracking stations and Apollo Orbit Determination Program. Mission Summary The spacecraft was placed in a cislunar trajectory and on August 5, 1967 was injected into an elliptical near polar lunar orbit with an inclination of 85 degrees and a period of 8 hours 30 minutes. On August 7 the perilune was lowered to , and on August 9 the orbit was lowered to a , 3 hour 11 minute period. The spacecraft acquired photographic data from August 6 to 18, 1967, and readout occurred until August 27, 1967. A total of 633 high resolution and 211 medium resolution frames at resolution down to were acquired, bringing the cumulati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LOIRP
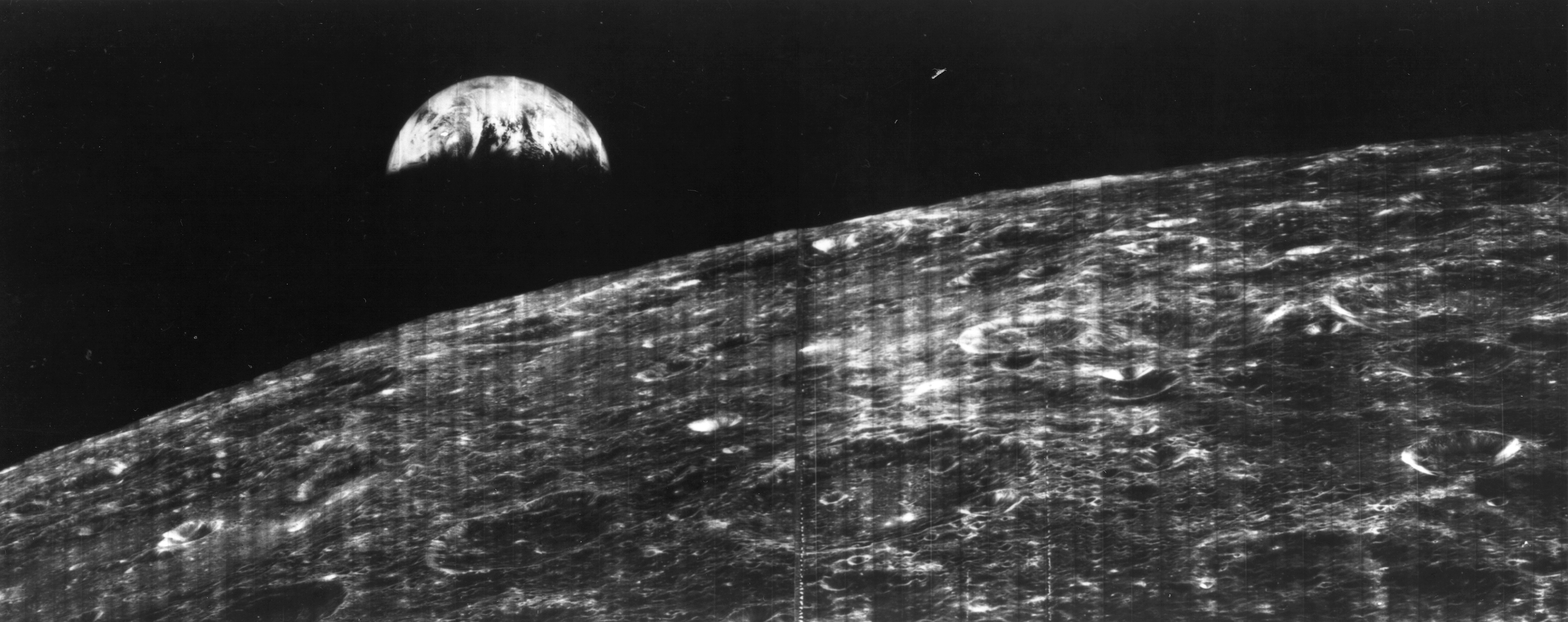
The Lunar Orbiter Image Recovery Project (LOIRP) is a project to digitize the original analog data tapes from the five Lunar Orbiter spacecraft that were sent to the Moon in 1966 and 1967; it is funded by NASA, SkyCorp, SpaceRef Interactive, and private individuals. The first image to be successfully recovered by the project was released in November 2008. It was the first photograph of the Earth from the Moon, taken in August 1966. On February 20, 2014, the project announced it had completed the primary tape capture portion of the project. One medium resolution image, most of one high resolution image and parts of three others are missing, apparently due to lapses at the time they were being recorded. The rest of the Lunar Orbiter images have been successfully recovered and have been published in NASA's Planetary Data System. Background The images taken by the Lunar Orbiter spacecraft were primarily used to locate landing sites for the manned Apollo missions. Once those m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trajectory
A trajectory or flight path is the path that an object with mass in motion follows through space as a function of time. In classical mechanics, a trajectory is defined by Hamiltonian mechanics via canonical coordinates; hence, a complete trajectory is defined by position and momentum, simultaneously. The mass might be a projectile or a satellite. For example, it can be an orbit — the path of a planet, asteroid, or comet as it travels around a central mass. In control theory, a trajectory is a time-ordered set of states of a dynamical system (see e.g. Poincaré map). In discrete mathematics, a trajectory is a sequence (f^k(x))_ of values calculated by the iterated application of a mapping f to an element x of its source. Physics of trajectories A familiar example of a trajectory is the path of a projectile, such as a thrown ball or rock. In a significantly simplified model, the object moves only under the influence of a uniform gravitational force field. This c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
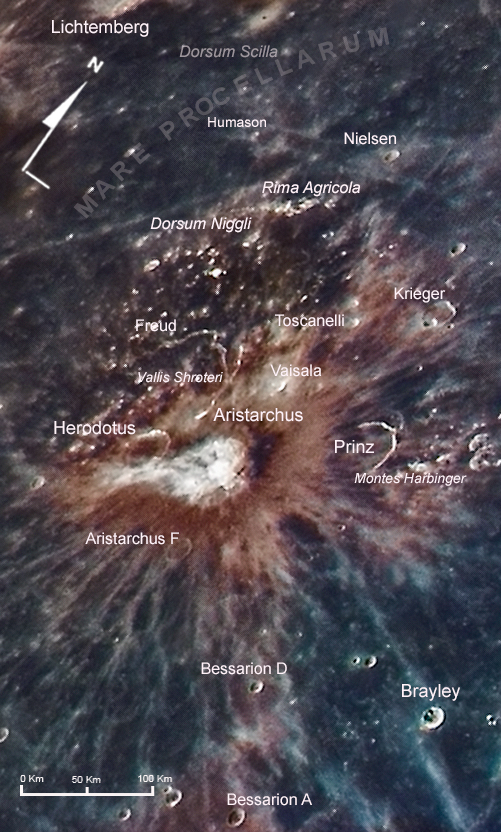
Schroter's Valley
Schroter's Valley, frequently known by the Latinized name Vallis Schröteri, is a sinuous valley or rille on the surface of the near side of the Moon. It is located on a rise of continental ground, sometimes called the Aristarchus plateau, that is surrounded by the Oceanus Procellarum to the south and west and the Mare Imbrium to the northwest. At the southern edge of this rise are the craters Aristarchus and Herodotus. This is the largest sinuous rille on the Moon. It begins at a 6 km diameter crater located 25 km to the north of Herodotus. (The start of the rille has been termed the "Cobra's Head" by some observers, due to its resemblance to a snake.) From the crater it follows a meandering path, first to the north, then setting a course toward the northwest, before finally bending back to the south until it reaches a 1 km high precipice at the edge of the Oceanus Procellarum. The rille has a maximum width of about 10 km, then gradually narrows to less ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
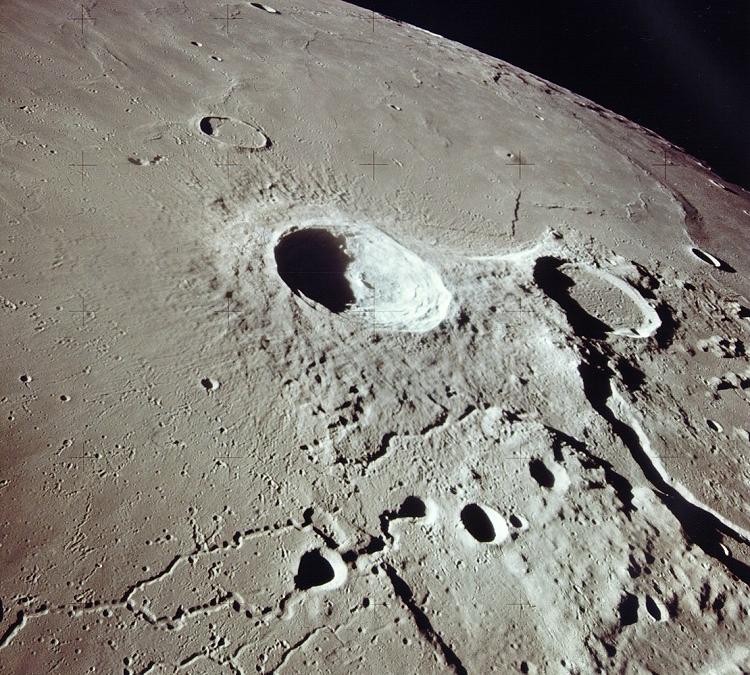
Aristarchus (crater)
Aristarchus is a lunar impact crater that lies in the northwest part of the Moon's near side. It is considered the brightest of the large formations on the lunar surface, with an albedo nearly double that of most lunar features. The feature is bright enough to be visible to the naked eye, and displays unusually bright features when viewed through a large telescope. It is also readily identified when most of the lunar surface is illuminated by earthshine. The crater is deeper than the Grand Canyon. The crater is named after the Greek astronomer Aristarchus of Samos. It is located at the southeastern edge of the Aristarchus plateau, an elevated area that contains a number of volcanic features, such as sinuous rilles. This area is also noted for the large number of reported transient lunar phenomena, as well as recent emissions of radon gas as measured by the Lunar Prospector spacecraft. Selenography Aristarchus is located on the Aristarchus plateau, an elevated rocky ris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prinz (crater)
Prinz is the lava-flooded remains of a lunar impact crater on the Oceanus Procellarum. It was named after German-Belgian astronomer . The formation lies to the southwest of the prominent crater Aristarchus. To the north-northeast is the flooded crater Krieger. The rim of Prinz is the most intact in its northeastern half, while a large gap exists in the southern end of the crater wall. The rim climbs to a maximum height of 1.0 km above the base. It is attached along the eastern rim by a low ridge that is part of the foothills of the small Montes Harbinger Montes Harbinger is an isolated cluster of lunar mountains at the western edge of the Mare Imbrium basin. The mountains consist of four primary ridges plus several smaller hills, each forming a small rise surrounded by the lunar mare. The clus ... range to the northeast. The region of the mare about Prinz is marked by rays and secondary craters from Aristarchus. Rimae Prinz Just to the north of Prinz is a syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mons Gruithuisen Gamma
Mons Gruithuisen Gamma (γ) is a lunar dome that lies to the north of the crater Gruithuisen at the western edge of the Mare Imbrium. This massif is shaped as a rounded dome in the surface, occupying a diameter of 20 km and climbing gently to a height of over 1500 meters. At the crest is a small crater. This formation appears foreshortened when viewed from the Earth, and it has been described by Antonin Rukl as resembling an "upturned bathtub". To the east lies the similar Mons Gruithuisen Delta (δ). Together they are often informally called the Gruithuisen domes. See also * List of mountains on the Moon by height * Volcanism on the Moon References External links Gruithuisen Domes - Constellation Region of Interest Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter article New Views of the Gruithuisen Domes Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) is a NASA robotic spacecraft currently orbiting the Moon in an eccentric polar mapping orbit. Data col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitello (crater)
Vitello is a lunar impact crater that lies along the southern edge of the small Mare Humorum, in the southwest part of the Moon's near side. It was named after 13th century Polish theologian and physicist Vitello. It lies just to the east of the lava-flooded crater Lee. To the northeast along the edge of the lunar mare is the Rupes Kelvin, an irregular fault line. Description This crater has a low, roughly circular rim with a sharp edge. The interior floor is irregular, rugged and hilly, with a ring of deep fractures surrounding the central peak. A low ridge projects out from the northwest rim into the mare. Vitello was once believed to be a caldera A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ... rather than an impact crater. In ''To A Rocky Moon'', lunar geologist Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gassendi (crater)
Gassendi is a large lunar impact crater feature located at the northern edge of Mare Humorum. It was named after French astronomer Pierre Gassendi. The formation has been inundated by lava during the formation of the mare, so only the rim and the multiple central peaks remain above the surface. The outer rim is worn and eroded, although it retains a generally circular form. A smaller crater – Gassendi A – intrudes into the northern rim, and joins a rough uplift at the northwest part of the floor. The crater pair bear a curious resemblance to a diamond ring. In the southern part of the crater floor is a semi-circular ridge-like formation that is concentric with the outer rim. It is in the southern part where the rim dips down to its lowest portion, and a gap appears at the most southern point. The rim varies in height from as little as 200 meters to as high as 2.5 kilometers above the surface. The floor has numerous hummocks and rough spots. There is also a system of ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copernicus (lunar Crater)
Copernicus is a lunar impact crater located in eastern Oceanus Procellarum. It was named after the astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus. It typifies craters that formed during the Copernican period in that it has a prominent ray system. It may have been created by debris from the breakup of the parent body of asteroid 495 Eulalia 800 million years ago. Characteristics Copernicus is visible using binoculars, and is located slightly northwest of the center of the Moon's Earth-facing hemisphere. South of the crater is the Mare Insularum, and to the south-south west is the crater Reinhold. North of Copernicus are the Montes Carpatus, which lie at the south edge of Mare Imbrium. West of Copernicus is a group of dispersed lunar hills. Due to its relative youth, the crater has remained in a relatively pristine shape since it formed. The circular rim has a discernible hexagonal form, with a terraced inner wall and a 30 km wide, sloping rampart that descends nearly a kilometer to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tycho (crater)
Tycho () is a prominent lunar impact crater located in the southern lunar highlands, named after the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe (1546–1601)., accessed 19 February 2019 It is estimated to be 108 million years old. To the south of Tycho is the crater Street, to the east is Pictet, and to the north-northeast is Sasserides. The surface around Tycho is replete with craters of various sizes, many overlapping still older craters. Some of the smaller craters are secondary craters formed from larger chunks of ejecta from Tycho. It is one of the Moon's brightest craters, with a diameter of and a depth of . Age and description Tycho is a relatively young crater, with an estimated age of 108 million years ( Ma), based on analysis of samples of the crater ray recovered during the Apollo 17 mission. This age initially suggested that the impactor may have been a member of the Baptistina family of asteroids, but as the composition of the impactor is unknown this remained conjecture. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messier (crater)
Messier is a relatively young lunar impact crater located on the Mare Fecunditatis. The crater has a discernible oblong shape that is not caused by foreshortening. The longer dimension is oriented in an east–west direction. Just to the west lies Messier A, a similar-sized crater with an oblong, doublet form. The longer dimension of this crater is oriented north–south, at right angles to Messier. This crater also has a curved bulge extending to the west. Messier and Messier A were photographed at high resolution by NASA's Lunar Orbiter 5 spacecraft In August 1967. The Lunar Orbiter V_041 image is archived at the Lunar and Planetary Institutebr>website The Lunar Orbiter V partial image shown here is derived from the Lunar Orbiter Image Recovery Project effort to reprocess these images from the original tapes. The interiors of Messier and Messier A have a higher albedo than the surrounding mare. There is also a dark streak in the center of each crater. Two prominent, nearly lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyginus (crater)
Hyginus is a lunar caldera located at the east end of the Sinus Medii. It was named after ancient Roman astronomer Gaius Julius Hyginus. Its rim is split by a 220 kilometer-long rille, Rima Hyginus, that branches to the northwest and to the east-southeast. The crater is deeper than the rille, and lies at intersection of the rille's branches. Together, the crater and the rille form a prominent feature in an otherwise flat surface. Smaller craters along the length of the rille may have been caused by the collapse of an underlying structure. Hyginus is one of the few craters on the Moon that was not created as a result of an impact, and is instead believed to be volcanic in origin. It lacks the raised outer rim that is typical with impact craters. Hyginus was considered a possible landing site during the Apollo Program, because it was thought to be a site of potentially active volcanism. The landing point would have been northwest of the crater, within a few kilometers of the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |