|
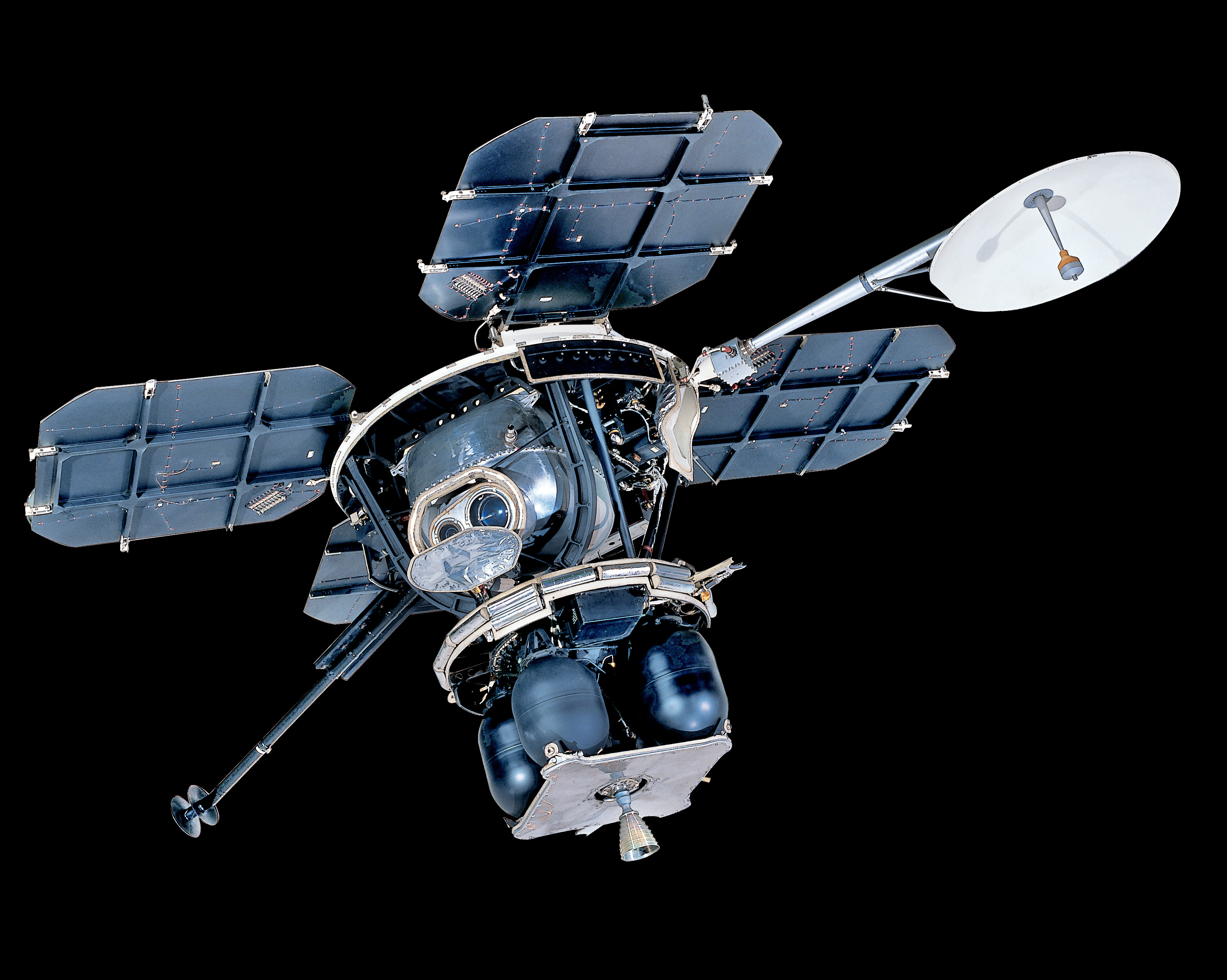
Luna 11
Luna 11 (E-6LF series) was an uncrewed space mission of the Soviet Union's Luna program. It was also called Lunik 11. Luna 11 was launched towards the Moon from an Earth-orbiting platform and entered lunar orbit on 27 August 1966. Overview The objectives of the mission included the study of: * lunar gamma and X-ray emissions in order to determine the Moon's chemical composition; * lunar gravitational anomalies; * the concentration of meteorite streams near the Moon; * the intensity of hard corpuscular radiation near the Moon. 137 radio transmissions and 277 orbits of the Moon were completed before the batteries failed on 1 October 1966. This subset of the "second-generation" Luna spacecraft, the E-6LF, was designed to take the first photographs of the surface of the Moon from lunar orbit. A secondary objective was to obtain data on mass concentrations ("mascons") on the Moon first detected by Luna 10. Using the Ye-6 bus, a suite of scientific instruments (plus an imaging sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NPO Lavochkin
NPO Lavochkin (russian: НПО Лавочкина, OKB-301, also called Lavochkin Research and Production Association or shortly Lavochkin Association, LA) is a Russian aerospace company. It is a major player in the Russian space program, being the developer and manufacturer of the Fregat upper stage, as well as interplanetary probes such as Fobos-Grunt. As of 2015, it was headed by Sergei Lemeshevskii. On August 10, 2017 the Lavochkin Association's Board of Directors appointed Vladimir Kolmykov Director General of the enterprise. Overview The company develops and manufactures spacecraft such as the Fregat rocket upper stages, satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a contractor for a number of military programs, such as the Oko early warning satellite, Prognoz and Araks programmes as well as the civilian program Kupon. One of the company's most notable projects was the participation in the failed Fobos-Grunt sample return mission. NPO Lavochkin has also developed the Elektr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luna Program
The Luna programme (from the Russian word "Luna" meaning "Moon"), occasionally called ''Lunik'' by western media, was a series of robotic spacecraft missions sent to the Moon by the Soviet Union between 1959 and 1976. Fifteen were successful, each designed as either an orbiter or lander, and accomplished many firsts in space exploration. They also performed many experiments, studying the Moon's chemical composition, gravity, temperature, and radiation. Twenty-four spacecraft were formally given the Luna designation, although more were launched. Those that failed to reach orbit were not publicly acknowledged at the time, and not assigned a Luna number. Those that failed in low Earth orbit were usually given Cosmos designations. The estimated cost of the Luna programme in 1964 was US$6–10 billion. Mission types The name ''Luna'' was used to designate a variety of spacecraft designs, to achieve several types of missions: Impactors Impactor spacecraft are designed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Launched By Molniya-M Rockets
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1966 In The Soviet Union
The following lists events that happened during 1966 in the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. Incumbents * General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union: Leonid Brezhnev (1964-1982) * Premier of the Soviet Union: Alexei Kosygin (1964–1980) Events February * February 3 – The unmanned Soviet Luna 9 spacecraft makes the first controlled rocket-assisted landing on the Moon. * February 10 – Soviet fiction writers Yuli Daniel and Andrei Sinyavsky are sentenced to five and seven years, respectively, for "anti-Soviet" writings. * February 20 – While Soviet author and translator Valery Tarsis is abroad, the Soviet Union negates his citizenship. March * March 1 - Soviet space probe ''Venera 3'' crashes on Venus, becoming the first spacecraft to land on another planet's surface. * March 29 – The 23rd Congress of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union is held: Leonid Brezhnev demands that U.S. troops leave Vietnam, and announces that Chinese-Soviet relations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Launched In 1966
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luna Programme
The Luna programme (from the Russian word "Luna" meaning "Moon"), occasionally called ''Lunik'' by western media, was a series of robotic spacecraft missions sent to the Moon by the Soviet Union between 1959 and 1976. Fifteen were successful, each designed as either an orbiter or lander, and accomplished many firsts in space exploration. They also performed many experiments, studying the Moon's chemical composition, gravity, temperature, and radiation. Twenty-four spacecraft were formally given the Luna designation, although more were launched. Those that failed to reach orbit were not publicly acknowledged at the time, and not assigned a Luna number. Those that failed in low Earth orbit were usually given Cosmos designations. The estimated cost of the Luna programme in 1964 was US$6–10 billion. Mission types The name ''Luna'' was used to designate a variety of spacecraft designs, to achieve several types of missions: Impactors Impactor spacecraft are designed to h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Orbiter
The Lunar Orbiter program was a series of five uncrewed lunar orbiter missions launched by the United States from 1966 through 1967. Intended to help select Apollo landing sites by mapping the Moon's surface, they provided the first photographs from lunar orbit and photographed both the Moon and Earth. All five missions were successful, and 99 percent of the lunar surface was mapped from photographs taken with a resolution of or better. The first three missions were dedicated to imaging 20 potential crewed lunar landing sites, selected based on Earth-based observations. These were flown at low-inclination orbits. The fourth and fifth missions were devoted to broader scientific objectives and were flown in high-altitude polar orbits. Lunar Orbiter 4 photographed the entire nearside and nine percent of the far side, and Lunar Orbiter 5 completed the far side coverage and acquired medium () and high () resolution images of 36 preselected areas. All of the Lunar Orbiter spacecraft w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zond 3
Zond 3 was a 1965 space probe which performed a flyby of the Moon far side, taking a number of quality photographs for its time. It was a member of the Soviet Zond program while also being part of the Mars 3MV project. It was unrelated to Zond spacecraft designed for manned circumlunar missions ( Soyuz 7K-L1). It is believed that Zond 3 was initially designed as a companion spacecraft to Zond 2 to be launched to Mars during the 1964 launch window. The opportunity to launch was missed, and the spacecraft was launched on a Mars-crossing trajectory as a spacecraft test, even though Mars was no longer attainable. Spacecraft design The spacecraft was of the 3MV-4 type, similar to Zond 2. In addition to a 106.4 mm focal length imaging system for visible light photography and ultraviolet spectrometry at 285-355 μm, it carried ultraviolet (190-275 μm) and infrared (3-4 μm) spectrophotometers, radiation sensors ( gas-discharge and scintillation counters), charged particle dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luna 10
Luna 10 (or Lunik 10) was a 1966 Soviet lunar robotic spacecraft mission in the Luna program. It was the first artificial satellite of the Moon. Luna 10 conducted extensive research in lunar orbit, gathering important data on the strength of the Moon's magnetic field, its radiation belts, and the nature of lunar rocks (which were found to be comparable to terrestrial basalt rocks), cosmic radiation, and micrometeoroid density. Perhaps its most important finding was the first evidence of mass concentrations (called "mascons") — areas of high density below the mare basins that distort lunar orbital trajectories. Their discovery has usually been credited to the American Lunar Orbiter series. The spacecraft Part of the ''E-6S'' series, Luna 10 was battery powered and had an on-orbit dry mass of 540 kg. Scientific instruments included a gamma-ray spectrometer for energies between 0.3–3 MeV (50–500 pJ), a triaxial magnetometer, a meteorite detector, instrum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
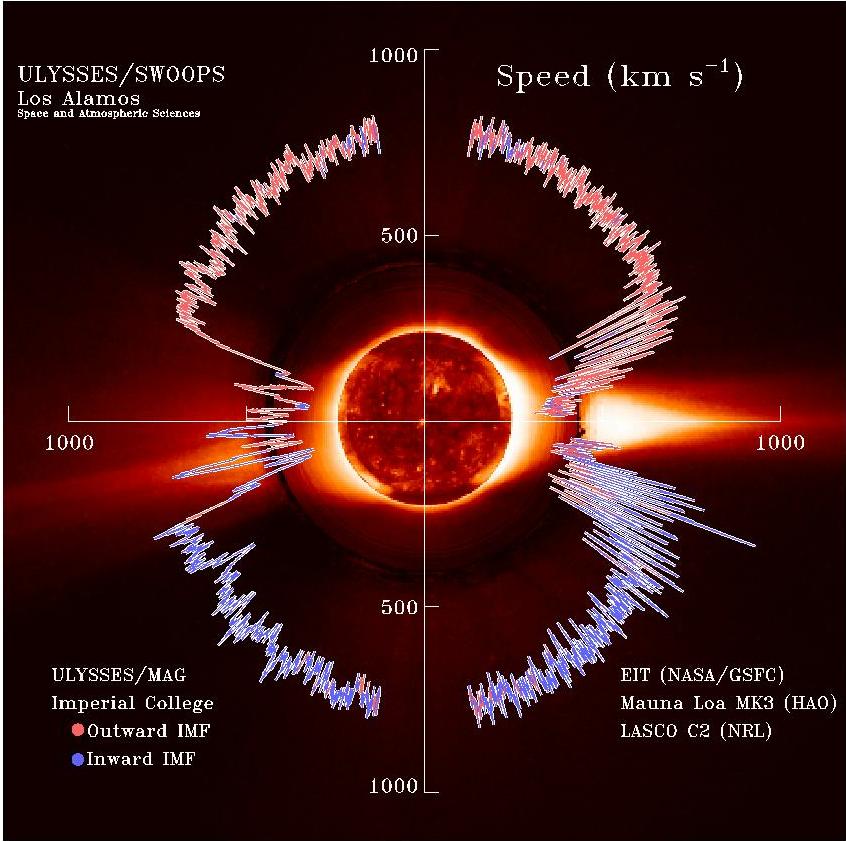
Corpuscular Radiation
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of materials found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei such as C, N, O, Ne, Mg, Si, S, and Fe. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as P, Ti, Cr, 54Fe and 56Fe, and 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field. The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface. At a distance o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |