|
Luca Comai
Luca Comai is an Italian plant biologist whose work has focused on trait discovery for improving agricultural crops and on developing protocols and systems for identifying new genes and mutations in plants. Through his work at Calgene, Comai was one of the first discoverers of the glyphosate resistance gene and is considered a pioneer in the field of plant biotechnology research. His research since then has focused on developing the Targeting Induced Local Lesions in Genomes ( TILLING) protocol that allows for new mutations and traits to be quickly identified within a target plant species through genome and sequence analysis. He has received a number of research and teaching awards, along with being named a Fellow for the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). In 2023, he was elected to the National Academy of Sciences. Education Comai received his bachelor's degree in agricultural sciences from the University of Bologna in 1976 and his Master's deg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Pathology
Plant pathology (also phytopathology) is the scientific study of diseases in plants caused by pathogens (infectious organisms) and environmental conditions (physiological factors). Organisms that cause infectious disease include fungus, fungi, oomycetes, bacterium, bacteria, plant virus, viruses, viroids, virus-like organisms, phytoplasmas, protozoa, nematodes and parasitic plants. Not included are ectoparasites like insects, mites, vertebrate, or other Plant defense against herbivory, pests that affect plant health by eating Plant tissue, plant tissues. Plant pathology also involves the study of pathogen identification, disease etiology, disease cycles, economic impact, plant disease epidemiology, plant disease resistance, how plant diseases affect humans and animals, pathosystem genetics, and management of plant diseases. Overview Control of plant diseases is crucial to the reliable production of food, and it provides significant problems in agricultural use of land, wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bachelor's Degree
A bachelor's degree (from Middle Latin ''baccalaureus'') or baccalaureate (from Modern Latin ''baccalaureatus'') is an undergraduate academic degree awarded by colleges and universities upon completion of a course of study lasting three to six years (depending on institution and academic discipline). The two most common bachelor's degrees are the Bachelor of Arts (BA) and the Bachelor of Science (BS or BSc). In some institutions and educational systems, certain bachelor's degrees can only be taken as graduate or postgraduate educations after a first degree has been completed, although more commonly the successful completion of a bachelor's degree is a prerequisite for further courses such as a master's or a doctorate. In countries with qualifications frameworks, bachelor's degrees are normally one of the major levels in the framework (sometimes two levels where non-honours and honours bachelor's degrees are considered separately). However, some qualifications titled bachelor's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmonella
''Salmonella'' is a genus of rod-shaped (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two species of ''Salmonella'' are ''Salmonella enterica'' and ''Salmonella bongori''. ''S. enterica'' is the type species and is further divided into six subspecies that include over 2,600 serotypes. ''Salmonella'' was named after Daniel Elmer Salmon (1850–1914), an American veterinary surgeon. ''Salmonella'' species are non-spore-forming, predominantly motile enterobacteria with cell diameters between about 0.7 and 1.5 μm, lengths from 2 to 5 μm, and peritrichous flagella (all around the cell body, allowing them to move). They are chemotrophs, obtaining their energy from oxidation and reduction reactions, using organic sources. They are also facultative anaerobes, capable of generating ATP with oxygen ("aerobically") when it is available, or using other electron acceptors or fermentation ("anaerobically") when oxygen is not available. ''Salmonella'' spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EPSP Synthase
5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate (EPSP) synthase is an enzyme produced by plants and microorganisms. EPSPS catalyzes the chemical reaction: : phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) + 3-phospho shikimate (S3P) phosphate + 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate (EPSP) Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and 3-phosphoshikimate, whereas its two products are phosphate and 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate. This enzyme is not present in animals. It presents an attractive biological target for herbicides, such as glyphosate. A glyphosate-resistant version of this gene has been used in genetically modified crops. Nomenclature The enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, to be specific those transferring aryl or alkyl groups other than methyl groups. The systematic name of this enzyme class is phosphoenolpyruvate:3-phosphoshikimate 5-''O''-(1-carboxyvinyl)-transferase. Other names in common use include: * 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase, * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press A university press is an academic publishing house specializing in monographs and scholarly journals. Most are nonprofit organizations and an integral component of a large research university. They publish work that has been reviewed by schola ... in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basic Books
Basic Books is a book publisher founded in 1950 and located in New York, now an imprint of Hachette Book Group. It publishes books in the fields of psychology, philosophy, economics, science, politics, sociology, current affairs, and history. History Basic Books originated as a small Greenwich Village-based book club marketed to psychoanalysts. Arthur Rosenthal took over the book club in 1950, and under his ownership it soon began producing original books, mostly in the behavioral sciences. Early successes included Ernest Jones's ''The Life and Work of Sigmund Freud'', as well as works by Claude Lévi-Strauss, Jean Piaget and Erik Erikson. Irving Kristol joined Basic Books in 1960, and helped Basic to expand into the social sciences. Harper & Row purchased the company in 1969. In 1997, HarperCollins announced that it would merge Basic Books into its trade publishing program, effectively closing the imprint and ending its publishing of serious academic books. That same year, Bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California, Riverside
The University of California, Riverside (UCR or UC Riverside) is a public land-grant research university in Riverside, California. It is one of the ten campuses of the University of California system. The main campus sits on in a suburban district of Riverside with a branch campus of in Palm Desert. In 1907, the predecessor to UCR was founded as the UC Citrus Experiment Station, Riverside which pioneered research in biological pest control and the use of growth regulators responsible for extending the citrus growing season in California from four to nine months. Some of the world's most important research collections on citrus diversity and entomology, as well as science fiction and photography, are located at Riverside. UCR's undergraduate College of Letters and Science opened in 1954. The Regents of the University of California declared UCR a general campus of the system in 1959, and graduate students were admitted in 1961. To accommodate an enrollment of 21,000 stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
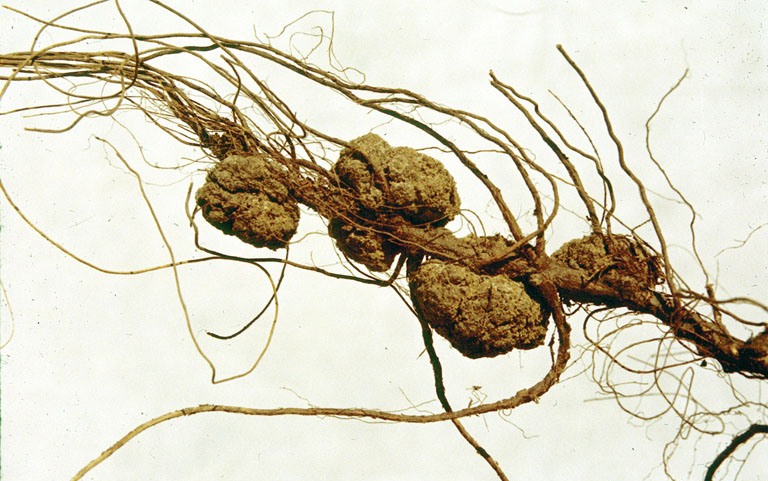
Agrobacterium
''Agrobacterium'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria established by H. J. Conn that uses horizontal gene transfer to cause tumors in plants. ''Agrobacterium tumefaciens'' is the most commonly studied species in this genus. ''Agrobacterium'' is well known for its ability to transfer DNA between itself and plants, and for this reason it has become an important tool for genetic engineering. Nomenclatural History Leading up to the 1990s, the genus ''Agrobacterium'' was used as a wastebasket taxon. With the advent of 16S sequencing, many ''Agrobacterium'' species (especially the marine species) were reassigned to genera such as ''Ahrensia'', ''Pseudorhodobacter'', ''Ruegeria'', and ''Stappia''. The remaining ''Agrobacterium'' species were assigned to three biovars: biovar 1 (''Agrobacterium tumefaciens''), biovar 2 (''Agrobacterium rhizogenes''), and biovar 3 (''Agrobacterium vitis''). In the early 2000s, ''Agrobacterium'' was synonymized with the genus ''Rhizobium''. This move pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-DNA
The transfer DNA (abbreviated T-DNA) is the transferred DNA of the tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmid of some species of bacteria such as ''Agrobacterium tumefaciens'' and ''Agrobacterium rhizogenes(actually an Ri plasmid)''. The T-DNA is transferred from bacterium into the host plant's nuclear DNA genome. The capability of this specialized tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmid is attributed to two essential regions required for DNA transfer to the host cell. The T-DNA is bordered by 25-base-pair repeats on each end. Transfer is initiated at the right border and terminated at the left border and requires the ''vir'' genes of the Ti plasmid. The bacterial T-DNA is about 24,000 base pairs long and contains plant-expressed genes that code for enzymes synthesizing opines and phytohormones. By transferring the T-DNA into the plant genome, the bacterium essentially reprograms the plant cells to grow into a tumor and produce a unique food source for the bacteria. The synthesis of the plant hormones auxin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Homology
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal (or lateral) gene transfer event (xenologs). Homology among DNA, RNA, or proteins is typically inferred from their nucleotide or amino acid sequence similarity. Significant similarity is strong evidence that two sequences are related by evolutionary changes from a common ancestral sequence. Alignments of multiple sequences are used to indicate which regions of each sequence are homologous. Identity, similarity, and conservation The term "percent homology" is often used to mean "sequence similarity”, that is the percentage of identical residues (''percent identity''), or the percentage of residues conserved with similar physicochemical properties (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indole-3-acetic Acid
Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA, 3-IAA) is the most common naturally occurring plant hormone of the auxin class. It is the best known of the auxins, and has been the subject of extensive studies by plant physiologists. IAA is a derivative of indole, containing a carboxymethyl substituent. It is a colorless solid that is soluble in polar organic solvents. Biosynthesis IAA is predominantly produced in cells of the apex (bud) and very young leaves of a plant. Plants can synthesize IAA by several independent biosynthetic pathways. Four of them start from tryptophan, but there is also a biosynthetic pathway independent of tryptophan. Plants mainly produce IAA from tryptophan through indole-3-pyruvic acid. IAA is also produced from tryptophan through indole-3-acetaldoxime in ''Arabidopsis thaliana''. In rats, IAA is a product of both endogenous and colonic microbial metabolism from dietary tryptophan along with tryptophol. This was first observed in rats infected by ''Trypanosoma bruc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postdoc
A postdoctoral fellow, postdoctoral researcher, or simply postdoc, is a person professionally conducting research after the completion of their doctoral studies (typically a PhD). The ultimate goal of a postdoctoral research position is to pursue additional research, training, or teaching in order to have better skills to pursue a career in academia, research, or any other field. Postdocs often, but not always, have a temporary academic appointment, sometimes in preparation for an academic faculty position. They continue their studies or carry out research and further increase expertise in a specialist subject, including integrating a team and acquiring novel skills and research methods. Postdoctoral research is often considered essential while advancing the scholarly mission of the host institution; it is expected to produce relevant publications in peer-reviewed academic journals or conferences. In some countries, postdoctoral research may lead to further formal qualificati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)