|
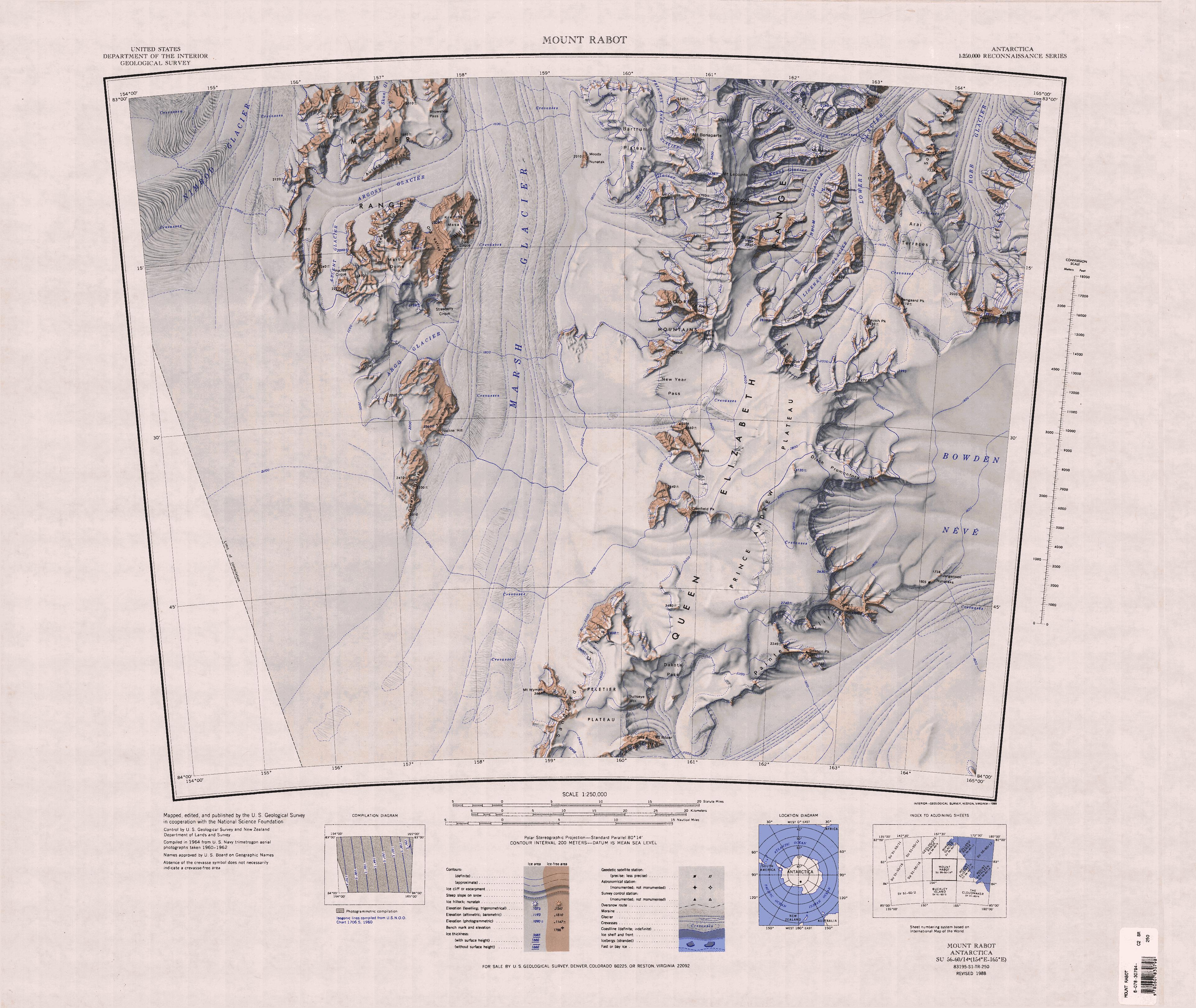
Lowery Glacier
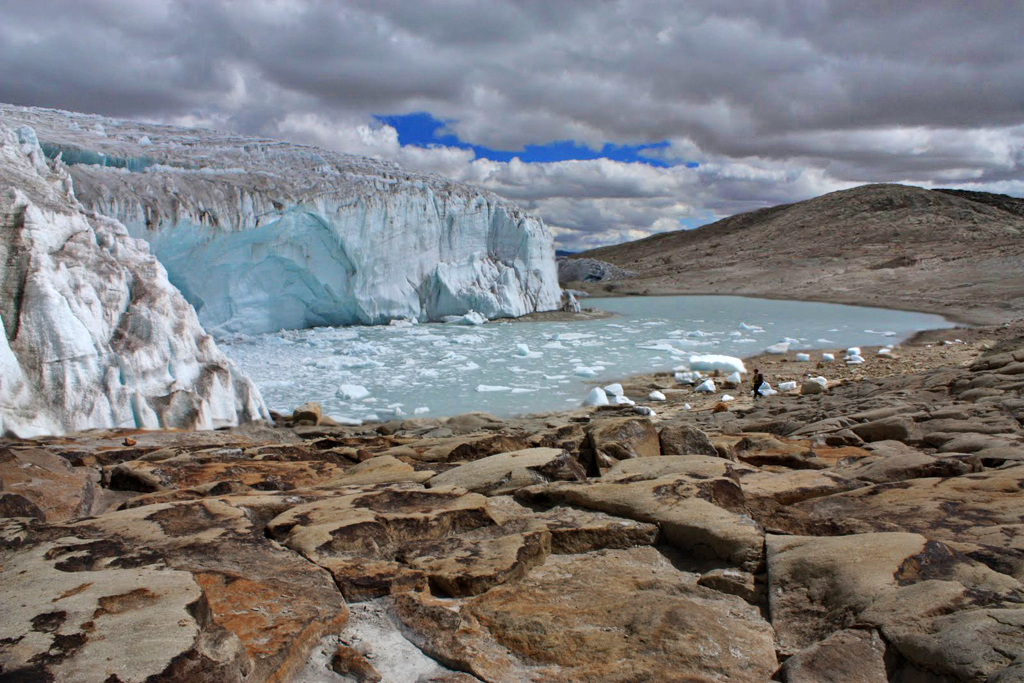
Lowery Glacier () is a glacier about long, which flows north from Prince Andrew Plateau, Antarctica, along the east side of the Queen Elizabeth Range to enter Nimrod Glacier. It was named by the New Zealand Geological and Topographical Survey Expedition (1959–60) for J.H. Lowery who, as a member of a field party, suffered injuries when a Sno-cat broke through a crevasse bridge off Cape Selborne Cape Selborne () is a high snow-covered cape at the south side of Barne Inlet, the terminus of Byrd Glacier at the west side of the Ross Ice Shelf. Discovered by the ''Discovery'' expedition (1901–1904) and named for William Waldegrave Palmer Se ... in November 1959. References Glaciers of the Ross Dependency Shackleton Coast {{ShackletonCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as Crevasse, crevasses and Serac, seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Between lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Andrew Plateau
Prince Andrew Plateau () is an ice-covered plateau, about long and wide, lying south of Mount Rabot in the Queen Elizabeth Range of Antarctica. Exploration and name The Prince Andrew Plateau was named by the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition (NZGSAE) (1961-62) for Prince Andrew, son of Queen Elizabeth II of Great Britain. Location The Prince Andrew Plateau is in the southern Queen Elizabeth Range between the Moore Mountains and Ārai Terraces to the north and the Peletier Plateau to the south. The Marsh Glacier is to the west and the Bowden Névé to the east. Features to the east include Painted Cliffs in the southeast, which include Dawson Peak and Mount Picciotto and the Disch Promontary further north. Features to the west include Dakota Pass in the south, Cranfield Peak, Mount Weeks and New Year Pass to the south of the Moore Mountains. Features to the north include Helm Glacier, Linehan Glacier, Turnabout Ridge, January Col, Claydon Peak and Baulch Pea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Elizabeth Range (Antarctica)
The Queen Elizabeth Range is a rugged mountain range of the Transantarctic Mountains System, located in the Ross Dependency region of Antarctica. It parallels the eastern side of Marsh Glacier for nearly from Nimrod Glacier in the north to Law Glacier in the south. Mount Markham (4,350 m), is the highest elevation in the range. Named by J.H. Miller of the New Zealand party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (1956–58) who, with G.W. Marsh, explored this area. It was named for Queen Elizabeth II, the patron of the expedition. Geological features Mount Bonaparte Mount Bonaparte () is a mountain, high, standing 4 mi NW of Mount Lecointe. Discovered by the British Antarctic Expedition (1907–09) under Shackleton, and named for Prince Roland Bonaparte, President of the Société de Géographie of Paris from 1910-1924. Inaccessible Cliffs Inaccessible Cliffs () is a line of steep cliffs, interrupted by several glaciers, which form the northern escarpment o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nimrod Glacier
The Nimrod Glacier is a major glacier about 135 km (85 mi) long, flowing from the polar plateau in a northerly direction through the Transantarctic Mountains between the Geologists and Miller Ranges, then northeasterly between the Churchill Mountains and Queen Elizabeth Range, and finally spilling into Shackleton Inlet and the Ross Ice Shelf between Capes Wilson and Lyttelton. It was photographed from the air by USN Operation Highjump, 1946–47. The name, given by US-ACAN, is in association with Shackleton Inlet and is for the '' Nimrod'', the ship of the British Antarctic Expedition (1907–09) under Ernest Shackleton Sir Ernest Henry Shackleton (15 February 1874 – 5 January 1922) was an Anglo-Irish Antarctic explorer who led three British expeditions to the Antarctic. He was one of the principal figures of the period known as the Heroic Age of .... See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic References * External links * Glacier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Geological And Topographical Survey Expedition
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created. New or NEW may refer to: Music * New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz Albums and EPs * ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013 * ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, 1995 Songs * "New" (Daya song), 2017 * "New" (Paul McCartney song), 2013 * "New" (No Doubt song), 1999 *"new", by Loona from '' Yves'', 2017 *"The New", by Interpol from ''Turn On the Bright Lights'', 2002 Acronyms * Net economic welfare, a proposed macroeconomic indicator * Net explosive weight, also known as net explosive quantity * Network of enlightened Women, a conservative university women's organization * Next Entertainment World, a South Korean film distribution company Identification codes * Nepal Bhasa language ISO 639 language code * New Century Financial Corporation (NYSE stock abbreviation) * Northeast Wrestling, a professional wrestling promotion in the northeastern United States Transport * New Orleans Lakefront Ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sno-cat
The Tucker Sno-Cat is a family of tracked vehicles for snow conditions, manufactured in Medford, Oregon by the company of the same name. Different models have been used for expeditions in the Arctic and the Antarctic during the second half of the 20th century. It differs from other truck-sized snow vehicles, commonly known as snowcats, by its use of four independently mounted sets of tracks. Early models While the majority of Tucker Sno-Cats utilized four sets of tracks, a few experimental models and early production models used two sets of tracks. Initially Tucker Sno-Cats employed two front-mounted steering skis and two sets of tracks mounted to the rear. However, there are at least three production models that only employed dual tracks—the small 222 Tucker Kitten, the 322, and the 323 models were all two-track Tucker Sno-Cats with a conventional front engine design. There are at least two variants of the Tucker Kitten, some have square corner doors while others have ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crevasse
A crevasse is a deep crack, that forms in a glacier or ice sheet that can be a few inches across to over 40 feet. Crevasses form as a result of the movement and resulting stress associated with the shear stress generated when two semi-rigid pieces above a plastic substrate have different rates of movement. The resulting intensity of the shear stress causes a breakage along the faces. Description Crevasses often have vertical or near-vertical walls, which can then melt and create seracs, arches, and other ice formations. These walls sometimes expose layers that represent the glacier's stratigraphy. Crevasse size often depends upon the amount of liquid water present in the glacier. A crevasse may be as deep as 45 metres and as wide as 20 metres. by |
Cape Selborne
Cape Selborne () is a high snow-covered cape at the south side of Barne Inlet, the terminus of Byrd Glacier at the west side of the Ross Ice Shelf. Discovered by the ''Discovery'' expedition (1901–1904) and named for William Waldegrave Palmer Selborne, Second Earl of Selborne, who entered the Cabinet as First Lord of the Admiralty in 1900. Cape Selborne marks the boundary between the Shackleton Coast to the south and the Hillary Coast The Hillary Coast is a portion of the coast of Antarctica along the western margin of the Ross Ice Shelf between Minna Bluff and Cape Selborne. It was named by the New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1961 for Sir Edmund Hillary, the le ... to the north. Headlands of the Ross Dependency Shackleton Coast Hillary Coast {{ShackletonCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaciers Of The Ross Dependency
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as Crevasse, crevasses and Serac, seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Between lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |