|
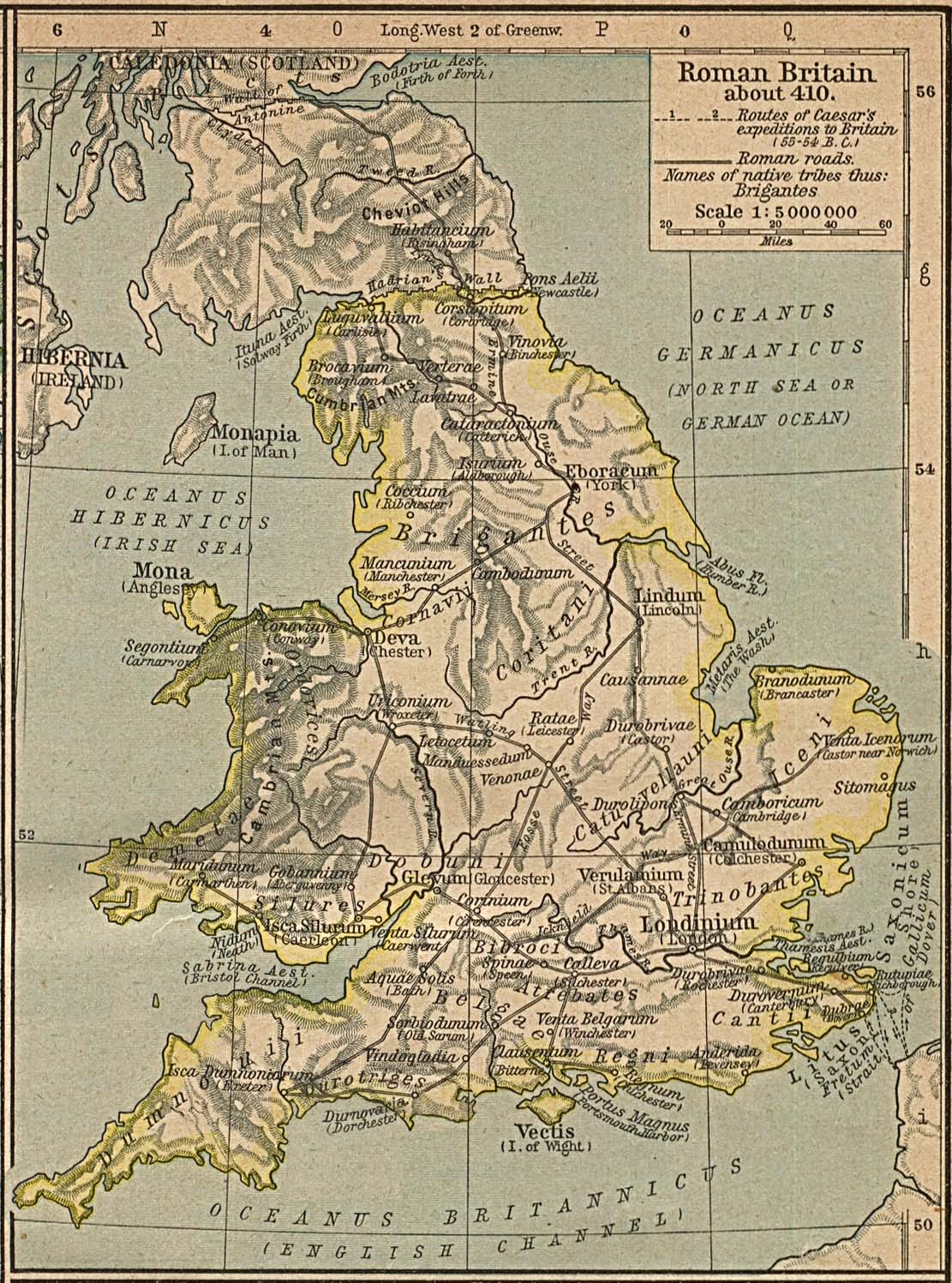
Lower Britain
Britannia Inferior (Latin for "Lower Britain") was a new province carved out of Roman Britain probably around AD 197 during the reforms of Septimius Severus although the division may have occurred later, between 211 and 220, under Caracalla. The removal of the governors in Londinium from control over the legions guarding Hadrian's Wall was aimed at reducing their power, given Clodius Albinus's recent bid to become emperor. The province was probably formalised around 214 by Severus's son Caracalla. Including most of modern northern England and the Midlands, the region was governed from the city of Eboracum (modern York) by a praetorian legate in command of a single legion stationed in the city. This subdivision of Britannia lasted throughout the Severan dynasty until the reorganisation of the empire under Diocletian in 296. Establishment During the reign of Commodus, the defences along the northern border of the empire in Britannia fell into neglect and disrepair. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Britannia Superior And Britannia Inferior (Map Of The Gallic Empire, 260 AD) Cropped
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great Britain, and the Roman province of Britain during the Roman Empire. Typically depicted reclining or seated with spear and shield since appearing thus on Roman coins of the 2nd century AD, the classical national allegory was revived in the early modern period. On coins of the pound sterling issued by Charles II of England, Scotland, and Ireland, Britannia appears with her shield bearing the Union Flag. To symbolise the Royal Navy's victories, Britannia's spear became the characteristic trident in 1797, and a helmet was added to the coinage in 1825. By the 1st century BC, Britannia replaced Albion as the prevalent Latin name for the island of Great Britain. After the Roman conquest in 43 AD, ''Britannia'' also came to refer to the Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severan Dynasty
The Severan dynasty was a Ancient Rome, Roman imperial dynasty that ruled the Roman Empire between 193 and 235, during the Roman imperial period (chronology), Roman imperial period. The dynasty was founded by the emperor Septimius Severus (), who rose to power after the Year of the Five Emperors as the victor of the civil war of 193–197, and his wife, Julia Domna. After the short reigns and assassinations of their two sons, Caracalla () and Geta (emperor), Geta (), who succeeded their father in the government of the empire, Julia Domna's relatives themselves assumed power by raising Elagabalus () and then Severus Alexander () to the imperial office. The dynasty's control over the empire was interrupted by the joint reigns of Macrinus () and his son Diadumenian (). The dynasty's women, including Julia Domna, the mother of Caracalla and Geta, and her nieces Julia Soaemias and Julia Mamaea, the mothers respectively of Elagabalus and Severus Alexander, and their own mother, Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Britannia Secunda
Britannia Secunda or Britannia II (Latin for "Second Britain") was one of the provinces of the Diocese of "the Britains" created during the Diocletian Reforms at the end of the 3rd century. It was probably created after the defeat of the usurper Allectus by Constantius Chlorus in AD 296 and was mentioned in the Verona List of the Roman provinces. Its position and capital remain uncertain, although it probably lay further from Rome than Britannia I. At present, most scholars place Britannia II in Yorkshire and northern England. If so, its capital would have been Eboracum (York). __NOTOC__ History Following the Roman conquest of Britain, it was administered as a single province from Camulodunum (Colchester) and then Londinium (London) until the Severan Reforms following the revolt of its governor Clodius Albinus. These divided the territory into Britannia Superior and Britannia Inferior, whose respective capitals were at Londinium and Eboracum. During the first phases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Britannia Superior
Britannia Superior (Latin for "Upper Britain") was a province of Roman Britain created after the civil war between Septimius Severus and Claudius Albinus. Although Herodian credits Severus with dividing Roman Britain into the Northern territory of Britannia Inferior and the Southern territory of Britannia Superior,Herodian. ''History of the Empire, Volume I: Books 1-4.'' Translated by C. R. Whittaker. Loeb Classical Library 454. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1969. Pg. 305. https://www-loebclassics-com.uwinnipeg.idm.oclc.org/view/herodian-history_empire/1969/pb_LCL454.3.xml modern scholarship argues that it is more likely that Caracella was the person who made the split sometime in the early 3rd century CE.Graham, A. J. “The Division of Britain.” ''The Journal of Roman Studies'' 56 (1966): pg. 92. https://uwinnipeg.on.worldcat.org/oclc/4928529095 The previous British capital Londinium remained the centre of Britannia Superior while Eboracum, or modern York was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxima Caesariensis
Maxima Caesariensis (Latin for "The Caesarian province of Maximus"), also known as Britannia Maxima, was one of the provinces of the Diocese of " the Britains" created during the Diocletian Reforms at the end of the 3rd century. It was probably created after the defeat of the usurper Allectus by Constantius Chlorus in AD 296 and was mentioned in the Verona List of the Roman provinces. Its position and capital remain uncertain, although it was probably adjacent to Flavia Caesariensis. On the basis of its governor's eventual consular rank, it is now usually considered to have consisted of Augusta or Londinium (London) and southeastern England. __NOTOC__ History Following the Roman conquest of Britain, Britain was administered as a single province from Camulodunum (Colchester) and then Londinium (London) until the Severan Reforms following the revolt of its governor Clodius Albinus. These divided the territory into Upper and Lower Britain (''Britannia Superior'' and ''Infer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Britannia Prima
Britannia Prima or Britannia I (Latin for "First Roman Britain, Britain") was one of the Roman province, provinces of the Diocese of Britain, Diocese of "the Roman Britain, Britains" created during the Diocletian Reforms at the end of the 3rd century. It was probably created after the defeat of the usurper Allectus by Constantius Chlorus in AD 296 and was mentioned in the Verona List of the Roman provinces. Its position and capital remain uncertain, although it was probably located closer to Rome than Britannia Secunda, Britannia II. At present, most scholars place Britannia I in Wales, Cornwall, and the lands connecting them. On the basis of a recovered inscription, its capital is now usually placed at Corinium Dobunnorum, Corinium of the Dobunni (Cirencester) but some emendations of the list of bishops attending the 315 Council of Arles would place a provincial capital in Isca Augusta, Isca (Caerleon) or Deva Victrix, Deva (Chester), which were known Roman legions, leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Britannia
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into dioceses based on the civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situation must have hardly survived Julian, 361–363. Episcopal courts are not heard of again in the East until 398 and in the West in 408. The quality of these courts was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodian
Herodian or Herodianus ( el, Ἡρωδιανός) of Syria, sometimes referred to as "Herodian of Antioch" (c. 170 – c. 240), was a minor Roman civil servant who wrote a colourful history in Greek titled ''History of the Empire from the Death of Marcus'' (τῆς μετὰ Μάρκον βασιλείας ἱστορία) in eight books covering the years 180 to 238. His work is not entirely reliable although his less biased account of Elagabalus is more useful than that of Cassius Dio. Herodian himself may have been a Syrian (perhaps from Antioch) who appears to have lived for a considerable period of time in Rome, but possibly without holding any public office. From his extant work, we gather that he was still living at an advanced age during the reign of Gordianus III, who ascended the throne in 238. Beyond this, nothing is known of his life. Herodian writes (1.1.3; 2.15.7) that the events described in his history occurred during his lifetime. Photius (Codex 99) gives an out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Syria
Roman Syria was an early Roman province annexed to the Roman Republic in 64 BC by Pompey in the Third Mithridatic War following the defeat of King of Armenia Tigranes the Great. Following the partition of the Herodian Kingdom of Judea into tetrarchies in 6 AD, it was gradually absorbed into Roman provinces, with Roman Syria annexing Iturea and Trachonitis. Provincia Syria Syria was annexed to the Roman Republic in 64 BC, when Pompey the Great had the Seleucid king Antiochus XIII Asiaticus executed and deposed his successor Philip II Philoromaeus. Pompey appointed Marcus Aemilius Scaurus to the post of Proconsul of Syria. Following the fall of the Roman Republic and its transformation into the Roman Empire, Syria became a Roman imperial province, governed by a Legate. During the early empire, the Roman army in Syria accounted for three legions with auxiliaries who defended the border with Parthia. In 6 AD Emperor Augustus deposed the ethnarch Herod Archelaus and united J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheppard Frere
Sheppard Sunderland Frere, CBE, FSA, FBA (23 August 1916 – 26 February 2015) was a British historian and archaeologist who studied the Roman Empire. He was a fellow at All Souls College, Oxford. Biography The son of Noel Gray Frere, of the Colonial Service, and his wife Agnes (née Sutherland), Sheppard "Sam" Frere was born in 1916. He was educated at Lancing College and Magdalene College, Cambridge. He was a master at Epsom College from 1938–41, and became classics master and housemaster at Lancing College from 1945 to 1954, when he was in charge of the excavations at Canterbury during his summer vacations. He made a number of broadcasts about his work at that time. He left Lancing in 1954 to become a university lecturer in archaeology at the University of Manchester. His family details and dates are given under the family of 'Frere' in ''Burke's Landed Gentry'' for 1969. For three seasons early in the 1970s, he was in charge of the archaeological summer school that exca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great Britain, and the Roman province of Britain during the Roman Empire. Typically depicted reclining or seated with spear and shield since appearing thus on Roman coins of the 2nd century AD, the classical national allegory was revived in the early modern period. On coins of the pound sterling issued by Charles II of England, Scotland, and Ireland, Britannia appears with her shield bearing the Union Flag. To symbolise the Royal Navy's victories, Britannia's spear became the characteristic trident in 1797, and a helmet was added to the coinage in 1825. By the 1st century BC, Britannia replaced Albion as the prevalent Latin name for the island of Great Britain. After the Roman conquest in 43 AD, ''Britannia'' also came to refer to the Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commodus
Commodus (; 31 August 161 – 31 December 192) was a Roman emperor who ruled from 177 to 192. He served jointly with his father Marcus Aurelius from 176 until the latter's death in 180, and thereafter he reigned alone until his assassination. His reign is commonly thought of as marking the end of a golden period of peace in the history of the Roman Empire, known as the Pax Romana. Commodus accompanied his father during the Marcomannic Wars in 172, and on a tour of the Eastern provinces in 176. Later that year he became the youngest emperor and consul up to that point, at the age of 15. During his solo reign, the Roman Empire enjoyed reduced military conflict compared with the reign of Marcus Aurelius. Intrigues and conspiracies abounded, leading Commodus to revert to an increasingly dictatorial style of leadership, culminating in his creating a deific personality cult, with his performing as a gladiator in the Colosseum. Throughout his reign, Commodus entrusted the management ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Cropped.jpg)