|
Lossiemouth Sandstone
The Lossiemouth Sandstone is a Middle to Late Triassic (Ladinian to Norian) age geological formation. It is exposed on the south side of the Moray Firth near Lossiemouth and near Golspie in Sutherland. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel et al., 2004, "Dinosaur distribution." pp.517-607 Fossil content See also * List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations ** List of stratigraphic units with indeterminate dinosaur fossils * List of fossiliferous stratigraphic units in Scotland * Ischigualasto Formation, contemporaneous fossiliferous formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin, Argentina * Candelária Formation, contemporaneous fossiliferous formation of the Paraná Basin in southeastern Brazil * Molteno Formation, contemporaneous fossiliferous formation of the Karoo Basin in southern Africa * Fremouw Formation The Fremouw Formation is a Triassic-age rock formation in the Transantarctic Mountains of Antarctica. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formation (geology)
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics ( lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exposed in a geographical region (the stratigraphic column). It is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy, the study of strata or rock layers. A formation must be large enough that it can be mapped at the surface or traced in the subsurface. Formations are otherwise not defined by the thickness of their rock strata, which can vary widely. They are usually, but not universally, tabular in form. They may consist of a single lithology (rock type), or of alternating beds of two or more lithologies, or even a heterogeneous mixture of lithologies, so long as this distinguishes them from adjacent bodies of rock. The concept of a geologic formation goes back to the beginnings of modern scientific geology. The term was used by Abraham Gottlob Wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is the subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya; their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, having evolved from earlier theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds. Dinosaurs are varied from taxonomic, morphological and ecological standpoints. Birds, at over 10,700 living species, are among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
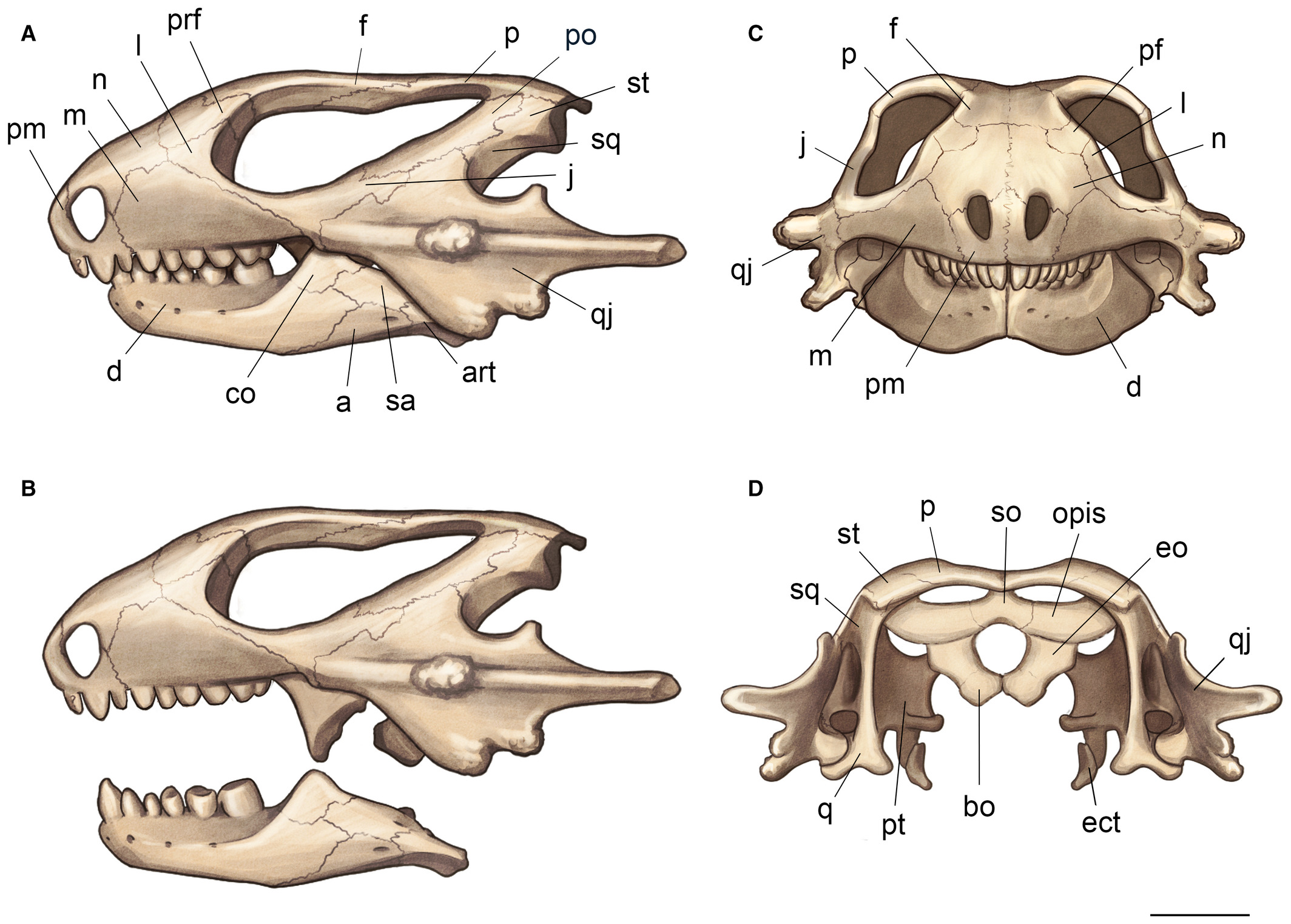
Ornithosuchid
Ornithosuchidae is an extinct family of pseudosuchian archosaurs (distant relatives of modern crocodilians) from the Triassic period. Ornithosuchids were quadrupedal and facultatively bipedal (e.g. like chimpanzees), meaning that they had the ability to walk on two legs for short periods of time. They had distinctive, downturned snouts, unique, "crocodile-reversed" ankle bones, and several other features that distinguish them from other archosaurs. Ornithosuchids were geographically widespread during the Carnian and Norian stages of the Late Triassic with members known from Argentina, Brazil, and the United Kingdom. Four genera, comprising ''Ornithosuchus'', '' Venaticosuchus, Dynamosuchus,'' and '' Riojasuchus'' are presently known. The family was first erected by German paleontologist Friedrich von Huene in 1908. Description Skull Ornithosuchids can be identified by the presence of an arched diastema, a gap between the teeth at the front of the snout. When the jaw is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithosuchus
''Ornithosuchus'' (meaning "bird crocodile") is an extinct genus of pseudosuchians from the Late Triassic (Carnian) Lossiemouth Sandstone of Scotland. It was originally thought to be the ancestor to the carnosaurian dinosaurs (such as ''Allosaurus''). However, it is now known to be more closely related to crocodilians than to dinosaurs. Description Despite this relationship to crocodiles, ''Ornithosuchus'' was able to walk on its hind legs, like many dinosaurs. However, it probably spent most of its time on all fours, only moving bipedally when it needed to run rapidly. Its skull also resembled those of theropod dinosaurs, but more primitive features included the presence of five toes on each foot and a double row of armoured plates along the animal's back. ''Ornithosuchus'' has traditionally been estimated at a length of about around . Classification A single species of ''Ornithosuchus'' is recognized, ''O. woodwardi''. ''Ornithosuchus taylori'' is a synonym.M. Belén von ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptopleuron Lacertinum
''Leptopleuron'' is an extinct genus of procolophonid that lived in the dry lands during the late Triassic in Elgin of northern Scotland and was the first to be included in the clade of Procolophonidae. First described by English paleontologist and biologist Sir Richard Owen, ''Leptopleuron'' is derived from two Greek bases, ''leptos'' for "slender" and ''pleuron'' for "rib," describing it as having slender ribs. The fossil is also known by a second name, ''Telerpeton'', which is derived from the Greek bases ''tele'' for "far off" and ''herpeton'' for "reptile." In Scotland, ''Leptopleuron'' was found specifically in the Lossiemouth Sandstone Formation. The yellow sandstone it was located in was poorly lithified with wind coming from the southwest. The environment is also described to consist of barchan dunes due to the winds, ranging up to 20 m tall that spread during dry phases into flood plains. Procolophonoids such as ''Leptopleuron'' were considered an essential addition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procolophonid
Procolophonidae is an extinct family of small, lizard-like parareptiles known from the Late Permian to Late Triassic that were distributed across Pangaea, having been reported from Europe, North America, China, South Africa, South America, Antarctica and Australia. The most primitive procolophonids were likely insectiovous or omnivorous, more derived members of the clade developed bicusped molars, and were likely herbivorous feeding on high fiber vegetation or durophagous omnivores. Many members of the group are noted for spines projecting from the quadratojugal bone of the skull, which likely served a defensive purpose as well as possibly also for display. At least some taxa were likely fossorial burrowers. While diverse during the Early and Middle Triassic, they had very low diversity during the Late Triassic, and were extinct by the beginning of the Jurassic. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptopleuron
''Leptopleuron'' is an extinct genus of procolophonid that lived in the dry lands during the late Triassic in Elgin of northern Scotland and was the first to be included in the clade of Procolophonidae. First described by English paleontologist and biologist Sir Richard Owen, ''Leptopleuron'' is derived from two Greek bases, ''leptos'' for "slender" and ''pleuron'' for "rib," describing it as having slender ribs. The fossil is also known by a second name, ''Telerpeton'', which is derived from the Greek bases ''tele'' for "far off" and ''herpeton'' for "reptile." In Scotland, ''Leptopleuron'' was found specifically in the Lossiemouth Sandstone Formation. The yellow sandstone it was located in was poorly lithified with wind coming from the southwest. The environment is also described to consist of barchan dunes due to the winds, ranging up to 20 m tall that spread during dry phases into flood plains. Procolophonoids such as ''Leptopleuron'' were considered an essential addition to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperodapedon BW2
''Hyperodapedon'' is a genus of rhynchosaurs (beaked, archosaur-like reptiles) from the Late Triassic period (Carnian stage). Fossils of the genus have been found in Africa, Asia, Europe and North and South America. Its first discovery and naming was found by Thomas Henry Huxley in 1859. ''Hyperodapedon'' was a herbivore that used its beaked premaxilla and hindlimbs to dig for plants in dry land. Description ''Hyperodapedon'' was a heavily built, stocky, animal. ''H. gordoni'' had total length around with skull length of to , but largest species, ''H. huxleyi'' had lower jaw about and skull length is estimated about . Apart from its beak, it had several rows of heavy teeth on each side of the upper jaw, and a single row on each side of the lower jaw, creating a powerful chopping action when it ate. It is believed to have been herbivorous, feeding mainly on seed ferns, and died out when these plants became extinct at the end of the Triassic. The diagnosis of ''Hyperodapedon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhynchosaur
Rhynchosaurs are a group of extinct herbivorous Triassic archosauromorph reptiles, belonging to the order Rhynchosauria. Members of the group are distinguished by their triangular skulls and elongated, beak like premaxillary bones. Rhynchosaurs first appeared in the Middle Triassic or possibly the Early Triassic, before becoming abundant and globally distributed during the Carnian stage of the Late Triassic. Description Rhynchosaurs were herbivores, and at times abundant (in some fossil localities accounting for 40 to 60% of specimens found), with stocky bodies and a powerful beak. Early primitive forms, like ''Mesosuchus'' and '' Howesia'', were generally small and more typically lizard-like in build, and had skulls rather similar to the early diapsid ''Youngina'', except for the beak and a few other features. Later and more advanced genera grew to medium to medium large size, up to two meters in length. The skull in these forms were short, broad, and triangular, becoming muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperodapedon
''Hyperodapedon'' is a genus of rhynchosaurs (beaked, archosaur-like reptiles) from the Triassic, Late Triassic period (Carnian stage). Fossils of the genus have been found in Africa, Asia, Europe and North and South America. Its first discovery and naming was found by Thomas Henry Huxley in 1859. ''Hyperodapedon'' was a herbivore that used its beaked premaxilla and hindlimbs to dig for plants in dry land. Description ''Hyperodapedon'' was a heavily built, stocky, animal. ''H. gordoni'' had total length around with skull length of to , but largest species, ''H. huxleyi'' had lower jaw about and skull length is estimated about . Apart from its beak, it had several rows of heavy teeth on each side of the upper jaw, and a single row on each side of the lower jaw, creating a powerful chopping action when it ate. It is believed to have been herbivorous, feeding mainly on seed ferns, and died out when these plants became extinct at Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, the end of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erpetosuchus BW
''Erpetosuchus'' is an extinct genus of pseudosuchian from the Late Triassic. The type species of ''Erpetosuchus'' is ''E. granti''. It was first described by E. T. Newton in 1894 for remains found in northeastern Scotland, including four specimens from the latest Carnian Lossiemouth Sandstone Formation. Additional remains of ''Erpetosuchus'' have been found in the New Haven Formation of Connecticut in the eastern United States, although they were not attributed to the species ''E. granti''. The relationship of ''Erpetosuchus'' to other archosaurs is uncertain. In 2000 and 2002, it was considered a close relative of the group Crocodylomorpha, which includes living crocodylians and many extinct relatives. However, this relationship was questioned in a 2012 analysis that found the phylogenetic placement of ''Erpetosuchus'' to be very uncertain. Material The first remains of ''Erpetosuchus'' were found in the Lossiemouth Sandstone Formation in Scotland, dating back to the late Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudosuchia
Pseudosuchia is one of two major divisions of Archosauria, including living crocodilians and all archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds. Pseudosuchians are also informally known as "crocodilian-line archosaurs". Prior to 2011, the clade Pseudosuchia was often called Crurotarsi in reference to the crurotarsal ankle found in almost all members of the group, which traditionally included phytosaurs, ornithosuchids, and suchians. However, a major 2011 study of Triassic archosaur relations proposed that phytosaurs were not closely related to other traditional "crurotarsans", at least compared to "bird-line archosaurs" (Avemetatarsalians) such as pterosaurs and dinosaurs. As a result, the possession of a crurotarsal ankle was considered a plesiomorphic ("primitive") feature retained by pseudosuchians. Crurotarsi now refers to a broader group of reptiles including Pseudosuchia, Phytosauria, and Avemetatarsalia. Despite Pseudosuchia meaning "false crocodiles", th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |