|
Long 18th Century
The long 18th century is a phrase used by many British historians to cover a more ''natural'' historical period than the simple use of the standard calendar definition. They expand the century to include larger British and Western European historical movements, with their subsequent "long" 18th century typically running from the Glorious Revolution and the beginning of the Nine Years' War in 1688 to the end of the Napoleonic wars in 1815. Other definitions, perhaps those with a more social or global interest, extend the period further to, for example, from the Stuart Restoration in 1660 to the end of the Georgian era. Possibly the earliest proponent of the long eighteenth century was Sir John Robert Seeley, who in 1883 defined the eighteenth century as "the period which begins with the Revolution of 1688 and ends with the peace of 1815". [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and VII of England and Scotland in November 1688, and his replacement by his daughter Mary II and her husband and James's nephew William III of Orange, de facto ruler of the Dutch Republic. A term first used by John Hampden (1653–1696), John Hampden in late 1689, it has been notable in the years since for having been described as the last successful invasion of England as well as an internal coup, with differing interpretations from the Dutch and English perspectives respectively. Despite his personal Catholicism, a religion opposed by the Protestant majority in England and Scotland, James became king in February 1685 with widespread support in both countries, since many feared that his exclusion would lead to a repetition of the 16391651 Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War (1688–1697), often called the War of the Grand Alliance or the War of the League of Augsburg, was a conflict between France and a European coalition which mainly included the Holy Roman Empire (led by the Habsburg monarchy), the Dutch Republic, England, Spain, Savoy, Sweden and Portugal. Although not the first European war to spill over to Europe's overseas colonies, the events of the war spread to such far away places as the Americas, India, and West Africa. It is for this reason that it is sometimes considered the first world war. The conflict encompassed the Glorious Revolution in England, where William of Orange deposed the unpopular James VII and II and subsequently struggled against him for control of Scotland and Ireland, and a campaign in colonial North America between French and English settlers and their respective Native American allies. Louis XIV of France had emerged from the Franco-Dutch War in 1678 as the most powerful monarch in Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of French domination over most of continental Europe. The wars stemmed from the unresolved disputes associated with the French Revolution and the French Revolutionary Wars consisting of the War of the First Coalition (1792–1797) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). The Napoleonic Wars are often described as five conflicts, each termed after the coalition that fought Napoleon: the Third Coalition (1803–1806), the Fourth (1806–1807), the Fifth (1809), the Sixth (1813–1814), and the Seventh (1815) plus the Peninsular War (1807–1814) and the French invasion of Russia (1812). Napoleon, upon ascending to First Consul of France in 1799, had inherited a republic in chaos; he subsequently created a state with stable financ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuart Restoration
The Restoration of the Stuart monarchy in the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland took place in 1660 when King Charles II returned from exile in continental Europe. The preceding period of the Protectorate and the civil wars came to be known as the Interregnum (1649–1660). The term ''Restoration'' is also used to describe the period of several years after, in which a new political settlement was established. It is very often used to cover the whole reign of King Charles II (1660–1685) and often the brief reign of his younger brother King James II (1685–1688). In certain contexts it may be used to cover the whole period of the later Stuart monarchs as far as the death of Queen Anne and the accession of the Hanoverian King George I in 1714. For example, Restoration comedy typically encompasses works written as late as 1710. The Protectorate After Richard Cromwell, Lord Protector from 1658 to 1659, ceded power to the Rump Parliament, Charles Fleetwood and J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgian Era
The Georgian era was a period in British history from 1714 to , named after the Hanoverian Kings George I, George II, George III and George IV. The definition of the Georgian era is often extended to include the relatively short reign of William IV, which ended with his death in 1837. The subperiod that is the Regency era is defined by the regency of George IV as Prince of Wales during the illness of his father George III. The transition to the Victorian era was characterized in religion, social values, and the arts by a shift in tone away from rationalism and toward romanticism and mysticism. The term ''Georgian'' is typically used in the contexts of social and political history and architecture. The term ''Augustan literature'' is often used for Augustan drama, Augustan poetry and Augustan prose in the period 1700–1740s. The term ''Augustan'' refers to the acknowledgement of the influence of Latin literature from the ancient Roman Republic. The term ''Georgian era'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir John Robert Seeley
Sir John Robert Seeley, KCMG (10 September 1834 – 13 January 1895) was an English Liberal historian and political essayist. A founder of British imperial history, he was a prominent advocate for the British Empire, promoting a concept of Greater Britain. This he expounded in his most widely known book ''The Expansion of England'' (1883). Whilst he was an early advocate of the establishment of political science as a distinct academic discipline, he retained a theological approach in which this was embedded. Early life Seeley was born in London. His father was Robert Benton Seeley, a publisher who issued books under the name of Seeley, Jackson and Halliday. He was a strong advocate of Evangelical Anglicanism and was the author of several religious books and of ''The Life and Times of Edward I''. His mother was Mary Ann Jackson (1809-1868), who shared her husband's religious views. Her brother, John Henry Jackson, was a partner in Robert Seeley's publishing company. John was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Nineteenth Century
The ''long nineteenth century'' is a term for the 125-year period beginning with the onset of the French Revolution in 1789 and ending with the outbreak of World War I in 1914. It was coined by Russian writer Ilya Ehrenburg and British Marxist historian Eric Hobsbawm. The term refers to the notion that the period reflects a progression of ideas which are characteristic to an understanding of the 19th century in Europe. Background The concept is an adaption of Fernand Braudel's 1949 notion of ''le long seizième siècle'' ("the long 16th century" 1450–1640) and "a recognized category of literary history", although a period often broadly and diversely defined by different scholars. Numerous authors, before and after Hobsbawm's 1995 publication, have applied similar forms of book titles or descriptions to indicate a selective time frame for their works, such as: S. Kettering, "French Society: 1589–1715 – the long seventeenth century", E. Anthony Wrigley, "British population d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Hundred Years' War
The Second Hundred Years' War is a periodization or historical era term used by some historians to describe the series of military conflicts between Great Britain and France that occurred from about 1689 (or some say 1714) to 1815. The Second Hundred Years' War is named after the Hundred Years' War, which occurred in the 14th and 15th century. The term appears to have been coined by J. R. Seeley in his influential work ''The Expansion of England'' (1883). Background Like the Hundred Years' War, this term does not describe a single military event but a persistent general state of war between the two primary belligerents. The use of the phrase as an overarching category indicates the interrelation of all the wars as components of the rivalry between France and Britain for world power. It was a war between and over the future of each state's colonial empires. The two countries remained continual antagonists even as their national identities underwent significant evolution. Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Twentieth Century
The term ''short 20th century'', originally proposed by Iván Berend (Hungarian Academy of Sciences) but defined by Eric Hobsbawm, a British Marxist historian and author, refers to the period of 78 years between the years 1914 and 1991. The convention is an answer to the long nineteenth and eighteenth centuries, in which it is an attempt to use a more natural approach to historical periods. The period begins with the start of the First World War and ends with the dissolution of the Soviet Union. The chain of events represented such significant changes in world history as to redefine the era. The First World War caused the end of the German, Ottoman, Austro-Hungarian and Russian empires. The Second World War was greatly influenced by the outcome of the First World War. The Cold War was a result of the Second World War and ended with the fall of the Soviet Union. __NOTOC__ See also *American Century *''The Age of Extremes'' *Long War (20th century) ''The Shield of Achil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th Century
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the Natural environment, environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV, Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
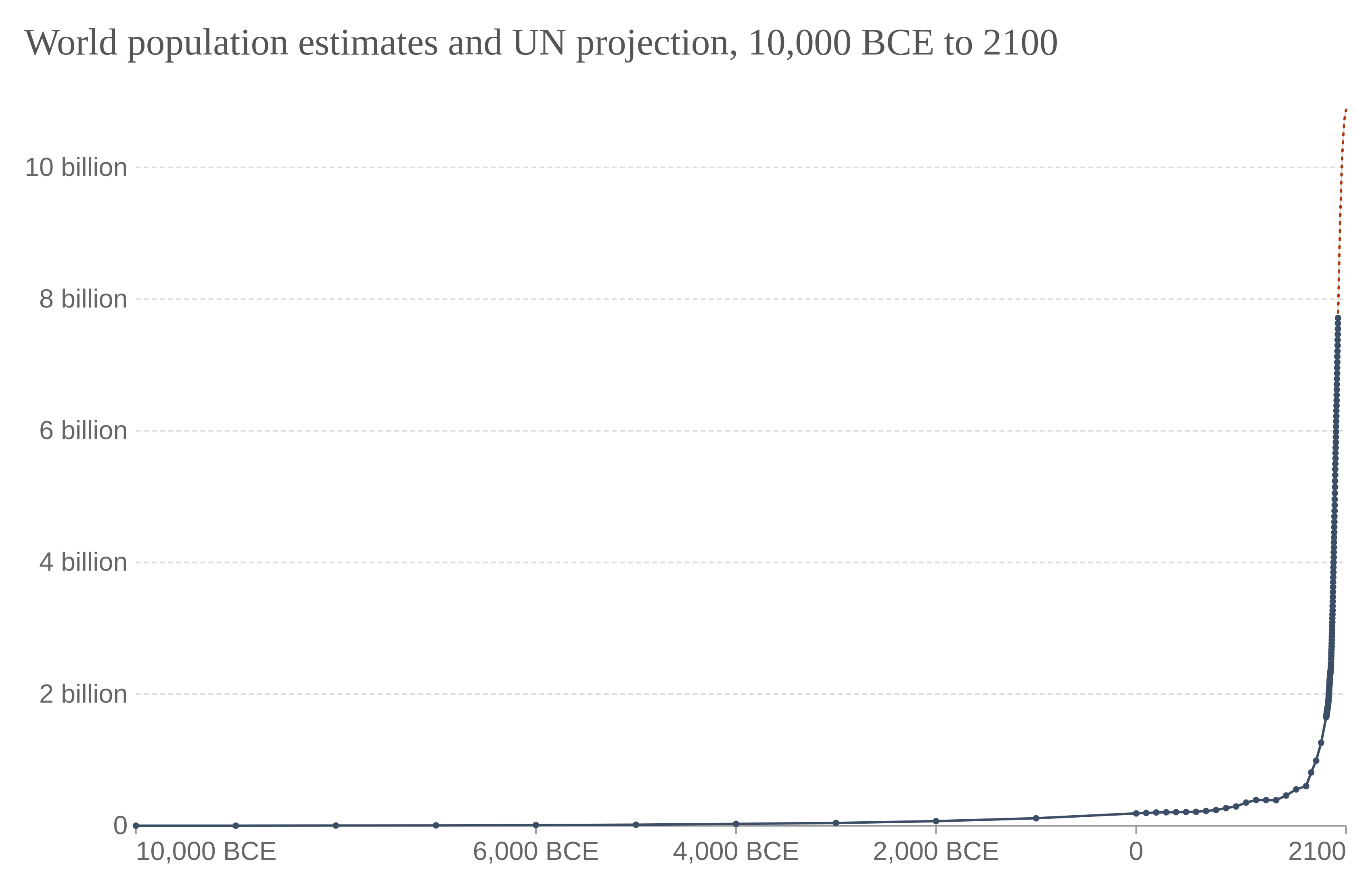
Historical Eras
Human history, also called world history, is the narrative of humanity's past. It is understood and studied through anthropology, archaeology, genetics, and linguistics. Since the invention of writing, human history has been studied through primary and secondary source documents. Humanity's written history was preceded by its prehistory, beginning with the Paleolithic ("Old Stone Age") era. This was followed by the Neolithic ("New Stone Age") era, which saw the Agricultural Revolution begin in the Middle East around 10,000 BCE. During this period, humans began the systematic husbandry of plants and animals. As agriculture advanced, most humans transitioned from a nomadic to a settled lifestyle as farmers in permanent settlements. The relative security and increased productivity provided by farming allowed communities to expand into increasingly larger units, fostered by advances in transportation. The earliest complex societies appeared in fertile river valleys. As f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |