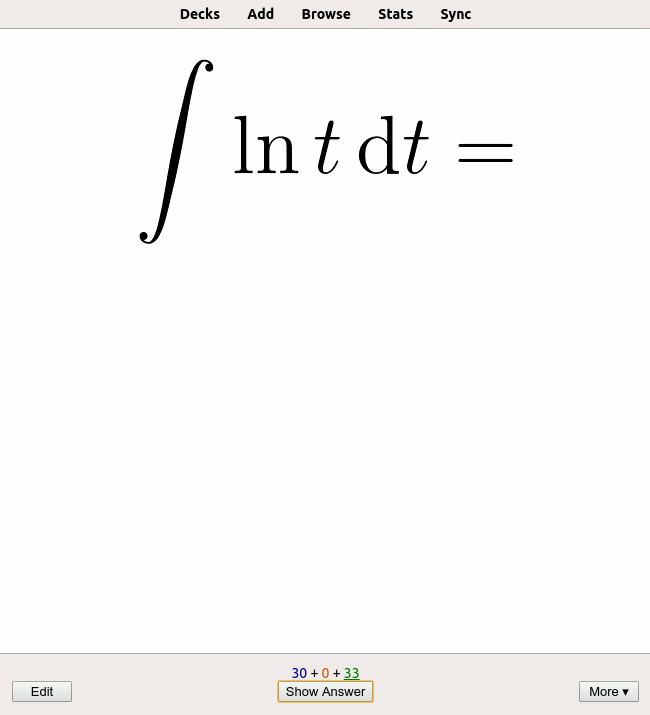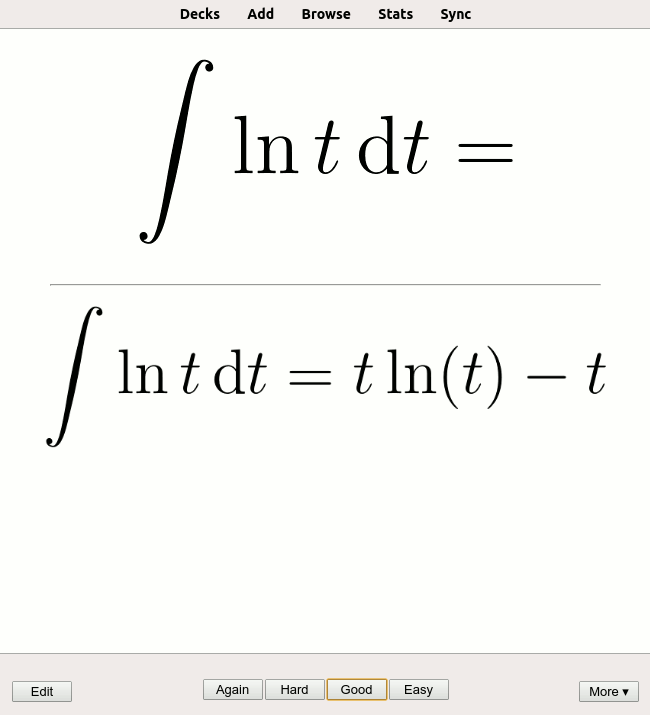|
Long-term Memory
Long-term memory (LTM) is the stage of the Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model in which informative knowledge is held indefinitely. It is defined in contrast to short-term and working memory, which persist for only about 18 to 30 seconds. Long-term memory is commonly labelled as explicit memory ( declarative), as well as episodic memory, semantic memory, autobiographical memory, and implicit memory ( procedural memory). Dual-store memory model According to Miller, whose paper in 1956 popularized the theory of the "magic number seven", short-term memory is limited to a certain number of chunks of information, while long-term memory has a limitless store. Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model According to the dual store memory model proposed by Richard C. Atkinson and Richard Shiffrin in 1968, memories can reside in the short-term "buffer" for a limited time while they are simultaneously strengthening their associations in long-term memory. When items are first presented, they en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atkinson–Shiffrin Memory Model
The Atkinson–Shiffrin model (also known as the multi-store model or modal model) is a model of memory proposed in 1968 by Richard Atkinson and Richard Shiffrin. The model asserts that human memory has three separate components: # a '' sensory register'', where sensory information enters memory, # a '' short-term store'', also called ''working memory'' or ''short-term memory'', which receives and holds input from both the sensory register and the long-term store, and # a '' long-term store'', where information which has been rehearsed (explained below) in the short-term store is held indefinitely. Since its first publication, this model has come under much scrutiny and has been criticized for various reasons (described below). However, it is notable for the significant influence it had in stimulating subsequent memory research. Summary The model of memories is an explanation of how memory processes work. The three-part, multi-store model was first described by Atkinson and S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engram (neuropsychology)
An engram is a unit of cognitive information imprinted in a physical substance, theorized to be the means by which memories are stored as biophysical or biochemical changes in the brain or other biological tissue, in response to external stimuli. Demonstrating the existence of, and the exact mechanism and location of, neurologically defined engrams has been a focus of persistent research for many decades. History The term "engram" was coined by memory researcher Richard Semon in reference to the physical substrate of memory in the organism. Semon warned, however: "In animals, during the evolutionary process, one organic system—the nervous system—has become specialised for the reception and transmission of stimuli. No monopoly of this function by the nervous system, however, can be deduced from this specialisation, not even in its highest state of evolution, as in Man." One of the first ventures on identifying the location of a memory in the brain was undertaken by Karl S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perirhinal Cortex
The perirhinal cortex is a cortical region in the medial temporal lobe that is made up of Brodmann areas 35 and 36. It receives highly processed sensory information from all sensory regions, and is generally accepted to be an important region for memory. It is bordered caudally by postrhinal cortex or parahippocampal cortex (homologous regions in rodents and primates, respectively) and ventrally and medially by entorhinal cortex. Structure The perirhinal cortex is composed of two regions: areas 36 and 35. Area 36 is sometimes divided into three subdivisions: 36d is the most rostral and dorsal, 36r ventral and caudal, and 36c the most caudal. Area 35 can be divided in the same manner, into 35d and 35v (for dorsal and ventral, respectively). Area 36 is six-layered, dysgranular, meaning that its layer IV is relatively sparse. Area 35 is agranular cortex (lacking any cells in layer IV). Function The perirhinal cortex is involved in both visual perception and memory; it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entorhinal Cortex
The entorhinal cortex (EC) is an area of the brain's allocortex, located in the medial temporal lobe, whose functions include being a widespread network hub for memory, navigation, and the perception of time.Integrating time from experience in the lateral entorhinal cortex Albert Tsao, Jørgen Sugar, Li Lu, Cheng Wang, James J. Knierim, May-Britt Moser & Edvard I. Moser Naturevolume 561, pages57–62 (2018) The EC is the main interface between the hippocampus and neocortex. The EC-hippocampus system plays an important role in declarative (autobiographical/episodic/semantic) memories and in particular spatial memories including memory formation, memory consolidation, and memory optimization in sleep. The EC is also responsible for the pre-processing (familiarity) of the input signals in the reflex nictitating membrane response of classical trace conditioning; the association of impulses from the eye and the ear occurs in the entorhinal cortex. Structure In rodents, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
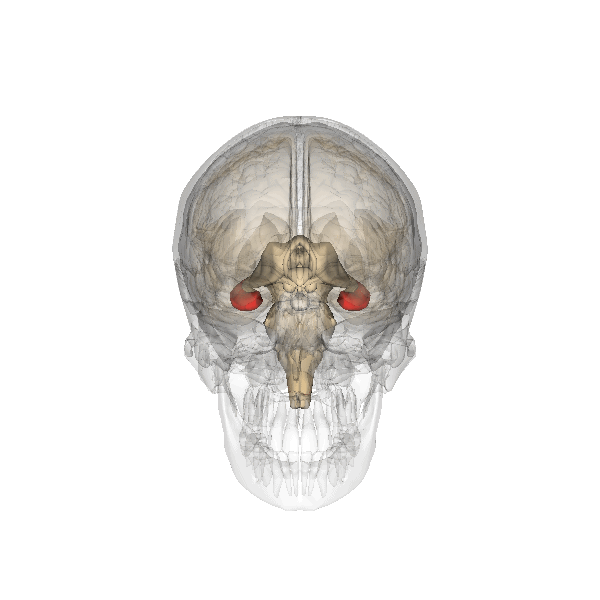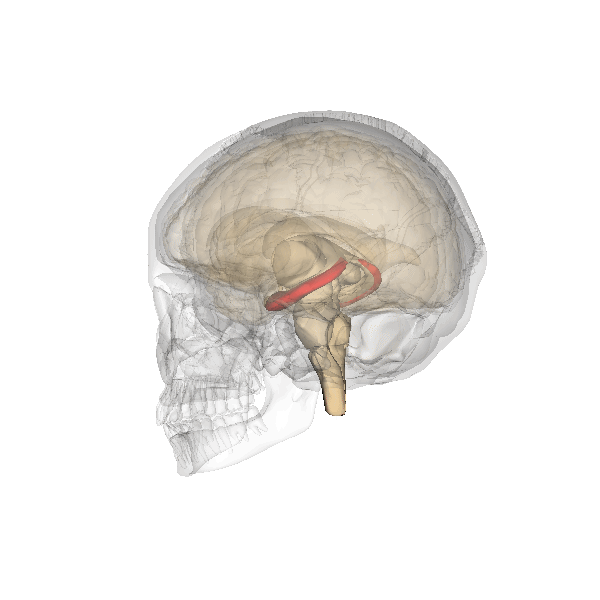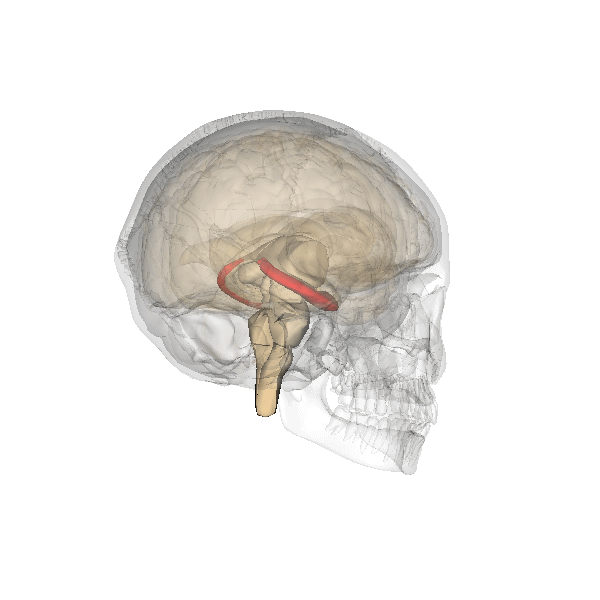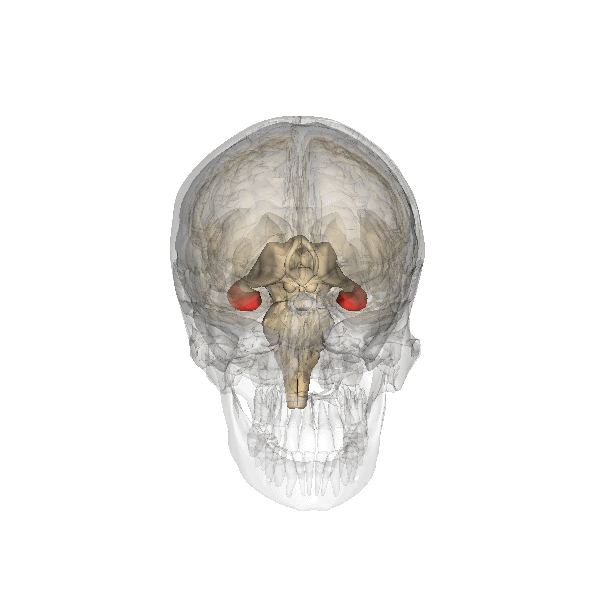
Hippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , ' seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables navigation. The hippocampus is located in the allocortex, with neural projections into the neocortex in humans, as well as primates. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In humans, it contains two main interlocking parts: the hippocampus proper (also called ''Ammon's horn''), and the dentate gyrus. In Alzheimer's disease (and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of the brain to suffer damage; short-term memory loss and disorientation are included among the early symptoms. Damage to the hippocampus can also result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explicit Memory
Explicit memory (or declarative memory) is one of the two main types of long-term human memory, the other of which is implicit memory. Explicit memory is the conscious, intentional recollection of factual information, previous experiences, and concepts. This type of memory is dependent upon three processes: acquisition, consolidation, and retrieval. Explicit memory can be divided into two categories: episodic memory, which stores specific personal experiences, and semantic memory, which stores factual information.Tulving E. 1972. Episodic and semantic memory. In Organization of Memory, ed. E Tulving, W Donaldson, pp. 381–403. New York: Academic Explicit memory requires gradual learning, with multiple presentations of a stimulus and response. The counterpart to explicit memory is known as implicit memory, refers to memories acquired and used unconsciously such as skills (e.g. knowing how to get dressed) or perception. Unlike explicit memory, implicit memory learns rapidly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Brain
The human brain is the central organ (anatomy), organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the human body, body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the Sensory nervous system, sense organs, and making decisions as to the instructions sent to the rest of the body. The brain is contained in, and protected by, the neurocranium, skull bones of the human head, head. The cerebrum, the largest part of the human brain, consists of two cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere has an inner core composed of white matter, and an outer surface – the cerebral cortex – composed of grey matter. The cortex has an outer layer, the neocortex, and an inner allocortex. The neocortex is made up of six Cerebral cortex#Layers of neocortex, neuronal layers, while the allocortex has three or four. Each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dream
A dream is a succession of images, ideas, emotions, and sensations that usually occur involuntarily in the mind during certain stages of sleep. Humans spend about two hours dreaming per night, and each dream lasts around 5 to 20 minutes, although the dreamer may perceive the dream as being much longer than this. The content and function of dreams have been topics of scientific, philosophical and religious interest throughout recorded history. Dream interpretation, practiced by the Babylonians in the third millennium BCE and even earlier by the ancient Sumerians, figures prominently in religious texts in several traditions, and has played a lead role in psychotherapy. The scientific study of dreams is called oneirology. Most modern dream study focuses on the neurophysiology of dreams and on proposing and testing hypotheses regarding dream function. It is not known where in the brain dreams originate, if there is a single origin for dreams or if multiple regions of the bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep And Learning
Multiple hypotheses explain the possible connections between sleep and learning in humans. Research indicates that sleep does more than allow the brain to rest; it may also aid the consolidation of long-term memories. REM sleep and slow-wave sleep play different roles in memory consolidation. REM is associated with the consolidation of nondeclarative (implicit) memories. An example of a nondeclarative memory would be a task that we can do without consciously thinking about it, such as riding a bike. Slow-wave, or non-REM (NREM) sleep, is associated with the consolidation of declarative (explicit) memories. These are facts that need to be consciously remembered, such as dates for a history class. Increased learning Popular sayings can reflect the notion that remolded memories produce new creative associations in the morning, and that performance often improves after a time-interval that includes sleep. Current studies demonstrate that a healthy sleep produces a significant learni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep
Sleep is a sedentary state of mind and body. It is characterized by altered consciousness, relatively inhibited Perception, sensory activity, reduced muscle activity and reduced interactions with surroundings. It is distinguished from wakefulness by a decreased ability to react to stimulus (physiology), stimuli, but more reactive than a coma or disorders of consciousness, with sleep displaying different, active brain patterns. Sleep occurs in sleep cycle, repeating periods, in which the body alternates between two distinct modes: REM sleep and non-rapid eye movement sleep, non-REM sleep. Although REM stands for "rapid eye movement", this mode of sleep has many other aspects, including virtual paralysis of the body. dream, Dreams are a succession of images, ideas, emotions, and sensations that usually occur involuntarily in the mind during certain stages of sleep. During sleep, most of the human body, body's systems are in an anabolic state, helping to restore the Immunity (medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testing Effect
The testing effect (also known as retrieval practice, active recall, practice testing, or test-enhanced learning) suggests long-term memory is increased when some of the learning period is devoted to retrieving information from memory. It is different from more general ''practice effect'', defined in the APA Dictionary of Psychology as "any change or improvement that results from practice or repetition of task items or activities." Cognitive psychologists are working with educators to look at how to take advantage of tests—not as an assessment tool, but as a teaching tools as testing prior knowledge is more beneficial for learning when compared to reading or passively studying material, even more so when the test is more challenging for memory. History Before much experimental evidence had been collected, the utility of testing was already evident to some perceptive observers including Francis Bacon who discussed it as a learning strategy as early as 1620. ''"Hence if you ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recall (memory)
Recall in memory refers to the mental process of retrieval of information from the past. Along with encoding and storage, it is one of the three core processes of memory. There are three main types of recall: free recall, cued recall and serial recall. Psychologists test these forms of recall as a way to study the memory processes of humansrecall. (2010). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved March 04, 2010, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online: http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/493353/recal/ref> and animals. Two main theories of the process of recall are the two-stage theory and the theory of Encoding specificity principle, encoding specificity. Theories Two-stage theory The ''two-stage theory'' states that the process of recall begins with a search and retrieval process, and then a decision or recognition process where the correct information is chosen from what has been retrieved. In this theory, recognition only involves the latter of these two stages, or processes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |