|
Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation
The Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation is an American aircraft, a member of the Lockheed Constellation aircraft line. The L-1049 was Lockheed's response to the successful Douglas DC-6 airliner, first flying in 1950. The aircraft was also produced for both the United States Navy as the WV / R7V and U.S. Air Force as the C-121 for transport, electronics, and airborne early warning and control aircraft. Development Beginning in 1943, Lockheed planned stretched variants of the Constellation family. The first was the L-049 with a fuselage lengthened by 13 feet (4 meters) and the second the L-749 stretched 18 feet (5.5 meters). Douglas launched a stretched version of its DC-6 airliner as a cargo transport, designated DC-6A, for both military and civilian operators. Douglas was soon to launch a passenger version (the DC-6B) of this new aircraft. The DC-6B could carry 23 more passengers than Lockheed's current production L-749 Constellation. In 1950, Lockheed had repurchased the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Aircraft Company
The Douglas Aircraft Company was an American aerospace manufacturer based in Southern California. It was founded in 1921 by Donald Wills Douglas Sr. and later merged with McDonnell Aircraft in 1967 to form McDonnell Douglas; it then operated as a division of McDonnell Douglas. McDonnell Douglas later merged with Boeing in 1997. History 1920s The company was founded as the Douglas Company by Donald Wills Douglas Sr. on July 22, 1921 in Santa Monica, California, following dissolution of the Davis-Douglas Company. An early claim to fame was the first circumnavigation of the world by air in Douglas airplanes in 1924. In 1923, the U.S. Army Air Service was interested in carrying out a mission to circumnavigate the Earth for the first time by aircraft, a program called "World Flight". Donald Douglas proposed a modified Douglas DT to meet the Army's needs. The two-place, open cockpit DT biplane torpedo bomber had previously been produced for the U.S. Navy.Rumerman, Judy. "The Dougla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qantas
Qantas Airways Limited ( ) is the flag carrier of Australia and the country's largest airline by fleet size, international flights, and international destinations. It is the world's third-oldest airline still in operation, having been founded in November 1920; it began international passenger flights in May 1935. ''Qantas'' is an acronym of the airline's original name, Queensland and Northern Territory Aerial Services, as it originally served Queensland and the Northern Territory, and is popularly nicknamed "The Flying Kangaroo". Qantas is a founding member of the Oneworld airline alliance. The airline is based in the Sydney suburb of Mascot, adjacent to its main hub at Sydney Airport. , Qantas had a 65 per cent share of the Australian domestic market and carried 14.9 per cent of all passengers travelling into and out of Australia. Various subsidiary airlines operate to regional centres and on some trunk routes within Australia under the QantasLink banner. Qantas also owns Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-Canada Air Lines
Trans-Canada Air Lines (also known as TCA in English, and Trans-Canada in French) was a Canadian airline that operated as the country's flag carrier, with corporate headquarters in Montreal, Quebec. Its first president was Gordon Roy McGregor. Founded in 1937, it was renamed Air Canada in 1965. History With heavy involvement from C. D. Howe, a senior minister in the Mackenzie King cabinet, TCA was created by the Crown Corporation Canadian National Railway (CNR), and launched its first flight on 1 September 1937, on a flight between Vancouver and Seattle. An air-mail contract with Royal Mail Canada was one of the methods by which TCA was financed.http://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.com/articles/postal-system The creation of TCA was partly by CNR management who wanted to expand the company into the new field of passenger aviation, and was partly by government direction. Prior to TCA, no large national airline existed in Canada. With war looming, and other nations (primarily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air France
Air France (; formally ''Société Air France, S.A.''), stylised as AIRFRANCE, is the flag carrier of France headquartered in Tremblay-en-France. It is a subsidiary of the Air France–KLM Group and a founding member of the SkyTeam global airline alliance. , Air France serves 36 destinations in France and operates worldwide scheduled passenger and cargo services to 175 destinations in 78 countries (93 including overseas departments and territories of France) and also carried 46,803,000 passengers in 2019. The airline's global hub is at Charles de Gaulle Airport with Orly Airport as the primary domestic hub. Air France's corporate headquarters, previously in Montparnasse, Paris, are located on the grounds of Charles de Gaulle Airport, north of Paris. Air France was formed on 7 October 1933 from a merger of Air Orient, Air Union, Compagnie Générale Aéropostale, Compagnie Internationale de Navigation Aérienne (CIDNA), and Société Générale de Transport Aérien (SGTA) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Fixture
A light fixture (US English), light fitting (UK English), or luminaire is an electrical device containing an electric lamp that provides illumination. All light fixtures have a fixture body and one or more lamps. The lamps may be in sockets for easy replacement—or, in the case of some LED fixtures, hard-wired in place. Fixtures may also have a switch to control the light, either attached to the lamp body or attached to the power cable. Permanent light fixtures, such as dining room chandeliers, may have no switch on the fixture itself, but rely on a wall switch. Fixtures require an electrical connection to a power source, typically AC mains power, but some run on battery power for camping or emergency lights. Permanent lighting fixtures are directly wired. Movable lamps have a plug and cord that plugs into a wall socket. Light fixtures may also have other features, such as reflectors for directing the light, an aperture (with or without a lens), an outer shell or housing f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armor Plating
Military vehicles are commonly armoured (or armored; see spelling differences) to withstand the impact of shrapnel, bullets, shells, rockets, and missiles, protecting the personnel inside from enemy fire. Such vehicles include armoured fighting vehicles like tanks, aircraft, and ships. Civilian vehicles may also be armoured. These vehicles include cars used by officials (e.g., presidential limousines), reporters and others in conflict zones or where violent crime is common. Civilian armoured cars are also routinely used by security firms to carry money or valuables to reduce the risk of highway robbery or the hijacking of the cargo. Armour may also be used in vehicles to protect from threats other than a deliberate attack. Some spacecraft are equipped with specialised armour to protect them against impacts from micrometeoroids or fragments of space debris. Modern aircraft powered by jet engines usually have them fitted with a sort of armour in the form of an aramid composite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced by a turbine can be used for generating electrical power when combined with a generator.Munson, Bruce Roy, T. H. Okiishi, and Wade W. Huebsch. "Turbomachines." Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics. 6th ed. Hoboken, NJ: J. Wiley & Sons, 2009. Print. A turbine is a turbomachine with at least one moving part called a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades so that they move and impart rotational energy to the rotor. Early turbine examples are windmills and waterwheels. Gas, steam, and water turbines have a casing around the blades that contains and controls the working fluid. Credit for invention of the steam turbine is given both to Anglo-Irish engineer Sir Charles Parsons (1854–1931) for invention of the reaction turbine, and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
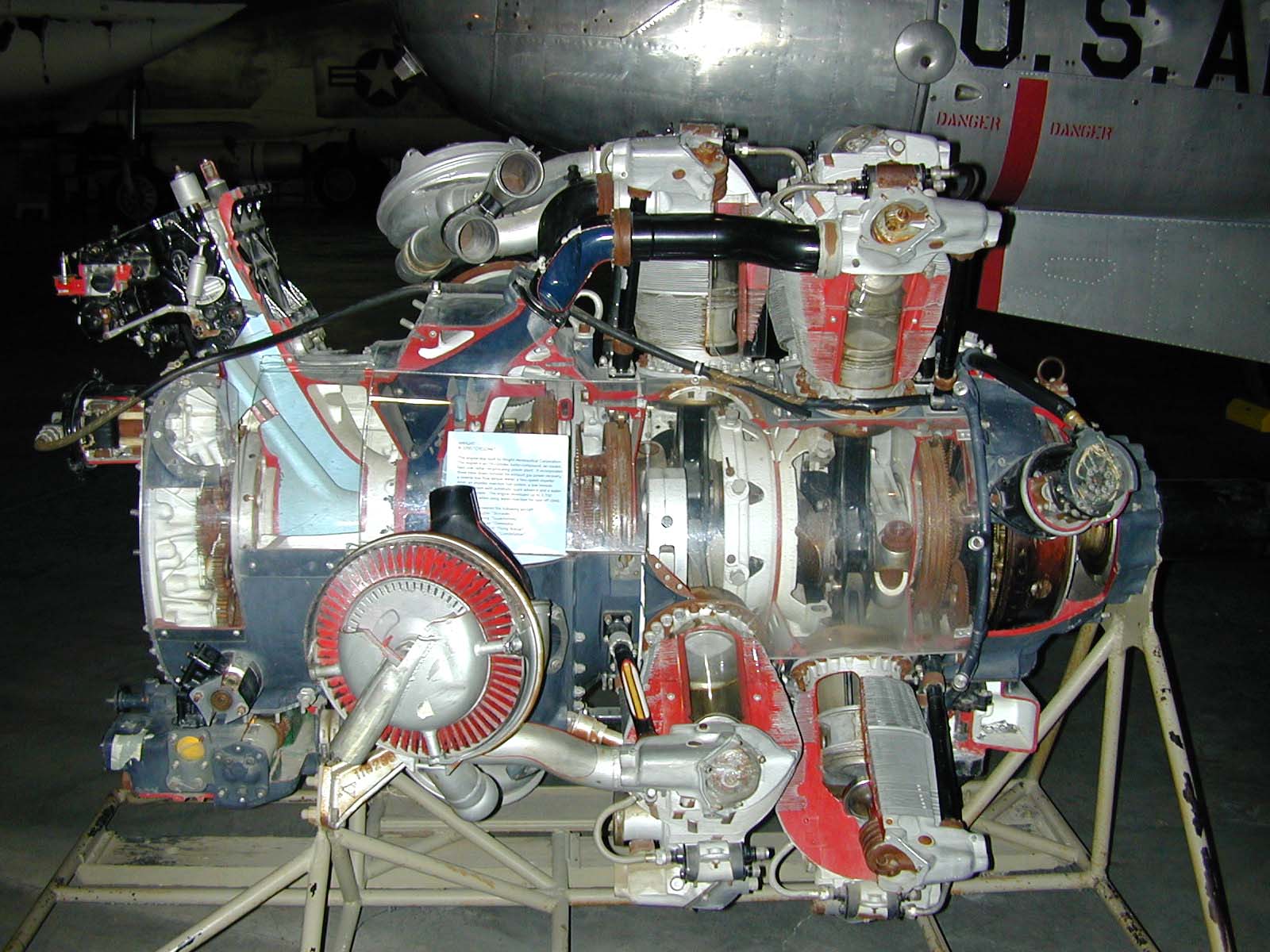
Turbo-compound Engine
A turbo-compound engine is a reciprocating engine that employs a turbine to recover energy from the exhaust gases. Instead of using that energy to drive a turbocharger as found in many high-power aircraft engines, the energy is instead sent to the output shaft to increase the total power delivered by the engine. The turbine is usually mechanically connected to the crankshaft, as on the Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone, but electric and hydraulic power recovery systems have been investigated as well. As this recovery process does not increase fuel consumption, it has the effect of reducing the specific fuel consumption, the ratio of fuel use to power. Turbo-compounding was used for commercial airliners and similar long-range, long-endurance roles before the introduction of turbojet engines. Examples using the Duplex-Cyclone include the Douglas DC-7B and Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation, while other designs did not see production use. Concept Most piston engines have a hot exhau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed L1049 F-BGNG Air France LAP 08
Lockheed (originally spelled Loughead) may refer to: Brands and enterprises * Lockheed Corporation, a former American aircraft manufacturer * Lockheed Martin, formed in 1995 by the merger of Lockheed Corporation and Martin Marietta ** Lockheed Martin Aeronautics ** Lockheed Martin Space Systems * Lockheed Shipbuilding and Construction Company People * Flora Haines Loughead (1855-1943), American writer, farmer, miner * The brothers who founded the original Lockheed Corporation: ** Allan Loughead (1889–1969), American aviation pioneer ** Malcolm Loughead, American aviation pioneer Other uses * Lockheed (comics) Lockheed is a fictional character appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. The character appears most commonly in association with the X-Men. He is an alien dragon and longtime companion of Shadowcat (Kitty Pryde), a member of ..., a Marvel Comics character * Lockheed Martin Transit Center, in Sunnyvale, California {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wright R-3350
The Wright R-3350 Duplex-Cyclone is an American twin-row, supercharged, air-cooled, radial aircraft engine with 18 cylinders displacing nearly . Power ranged from 2,200 to over 3,700 hp (1,640 to 2,760 kW), depending on the model. Developed before World War II, the R-3350's design required a long time to mature before finally being used to power the Boeing B-29 Superfortress. After the war, the engine had matured sufficiently to become a major civilian airliner design, notably in its turbo-compound forms, and was used in the Lockheed L-1049 Super Constellation airliners into the 1990s. The engine is commonly used on Hawker Sea Fury and Grumman F8F Bearcat Unlimited Class Racers at the Reno Air Races. Its main rival was the , Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major, first run some seven years after the Duplex-Cyclone's beginnings. Design and development In 1927, Wright Aeronautical introduced its famous "Cyclone" engine, which powered a number of designs in the 193 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratt & Whitney R-2800
The Pratt & Whitney R-2800 Double Wasp is an American twin-row, 18-cylinder, air-cooled radial aircraft engine with a displacement of , and is part of the long-lived Wasp family of engines. The R-2800 saw widespread use in many important American aircraft during and after World War II. During the war years, Pratt & Whitney continued to develop new ideas to upgrade the engine, including water injection for takeoff in cargo and passenger planes and to give emergency power in combat. Design and development First run in 1937, near the time that the larger competing 18-cylinder Wright Duplex-Cyclone's development had been started in May of that year, the displacement R-2800 was first-flown by 1940, one year before the Duplex-Cyclone. The Double Wasp was more powerful than the world's only other modern 18-cylinder engine, the Gnome-Rhône 18L of . The Double Wasp was much smaller in displacement than either of the other 18-cylinder designs, and heat dissipation was a gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |