|
Lizzy Lind Af Hageby
Emilie Augusta Louise "Lizzy" Lind af Hageby (20 September 1878 – 26 December 1963) was a Swedish-British feminist and animal rights advocate who became a prominent anti-vivisection activist in England in the early 20th century. Born to a distinguished Swedish family, Lind af Hageby and another Swedish activist enrolled at the London School of Medicine for Women in 1902 to advance their anti-vivisectionist education. The women attended vivisections at University College London, and in 1903 published their diary, ''The Shambles of Science: Extracts from the Diary of Two Students of Physiology'', which accused researchers of having vivisected a dog without adequate anaesthesia. The ensuing scandal, known as the Brown Dog affair, included a libel trial, damages for one of the researchers, and rioting in London by medical students.Coral Lansbury, ''The Old Brown Dog: Women, Workers, and Vivisection in Edwardian England'', University of Wisconsin Press, 1985, pp. 9–11. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jönköping
Jönköping (, ) is a city in southern Sweden with 112,766 inhabitants (2022). Jönköping is situated on the southern shore of Sweden's second largest lake, Vättern, in the province of Småland. The city is the seat of Jönköping Municipality, which has a population of 144,699 (2022) and is Småland's most populous municipality. Jönköping is also the seat of Jönköping County which has a population of 367,064 (2022). Jönköping is the seat of a district court and a court of appeal as well as the Swedish National Courts Administration. It is the seat of the Swedish Board of Agriculture. County government The Jönköping municipality has its headquarters in a place called "rådhuset". Rådhuset is an important component of the function of the municipality as it works as a state office for different departments of and in jönköping. Rådhuset is dependent on the municipality but is its own entity, the head of the rådhuset has political power but is not the head of the jö ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helen Rappaport
Helen F. Rappaport (née Ware; born June 1947), is a British author and former actress. She specialises in the Victorian era and revolutionary Russia. Early life and education Rappaport was born Helen Ware in Bromley, grew up near the River Medway in North Kent and attended Chatham Grammar School for Girls. Her older brother Mike Ware, born 1939, is a photographer, chemist, and writer. She has twin younger brothers, Peter (also a photographer) and Christopher, born in 1953. She studied Russian at Leeds University where she was involved in the university Theatre Group and launched her acting career. Career Acting After acting with the Leeds University Theatre Group she appeared in several television series including ''Crown Court'', ''Love Hurts'' and ''The Bill''. She later claimed to have spent '20 years in the doldrums as an out of work, broke and miserable actress'... Writing In the early nineties she became a copy editor for academic publishers Blackwell and OUP and also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Coleridge
Stephen William Buchanan Coleridge (31 May 1854 – 10 April 1936) was an English author, barrister, opponent of vivisection, and co-founder of the National Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Children. Biography Coleridge was the second son of John Duke Coleridge, Lord Chief Justice of England, and Jane Fortescue Seymour, an accomplished artist. His grandfather was nephew to the famous poet Samuel Taylor Coleridge. At fourteen he was sent to the public school Bradfield College; this seems to have rankled since his father, grandfather and elder brother were all educated at the more prestigious Eton. He attended Trinity College, Cambridge, where he graduated in 1878. Coleridge came to widespread public attention in England in 1903, when he publicly accused William Bayliss of the Department of Physiology at University College London of having broken the law during an experiment on a dog, thereby sparking the Brown Dog affair. Bayliss sued for libel and was awarded damages o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
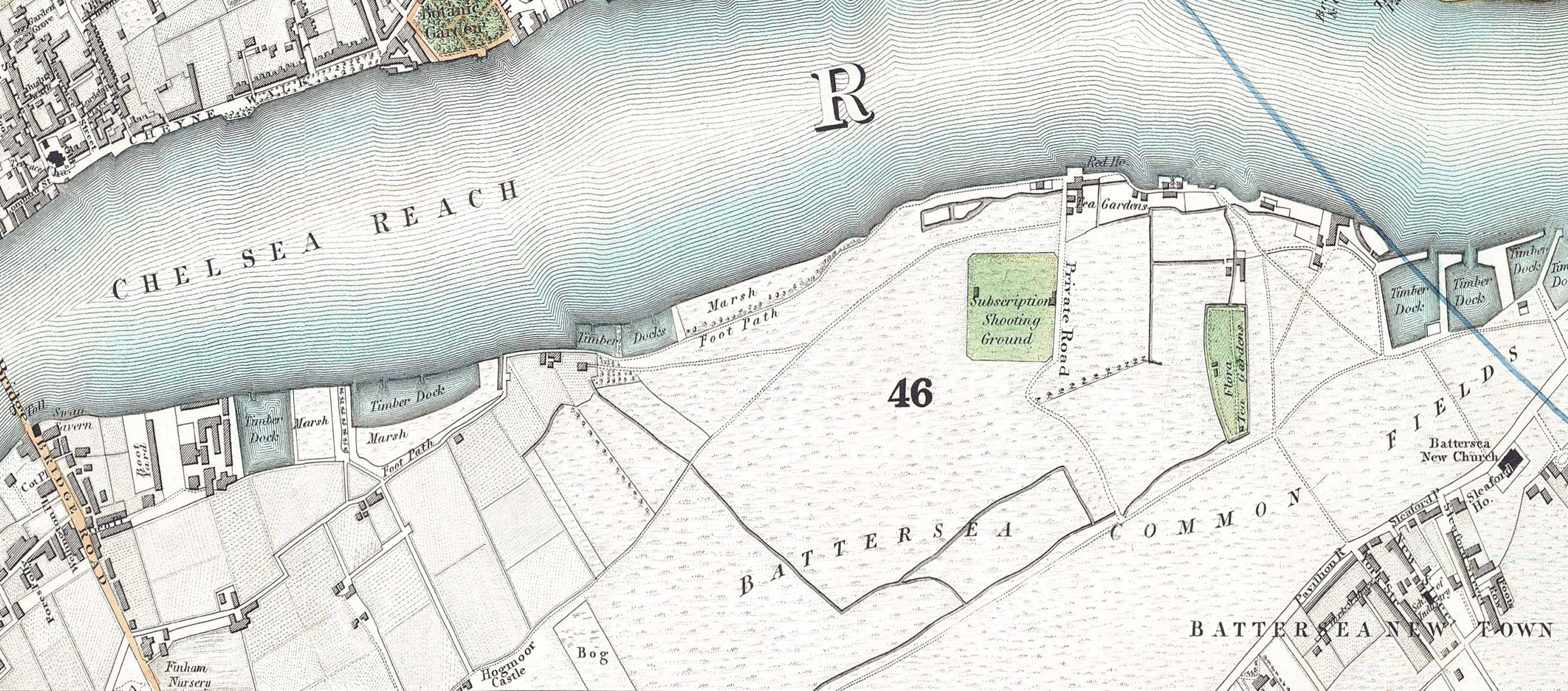
Battersea Park
Battersea Park is a 200-acre (83-hectare) green space at Battersea in the London Borough of Wandsworth in London. It is situated on the south bank of the River Thames opposite Chelsea and was opened in 1858. The park occupies marshland reclaimed from the Thames and land formerly used for market gardens. The park is Grade II* listed on the Register of Historic Parks and Gardens. History Prior to 1846, the area now covered by the park was known as Battersea fields, a popular spot for duelling. On 21 March 1829, the Duke of Wellington and the Earl of Winchilsea met on Battersea fields to settle a matter of honour. When it came time to fire, the duke aimed his duelling pistol wide and Winchilsea fired his into the air. Winchilsea later wrote the duke a groveling apology. Separated from the river by a narrow raised causeway, the fields consisted of low, fertile marshes intersected by streams and ditches with the chief crops being carrots, melons, lavender (all the way up to Lave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trafalgar Square
Trafalgar Square ( ) is a public square in the City of Westminster, Central London, laid out in the early 19th century around the area formerly known as Charing Cross. At its centre is a high column bearing a statue of Admiral Nelson commemorating the victory at the Battle of Trafalgar. The battle of 21 October 1805, established the British navy's dominance at sea in the Napoleonic Wars over the fleets of France and Spain. The site around Trafalgar Square had been a significant landmark since the 1200s. For centuries, distances measured from Charing Cross have served as location markers. The site of the present square formerly contained the elaborately designed, enclosed courtyard of the King's Mews. After George IV moved the mews to Buckingham Palace, the area was redeveloped by John Nash, but progress was slow after his death, and the square did not open until 1844. The Nelson's Column at its centre is guarded by four lion statues. A number of commemorative statues and sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Bayliss
Sir William Maddock Bayliss (2 May 1860 – 27 August 1924) was an English physiologist. Life He was born in Wednesbury, Staffordshire but shortly thereafter his father, a successful merchant of ornamental ironwork, moved his family to a house he had built on West Heath Road in Hampstead in north London, which he named St Cuthberts. It stood in four acres of gardens. William was his sole heir. He began to study medicine at University College London in 1880, but dropped out when he failed anatomy. Attracted to physiology, he studied under John Burdon Sanderson at Wadham College, Oxford, where he won a first class degree, investigating electrical changes occurring during salivary secretion. He returned to University College London in 1888 as an assistant to Edward Sharpey-Schafer. In 1890 he began to collaborate with Ernest Starling, who was at Guy's Hospital, on the electrical activity of the heart. They complemented each other in many ways: for instance, Bayliss dealt with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasteur Institute
The Pasteur Institute (french: Institut Pasteur) is a French non-profit private foundation dedicated to the study of biology, micro-organisms, diseases, and vaccines. It is named after Louis Pasteur, who invented pasteurization and vaccines for anthrax and rabies. The institute was founded on 4 June 1887, and inaugurated on 14 November 1888. For over a century, the Institut Pasteur has researched infectious diseases. This worldwide biomedical research organization based in Paris was the first to isolate HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, in 1983. Over the years, it has been responsible for discoveries that have enabled medical science to control diseases such as diphtheria, tetanus, tuberculosis, poliomyelitis, influenza, yellow fever, and plague. Since 1908, ten Institut Pasteur scientists have been awarded the Nobel Prize for medicine and physiology—the 2008 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was shared between two Pasteur scientists. History The Institut Pasteur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embroidery
Embroidery is the craft of decorating fabric or other materials using a needle to apply thread or yarn. Embroidery may also incorporate other materials such as pearls, beads, quills, and sequins. In modern days, embroidery is usually seen on caps, hats, coats, overlays, blankets, dress shirts, denim, dresses, stockings, scarfs, and golf shirts. Embroidery is available in a wide variety of thread or yarn colour. Some of the basic techniques or stitches of the earliest embroidery are chain stitch, buttonhole or blanket stitch, running stitch, satin stitch, and cross stitch. Those stitches remain the fundamental techniques of hand embroidery today. History Origins The process used to tailor, patch, mend and reinforce cloth fostered the development of sewing techniques, and the decorative possibilities of sewing led to the art of embroidery. Indeed, the remarkable stability of basic embroidery stitches has been noted: The art of embroidery has been found worldwide and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheltenham Ladies College
Cheltenham Ladies' College is an independent boarding and day school for girls aged 11 to 18 in Cheltenham, Gloucestershire, England. Consistently ranked as one of the top all-girls' schools nationally, the school was established in 1853 to provide "a sound academic education for girls". It is also a member of the Headmasters' and Headmistresses' Conference. The school badge depicts two pigeons, taken from the Cheltenham town coat of arms, above three stars, which are in turn above a daisy, a school symbol. In 2020, Cheltenham Ladies' College was named Southwest Independent School of the Decade by ''The Times and The Sunday Times''. History The school was founded in 1853 after six individuals, including the Principal and Vice-Principal of Cheltenham College for Boys and four other men, decided to create a girls' school that would be similar to Cheltenham College for Boys. On 13 February 1854, the first 82 pupils began attending the school, with Annie Procter serving as the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamberlain (office)
A chamberlain (Medieval Latin: ''cambellanus'' or ''cambrerius'', with charge of treasury ''camerarius'') is a senior royal official in charge of managing a royal household. Historically, the chamberlain superintends the arrangement of domestic affairs and was often also charged with receiving and paying out money kept in the royal chamber. The position was usually honoured upon a high-ranking member of the nobility (nobleman) or the clergy, often a royal favourite. Roman emperors appointed this officer under the title of ''cubicularius''. The Chamberlain of the Holy Roman Church enjoys very extensive powers, having the revenues of the papal household under his charge. As a sign of their dignity, they bore a key, which in the seventeenth century was often silvered, and actually fitted the door-locks of chamber rooms. Since the eighteenth century, it has turned into a merely symbolic, albeit splendid, rank-insignia of gilded bronze. In many countries there are ceremonial posts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Nation And Athenæum
''The Nation and Athenaeum'', or simply ''The Nation'', was a United Kingdom political weekly newspaper with a Liberal/Labour viewpoint. It was formed in 1921 from the merger of the ''Athenaeum'', a literary magazine published in London since 1828, and the smaller and newer ''Nation'', edited by Henry William Massingham. The enterprise was purchased by a group led by the economist John Maynard Keynes in 1923. From then on, it carried numerous articles by Keynes. From 1923 to 1930, the editor was Liberal economist Hubert Douglas Henderson, and the literary editor was Leonard Woolf, who would help impecunious young authors, including Robert Graves and E. M. Forster he knew through the Hogarth Press by commissioning them to write reviews and articles; there were others, such as Edwin Muir who had come to his attention at the Nation and whose work he would publish at Hogarth. Other contributors included Edmund Blunden, H. E. Bates, H. N. Brailsford, J. A. Hobson, Harold Laski, David ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |