|
Liye
Liye () is a town of Longshan County, Hunan Province, China. Located on the northern bank of You River (), Liye is the southernmost town of the county, and bordered to the west by Youshuihe Town () and Keda Township () of Youyang County, Daxi Township () of Xiushan County of Chongqing Municipality, to the south by Qingshuiping () and Bier Towns () of Baojing County, to the east and southeast by Maoertan Town (), to the southwest by Zaguo Township (). The present-day Liye was reformed on November 30, 2015. It covers an area of , as of November, 2015, it has a registered population of 43,300, the seat is Liye Community.the divisions of Longshan County in 2015, according to the result on adjustment of township-level administrative divisions of Longshan County on November 30, 2015 - 《湖南省民政厅关于同意龙山县乡镇区划调整方案的批复》(湘民行发〔2015〕117号)rednet.cn also see 《湖南省乡镇区划调整改革109个县市区批复方案》o/ref> Cultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qin Slips Of Liye
The Liye Qin Slips () is a large collection of bamboo slips which were unearthed from Liye Ancient City in Longshan County, Hunan, China in 2002. It is one of China's most important archaeological discoveries of the 21st century.The archaeological discovery of Liye bamboo slips of the Qin dynastychina.org.cn (19-Jul-02) Archaeologists found more than 37,000 pieces of bamboo slips, on which more than 200,000 Chinese characters record government and legal documents of the Qin dynasty. It is considered the most important archaeological discovery of the Qin dynasty after the Terracotta Army unearthed in 1973 in Xi'an. Main content The Liye bamboo slip documents and archives fully embody a wide range of document types and terms, the constant growth of administrative and judicial document styles. Among them are more than 68 types of archives and content, which have high value of supplementing and testifying history facts. Some in the academic circles have argued that its importance is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient City Ruins Of Liye
The Liye Ancient City () is an archaeological site in Liye Town, Longshan County, Hunan Province, China. It was of seat of the ancient Qianling County () in Dongting Commandery () of the Qin dynasty (221–206 BC). It is known for 37,400 Qin bamboo slips unearthed in 2002. The city was built by the Kingdom of Chu in the late Warring States period, reconstructed in the Qin dynasty and abandoned in the early Western Han dynasty. It was approved as a historical and cultural site protected at the national level in Hunan on November 22, 2002. The Liye Qin Slips Museum and the Ruins Park were officially opened on October 28, 2010.About the Ancient City Ruins of Liye - 里耶古城遗址lygcyz.com Archeology In June 1985, a group of bricklayers digging to make bricks excavated ancient potteries and weapons, the archaeologists had gradually carried out archaeological excavations there since then. As part of the Wanmipo Hydropower station () construction, the archaeologists from Hunan Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
You River (Tributary Of Yuan River)
The You River () is the largest tributary of the Yuan River, one of main rivers in the Wuling Mountains in Southwest China. Its other name is Gengshi River (); it was called Youxi River () in ancient times.酉水的魅力 (Chinese)enshi.cn (25-Jun-15)/ref> Its trunk stream flows through Hubei, Chongqing and Hunan, and its drainage basin reaches into Guizhou. Its watershed covers an area of , including of Hubei, of Hunan, of Chongqing and of Guizhou; it has a length of . The valley of the You River was home of the ancient Ba people, the ancestors of the Tujia people. The You River basin is one of the birthplaces of Chinese civilization: the Qin Dynasty Bamboo Slips of Liye and the Tusi Sites of Laosicheng and Tangya were discovered in the region. Headwaters The You River has two headstreams, the north and south sources. The north source, the Beihe River () is the main stream; it originates in the Qizimei Mountains () in Xuan'en County of Hubei. The south source, commonly na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longshan County
Longshan County () is a county of Hunan Province, China, it is under the administration of Xiangxi Autonomous Prefecture. Located on the western margin of the province and the north western Xiangxi, it is immediately adjacent to the borders of Chongqing Municipality and Hubei Province. The county is bordered to the northeast by Sangzhi County, to the east by Yongshun County, to the southeast and the south by Baojing County, to the west by Youyang County of Chongqing, Laifeng County and Xuan'en County of Hubei. Longshan County covers , as of 2015, It had a registered population of 601,000 and a resident population of 492,800.the population of Longshan County in 2015, according to the oahmhxc.com/ref> The county has 12 towns, 5 townships and 4 subdistricts under its jurisdiction, the county seat is Min'an Subdistrict ().the divisions of Longshan County in 2015, according to the , also see oxinhuanet.com/ref> History The 2014 Hunan military training incident occurred at a seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Township-level Divisions Of Hunan
This is a list of Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China#Township level, township-level divisions of the province of Hunan, China. Changsha City Furong District Tianxin District Yuelu District Kaifu District Yuhua District Wangcheng District Changsha County Ningxiang City Liuyang City Zhuzhou City Hetang District Lusong District Shifeng District Tianyuan District Liling City Chaling County Yanling County You County Lukou District Xiangtan City Yuetang District Yuhu District Shaoshan City Xiangxiang City Xiangtan County Hengyang City Nanyue District Shigu District Yanfeng District Zhengxiang District Zhuhui District Changning City Leiyang City Hengdong County Hengnan County Hengshan County Hengyang County Qidong County Shaoyang City Beita District Daxiang District Shuangqing District Wugang City Chengbu County Dongkou County Longhui Count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Towns Of China
When referring to political divisions of China, town is the standard English translation of the Chinese (traditional: ; ). The Constitution of the People's Republic of China classifies towns as third-level administrative units, along with for example townships (). A township is typically smaller in population and more remote than a town. Similarly to a higher-level administrative units, the borders of a town would typically include an urban core (a small town with the population on the order of 10,000 people), as well as rural area with some villages (, or ). Map representation A typical provincial map would merely show a town as a circle centered at its urban area and labeled with its name, while a more detailed one (e.g., a map of a single county-level division) would also show the borders dividing the county or county-level city into towns () and/or township () and subdistrict (街道) units. The town in which the county level government, and usually the division's mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Towns Of Xiangxi Tujia And Miao Autonomous Prefecture
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world. Origin and use The word "town" shares an origin with the German word , the Dutch word , and the Old Norse . The original Proto-Germanic word, *''tūnan'', is thought to be an early borrowing from Proto-Celtic *''dūnom'' (cf. Old Irish , Welsh ). The original sense of the word in both Germanic and Celtic was that of a fortress or an enclosure. Cognates of ''town'' in many modern Germanic languages designate a fence or a hedge. In English and Dutch, the meaning of the word took on the sense of the space which these fences enclosed, and through which a track must run. In England, a town was a small community that could not afford or was not allowed to build walls or other larger fortifications, and built a palisade or stockade instead. In the Netherlands, this space was a garden, more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terracotta Army
The Terracotta Army is a collection of terracotta sculptures depicting the armies of Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of China. It is a form of funerary art buried with the emperor in 210–209 BCE with the purpose of protecting the emperor in his afterlife. The figures, dating from approximately the late third century BCE, were discovered in 1974 by local farmers in Lintong County, outside Xi'an, Shaanxi, China. The figures vary in height according to their roles, the tallest being the generals. The figures include warriors, chariots and horses. Estimates from 2007 were that the three pits containing the Terracotta Army held more than 8,000 soldiers, 130 chariots with 520 horses, and 150 cavalry horses, the majority of which remained buried in the pits near Qin Shi Huang's mausoleum. Other terracotta non-military figures were found in other pits, including officials, acrobats, strongmen, and musicians. History The construction of the tomb was described by historian Sima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qin Dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ; zh, c=秦朝, p=Qín cháo, w=), or Ch'in dynasty in Wade–Giles romanization ( zh, c=, p=, w=Ch'in ch'ao), was the first Dynasties in Chinese history, dynasty of Imperial China. Named for its heartland in Qin (state), Qin state (modern Gansu and Shaanxi), the Qin dynasty arose as a fief of the Western Zhou and endured for over five centuries until 221 BCE when it founded its brief empire, which lasted only until 206 BCE. It often causes confusion that the ruling family of the Qin kingdom (what is conventionally called a "dynasty") ruled for over five centuries, while the "Qin Dynasty," the conventional name for the first Chinese empire, comprises the last fourteen years of Qin's existence. The divide between these two periods occurred in 221 BCE when King Zheng of Qin declared himself the Qin Shi Huang, First Emperor of Qin, though he had already been king of Qin since 246 BCE. Qin was a minor power for the early centuries of its existence. The streng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relic
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains of a saint or the personal effects of the saint or venerated person preserved for purposes of veneration as a tangible memorial. Relics are an important aspect of some forms of Buddhism, Christianity, Islam, shamanism, and many other religions. ''Relic'' derives from the Latin ''reliquiae'', meaning "remains", and a form of the Latin verb ''relinquere'', to "leave behind, or abandon". A reliquary is a shrine that houses one or more religious relics. In classical antiquity In ancient Greece, a polis, city or Greek temple, sanctuary might claim to possess, without necessarily displaying, the remains of a venerated hero as a part of a Greek hero cult, hero cult. Other venerable objects associated with the hero were more likely to be on display in sanctuaries, such as spears, shields, or other weaponry; chariots, ships or Figurehead (object), figureheads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and porcelain. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is also called a ''pottery'' (plural "potteries"). The definition of ''pottery'', used by the ASTM International, is "all fired ceramic wares that contain clay when formed, except technical, structural, and refractory products". In art history and archaeology, especially of ancient and prehistoric periods, "pottery" often means vessels only, and sculpted figurines of the same material are called "terracottas". Pottery is one of the oldest human inventions, originating before the Neolithic period, with ceramic objects like the Gravettian culture Venus of Dolní Věstonice figurine discovered in the Czech Republic dating back to 29,000–25,000 BC, and pottery vessels that were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
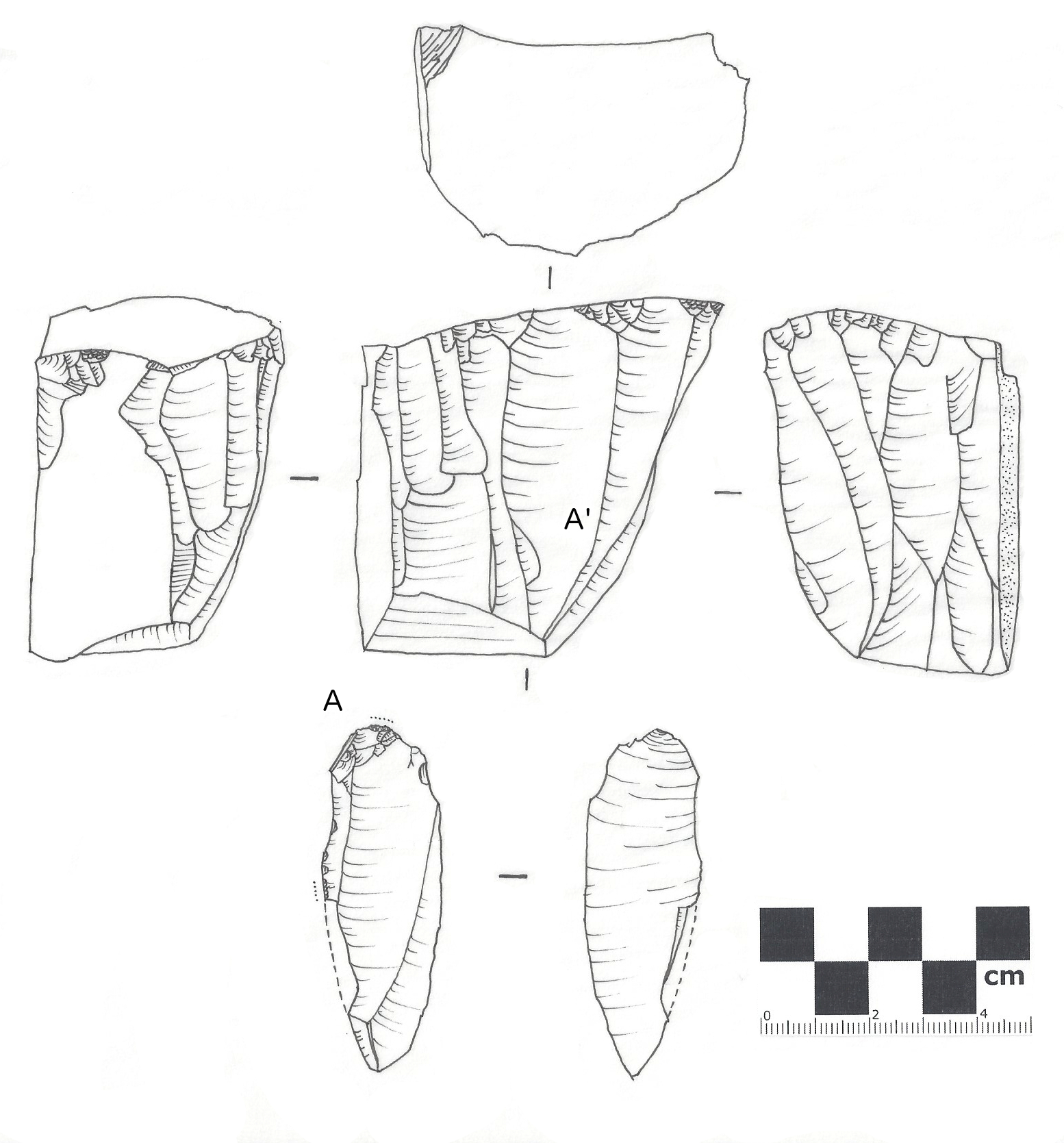
Stone Chip
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and may also be referred to as simply a ''flake'', or collectively as debitage. The objective piece, or the rock being reduced by the removal of flakes, is known as a core.Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press Once the proper tool stone has been selected, a percussor or pressure flaker (e.g., an antler tine) is used to direct a sharp blow, or apply sufficient force, respectively, to the surface of the stone, often on the edge of the piece. The energy of this blow propagates through the material, often ( but not always) producing a Hertzian cone of force which causes the rock to fracture in a controllable fashion. Since cores are often struck on an edge with a suitable angle (<90°) f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)