|
Living Planet Programme
The Living Planet Programme (LPP) is a programme within the European Space Agency which is managed by the Earth Observation Programmes Directorate. LPP consists of two classes of Earth observation missions (listed below) including research missions known as Earth Explorers, and the Earth Watch class of missions whose objective is to develop support operational applications such as numerical weather forecasting or resource management. List of Earth Explorers missions Selected missions Currently there are ten approved Earth Explorer missions, four (SMOS, CryoSat-2, SWARM, Aeolus) of which are in orbit and operating: * GOCE – Gravity Field and Steady-State Ocean Circulation Explorer; it was launched on 17 March 2009. It reentered the atmosphere on 11 November 2013. * SMOS – Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity satellite will study ocean salinity and soil moisture; it was launched on 2 November 2009. * CryoSat – a program designed to map the Earth's ice cover. ** CryoSat-1 was lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Field And Steady-State Ocean Circulation Explorer
The Gravity Field and Steady-State Ocean Circulation Explorer (GOCE) was the first of ESA's Living Planet Programme satellites intended to map in unprecedented detail the Earth's gravity field. The spacecraft's primary instrumentation was a highly sensitive gravity gradiometer consisting of three pairs of accelerometers which measured gravitational gradients along three orthogonal axes. Launched on 17 March 2009, GOCE mapped the deep structure of the Earth's mantle and probed hazardous volcanic regions. It brought new insight into ocean behaviour; this in particular, was a major driver for the mission. By combining the gravity data with information about sea surface height gathered by other satellite altimeters, scientists were able to track the direction and speed of geostrophic ocean currents. The low orbit and high accuracy of the system greatly improved the known accuracy and spatial resolution of the geoid (the theoretical surface of equal gravitational potential on the E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swarm (spacecraft)
Swarm is a European Space Agency (ESA) mission to study the Earth's magnetic field. High-precision and high-resolution measurements of the strength, direction and variations of the Earth's magnetic field, complemented by precise navigation, accelerometer and electric field measurements, will provide data for modelling the geomagnetic field and its interaction with other physical aspects of the Earth system. The results offer a view of the inside of the Earth from space, enabling the composition and processes of the interior to be studied in detail and increase our knowledge of atmospheric processes and ocean circulation patterns that affect climate and weather. Overview The overall objective of the Swarm mission is to build on the experience from the Ørsted and CHAMP missions and to provide the best ever survey of the geomagnetic field (multi-point measurements) and its temporal evolution, to gain new insights into the Earth system by improving our understanding of the Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADM-Aeolus
Aeolus, or, in full, Atmospheric Dynamics Mission-Aeolus (ADM-Aeolus), is an Earth observation satellite operated by the European Space Agency (ESA). It was built by Airbus Defence and Space and launched on 22 August 2018. ADM-Aeolus is the first satellite with equipment capable of performing global wind-component-profile observation and will provide much-needed information to improve weather forecasting. Aeolus is the first satellite capable of observing what the winds are doing on Earth, from the surface of the planet and into the stratosphere 30 km high. The satellite was named after Aeolus, a god from the Greek mythology, the ruler of the winds. Program The program was initially approved in 1999 for a 2007 launch but technological obstacles caused 11 years of delay, as it was launched on 22 August 2018. For an estimated €481 million (US$568 million) program cost, it should provide 64,000 daily profiles from March or April 2019. Its altitude is a low for enough back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Space Agency
, owners = , headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France , coordinates = , spaceport = Guiana Space Centre , seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png , seal_size = 130px , image = Views in the Main Control Room (12052189474).jpg , size = , caption = , acronym = , established = , employees = 2,200 , administrator = Director General Josef Aschbacher , budget = €7.2 billion (2022) , language = English and French (working languages) , website = , logo = European Space Agency logo.svg , logo_caption = Logo , image_caption = European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) Main Control Room The European Space Agency (ESA; french: Agence spatiale européenne , it, Agenzia Spaziale Europea, es, Agencia Espacial Europea ASE; german: Europäische Weltraumorganisation) is an intergovernmental organisation of 22 member states dedicated to the exploration of space. Established in 1975 and headquartered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Far-infrared Outgoing Radiation Understanding And Monitoring
FORUM (Far-infrared Outgoing Radiation Understanding and Monitoring) is an Earth observing satellite that is scheduled to launch in 2027. The FORUM mission is led by the European Space Agency (ESA) and has as its main goal the study of the Earth's radiation budget. It is expected that FORUM's measurements will be improving climate models and offer new insights into the way climate change is affecting the planet. Background On 24 September 2019, ESA announced that FORUM was selected to become the ninth Earth Explorer mission, beating the Sea surface KInematics Multiscale monitoring (SKIM) proposal following a two-year feasibility study phase. The main scientific purpose of FORUM is to better understand the Earth's radiation budget - the balance between the incoming radiation mostly from the Sun at short wavelengths, and outgoing radiation, which is a combination of reflected radiation from the Sun and radiation emitted by the Earth system, much of it a longer wavelengths - a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
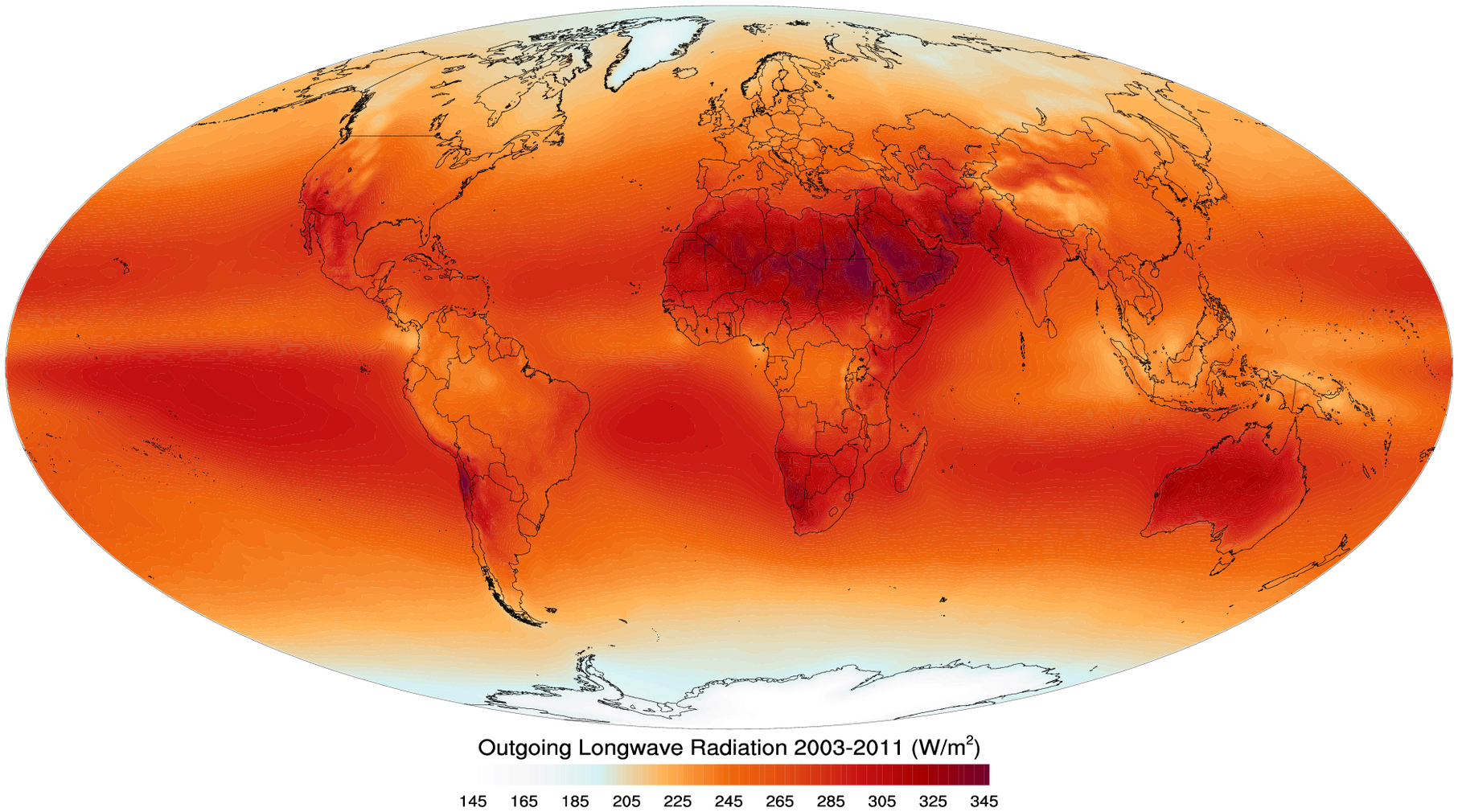
Outgoing Longwave Radiation
Outgoing Long-wave Radiation (OLR) is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths from 3–100 μm emitted from Earth and its atmosphere out to space in the form of thermal radiation. It is also referred to as up-welling long-wave radiation and terrestrial long-wave flux, among others. The flux of energy transported by outgoing long-wave radiation is measured in W/m2. In the Earth's climate system, long-wave radiation involves processes of absorption, scattering, and emissions from atmospheric gases, aerosols, clouds and the surface. Over 99% of outgoing long-wave radiation has wavelengths between 4 μm and 100 μm, in the thermal infrared part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Contributions with wavelengths larger than 40 μm are small, therefore often only wavelengths up to 50 μm are considered . In the wavelength range between 4 μm and 10 μm the spectrum of outgoing long-wave radiation overlaps that of solar radiation, and for various applica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Far-infrared
Far infrared (FIR) is a region in the infrared spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. Far infrared is often defined as any radiation with a wavelength of 15 micrometers (μm) to 1 mm (corresponding to a range of about 20 THz to 300 GHz), which places far infrared radiation within the CIE IR-B and IR-C bands. The long-wave side of the FIR spectrum overlaps with so named terahertz radiation. A.Glagoleva-Arkadiewa. (1924). "Short Electromagnetic Waves of wave-length up to 82 Microns". ''Nature'' 2844 113. do10.1038/113640a0/ref> Different sources use different boundaries for the far infrared; for example, astronomers sometimes define far infrared as wavelengths between 25 μm and 350 μm. Visible light includes radiation with wavelengths between 400 nm and 700 nm, meaning that far infrared photons have tens to hundreds of times less energy than visible light photons. Applications Astronomy Due to black-body radiation, objects with temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
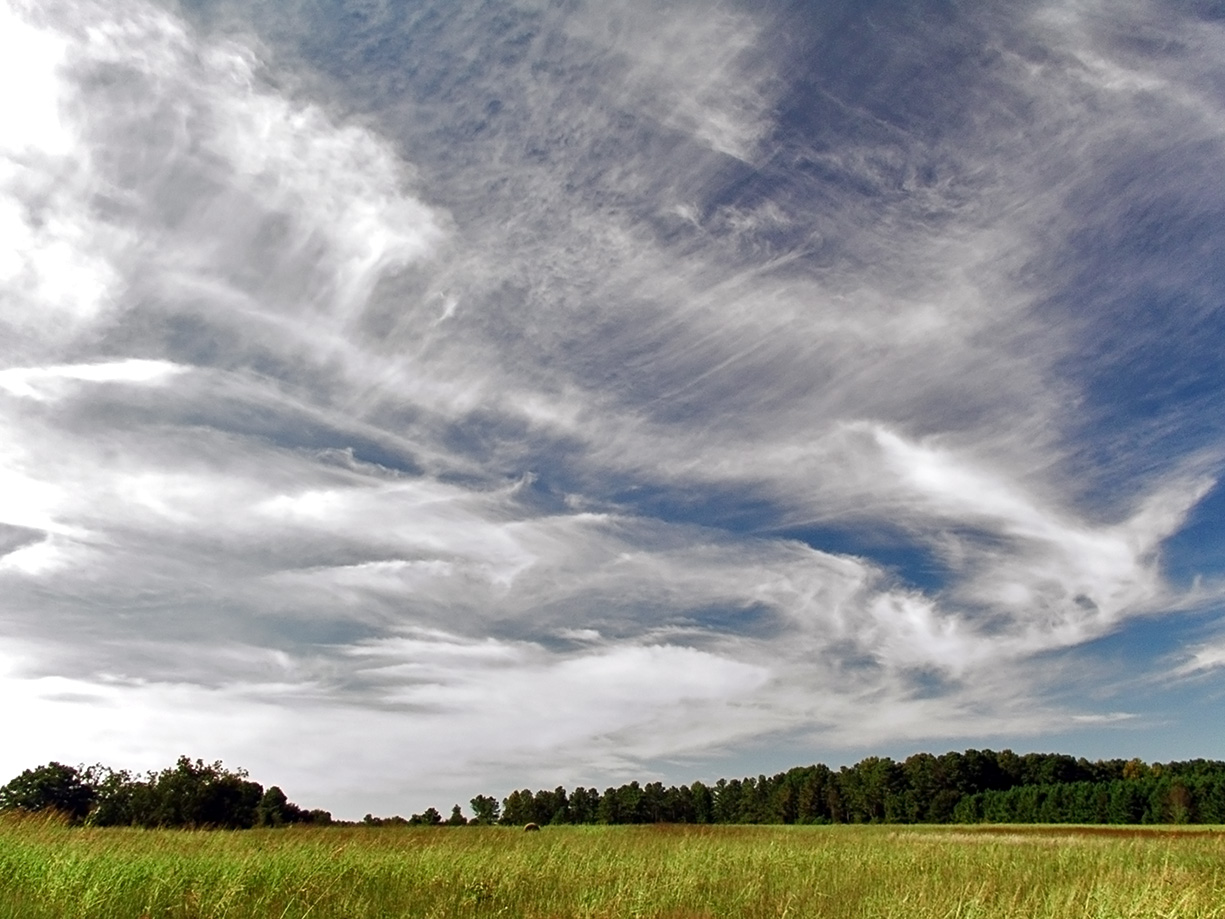
Cirrus Cloud
Cirrus ( cloud classification symbol: Ci) is a genus of high cloud made of ice crystals. Cirrus clouds typically appear delicate and wispy with white strands. Cirrus are usually formed when warm, dry air rises, causing water vapor deposition onto rocky or metallic dust particles at high altitudes. Globally, they form anywhere between above sea level, with the higher elevations usually in the tropics The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referr ... and the lower elevations in more Polar regions of Earth, polar regions. Cirrus clouds can form from the tops of cumulonimbus cloud, thunderstorms and tropical cyclones and sometimes predict the arrival of precipitation, rain or storms. Although they are a sign that rain and maybe storms are on the way, cirrus themselves drop no more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, including websites, software applications/games, music, movies/videos, moving images, and millions of books. In addition to its archiving function, the Archive is an activist organization, advocating a free and open Internet. , the Internet Archive holds over 35 million books and texts, 8.5 million movies, videos and TV shows, 894 thousand software programs, 14 million audio files, 4.4 million images, 2.4 million TV clips, 241 thousand concerts, and over 734 billion web pages in the Wayback Machine. The Internet Archive allows the public to upload and download digital material to its data cluster, but the bulk of its data is collected automatically by its web crawlers, which work to preserve as much of the public web as possible. Its web archiving, web archive, the Wayback Machine, contains hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Group For Meteorological Satellites
The Coordination Group for Meteorological Satellites (CGMS) is an international organization created in 1972 to coordinate the satellite systems that support global operational meteorology. Description CGMS came into being on 19 September 1972, when representatives of the European Space Research Organisation (since 1975 the European Space Agency), Japan, the United States of America, and observers from the World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) and the Joint Planning Staff for the Global Atmospheric Research Program, Global Atmospheric Research Programme, met in Washington, D.C., Washington to discuss questions of compatibility among geostationary Weather satellite, meteorological satellites. Since the formation the mandate of CGMS has been extended to include Low Earth Orbit meteorological satellites and to cover other areas of operational space-based environmental monitoring as well as space weather observations from satellites. The objectives of CGMS are formally laid dow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLEX (satellite)
The FLuorescence EXplorer (FLEX) is a planned mission by the European Space Agency to launch a satellite to monitor the global steady-state chlorophyll fluorescence in terrestrial vegetation. FLEX was selected for funding on 19 November 2015 and will be launched on a Vega C rocket from Guiana Space Centre in mid-2025. Overview The FLuorescence EXplorer (FLEX) mission is the eighth mission in the Earth Explorer programme, (part of ESA's Living Planet Programme). It comprises a satellite for the global monitoring of steady-state chlorophyll fluorescence in terrestrial vegetation. Leaf photosynthesis releases energy not required in the biochemical process in the form of light in wavelength between 640 and 800 nanometres. After more than 70 years of basic and applied research in chlorophyll fluorescence, it is now established that fluorescence is a sensitive indicator of photosynthesis in both healthy and physiologically perturbed vegetation that can be used to monitor croplands an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmony (satellite)
In music, harmony is the process by which individual sounds are joined together or composed into whole units or compositions. Often, the term harmony refers to simultaneously occurring frequencies, pitches ( tones, notes), or chords. However, harmony is generally understood to involve both vertical harmony (chords) and horizontal harmony (melody). Harmony is a perceptual property of music, and, along with melody, one of the building blocks of Western music. Its perception is based on consonance, a concept whose definition has changed various times throughout Western music. In a physiological approach, consonance is a continuous variable. Consonant pitch relationships are described as sounding more pleasant, euphonious, and beautiful than dissonant relationships which sound unpleasant, discordant, or rough. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Counterpoint, which refers to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(2).jpg)