|
Liverpool Riverside Railway Station
Liverpool Riverside was a railway station owned by the Mersey Docks and Harbour Board and located at Liverpool's Pier Head ocean liner terminal. History The station was specifically used for ship liner traffic, opening on 12 June 1895. It was accessed via the Victoria and Waterloo tunnels. It had two main platforms of and , with a centre release track between them, and a bay platform, all covered by a roof. Beyond the buffers were waiting rooms and an inspector's office. It was rebuilt in 1945 after bomb damage. On the opposite side of Princes Parade from the station were the Customs examination rooms and the floating Princes Landing Stage, where the ships berthed. Due to weight restrictions on the line, it was worked by a pair of LNWR Webb Coal Tank locomotives which took trains from Edge Hill railway station until strengthening of the infrastructure around the docks area in 1950 allowed large mainline locomotives to travel through. To open the line for a train the signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.24 million. On the eastern side of the Mersey Estuary, Liverpool historically lay within the ancient hundred of West Derby in the county of Lancashire. It became a borough in 1207, a city in 1880, and a county borough independent of the newly-created Lancashire County Council in 1889. Its growth as a major port was paralleled by the expansion of the city throughout the Industrial Revolution. Along with general cargo, freight, and raw materials such as coal and cotton, merchants were involved in the slave trade. In the 19th century, Liverpool was a major port of departure for English and Irish emigrants to North America. It was also home to both the Cunard and White Star Lines, and was the port of registry of the ocean li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
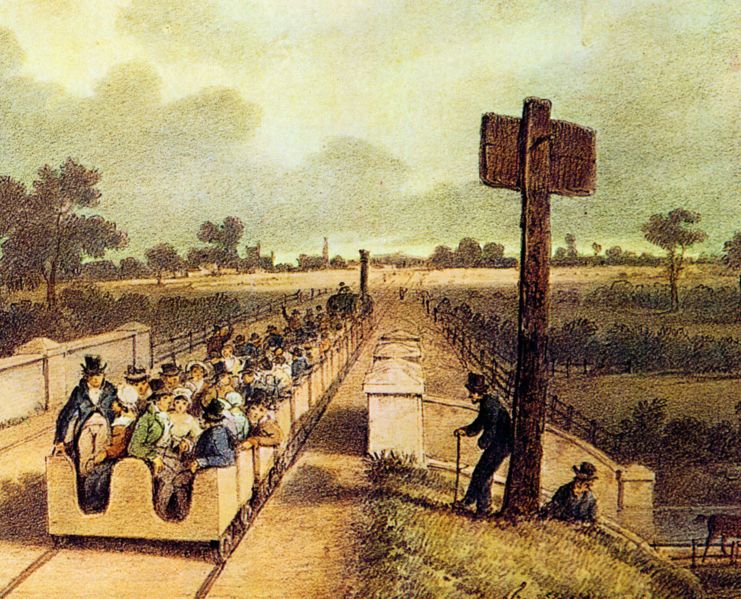
Edge Hill Railway Station
Edge Hill railway station is a railway station that serves the district of Edge Hill, Liverpool, England and is one of the oldest railway stations in the world There have been two stations of that name. The first stood a short distance south-west of the present station and its remains are still visible, although the site is not open to the public. Edge Hill is the first station after departure from . The station, and all trains serving it, are operated by Northern Trains. Avanti West Coast, East Midlands Railway, TransPennine Express and West Midlands Trains services pass through the station, although, they are non stop. Early history The first station opened on 15 September 1830 as part of the Liverpool and Manchester Railway. It was located in a wide by long, deep sandstone cutting, with three tunnels at the west end. The largest bore, in the centre, was the Wapping Tunnel, a long downwards incline leading to Wapping Dock and the world's first tunnel to be bored un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belfast
Belfast ( , ; from ga, Béal Feirste , meaning 'mouth of the sand-bank ford') is the capital and largest city of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan on the east coast. It is the 12th-largest city in the United Kingdom and the second-largest in Ireland. It had a population of 345,418 . By the early 19th century, Belfast was a major port. It played an important role in the Industrial Revolution in Ireland, briefly becoming the biggest linen-producer in the world, earning it the nickname "Linenopolis". By the time it was granted city status in 1888, it was a major centre of Irish linen production, tobacco-processing and rope-making. Shipbuilding was also a key industry; the Harland and Wolff shipyard, which built the , was the world's largest shipyard. Industrialisation, and the resulting inward migration, made Belfast one of Ireland's biggest cities. Following the partition of Ireland in 1921, Belfast became the seat of government for Northern Ireland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
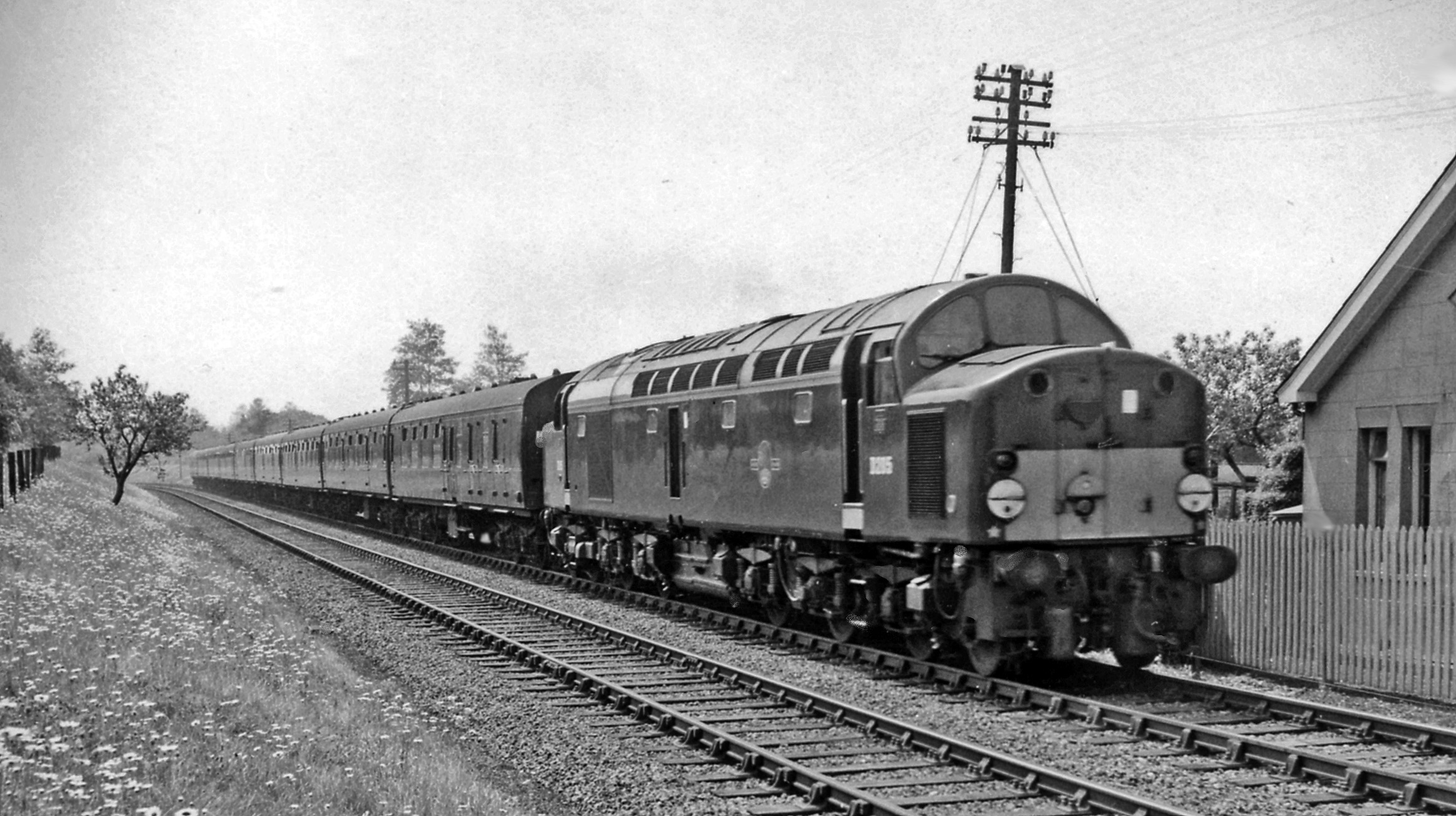
British Rail Class 40
The British Rail Class 40 is a type of British railway diesel electric locomotive. A total of 200 were built by English Electric between 1958 and 1962. They were numbered D200-D399. They were, for a time, the pride of British Rail's early diesel fleet. However, despite their initial success, by the time the last examples were entering service they were already being replaced on some top-level duties by more powerful locomotives. As they were slowly relegated from express passenger uses, the type found work on secondary passenger and freight services where they worked for many years. The final locomotives ended regular service in 1985. The locomotives were commonly known as "Whistlers" because of the distinctive noise made by their turbochargers. Origins The origins of the Class 40 fleet lay in the prototype diesel locomotives ( LMS No. 10000 and 10001 ordered by the London, Midland and Scottish Railway and British Railways and D16/2 ordered by British Railways between 1947 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liverpool Riverside Railway Station Branchline
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a population of 2.24 million. On the eastern side of the Mersey Estuary, Liverpool historically lay within the ancient hundred of West Derby in the county of Lancashire. It became a borough in 1207, a city in 1880, and a county borough independent of the newly-created Lancashire County Council in 1889. Its growth as a major port was paralleled by the expansion of the city throughout the Industrial Revolution. Along with general cargo, freight, and raw materials such as coal and cotton, merchants were involved in the slave trade. In the 19th century, Liverpool was a major port of departure for English and Irish emigrants to North America. It was also home to both the Cunard and White Star Lines, and was the port of registry of the ocean line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince's Dock, Liverpool
Prince's DockAlthough many texts give the name without an apostrophe as ''Princes Dock'', this is an incorrect plural form. The dock is named for one prince; the Prince Regent, only. is a dock on the River Mersey, England, and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is the most southerly of the docks situated in the northern part of the Liverpool dock system, connected to Prince's Half-Tide Dock to the north. The dock is now in the buffer zone to one of Liverpool's World Heritage Sites. History Initially, William Jessop and John Rennie were consulted about the plans for the dock. The dock was built by John Foster, with construction starting around 1810. During the construction, Foster ordered many times more stone than was needed. Allegedly, Foster diverted it to his family's building company. He resigned when this was discovered. The dock was named for the Prince Regent. Still unfinished, it opened on the day of the Prince Regent's coronation as George IV on 19 July 1821. Access ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belfast Steamship Company
The Belfast Steamship Company provided shipping services between Belfast in Ireland (later Northern Ireland) and Liverpool in England from 1852 to 1975.''Sea breezes: the ship lovers' digest'', Volume 42. Pacific Steam Navigation Company. 1968. History The company started life in 1824 as the Liverpool and Belfast Steam Packet Company. operated by Langtry & Herdman. They began a steam ship service from Belfast to Liverpool.''The Belfast and Province of Ulster Directory for 1852''. Vessels introduced were as follows: *PS Chieftain, 1826 *PS Corsair, 1827 *PS Falcon, 1835 *PS Reindeer, 1838 *PS Sea-King, 1845 *PS Blenheim, 1848 About 1830 the Dublin Steam Packet Company began a weekly service in competition. On 31 January 1852 the Liverpool and Belfast Steam Packet Company was registered as The Belfast Steamship Company Ltd. In 1859, it expanded and absorbed the Cork Steamship Company and in 1866 it absorbed the Londonderry Steamboat Company. It was absorbed into Coast Lines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
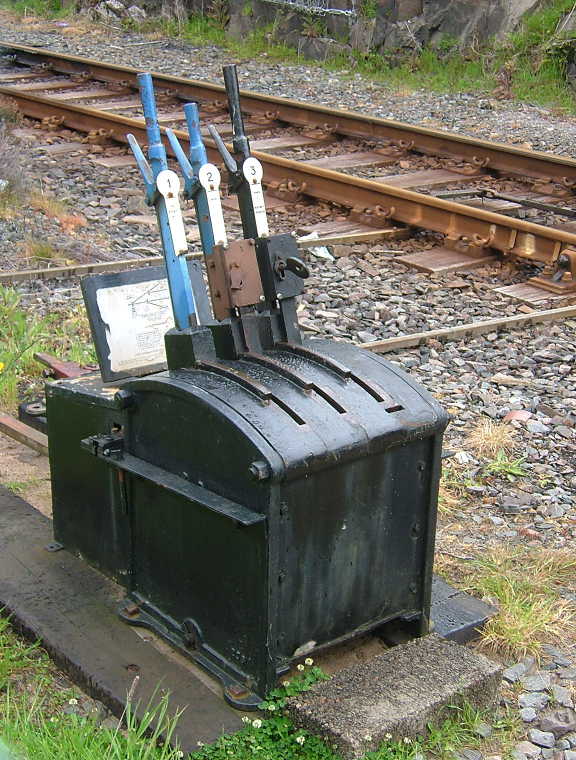
Annett's Key
In British, Australian, French, and Swiss railway signalling, an Annett's key is a form of trapped-key interlocking that locks levers or other items of signalling apparatus, thereby serving as a portable form of interlocking. The purpose is to prevent access from sidings to the running line without authority. When not in use, the key is normally held in an Annett's lock that is fixed to the lever or concerned apparatus. History The Annett's key takes its name from its inventor, J. E. Annett of the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway. Annett patented his design in 1875; in 1881 that patent was bought out by Saxby and Farmer. Operation In British usage, the key may be held in a locked container in the signal box that can only be opened when the corresponding signal lever is turned to ''danger'' for traffic on the running line; the lever is locked in position until the key is returned. Alternatively, the key may be attached to the train staff for the section of running li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
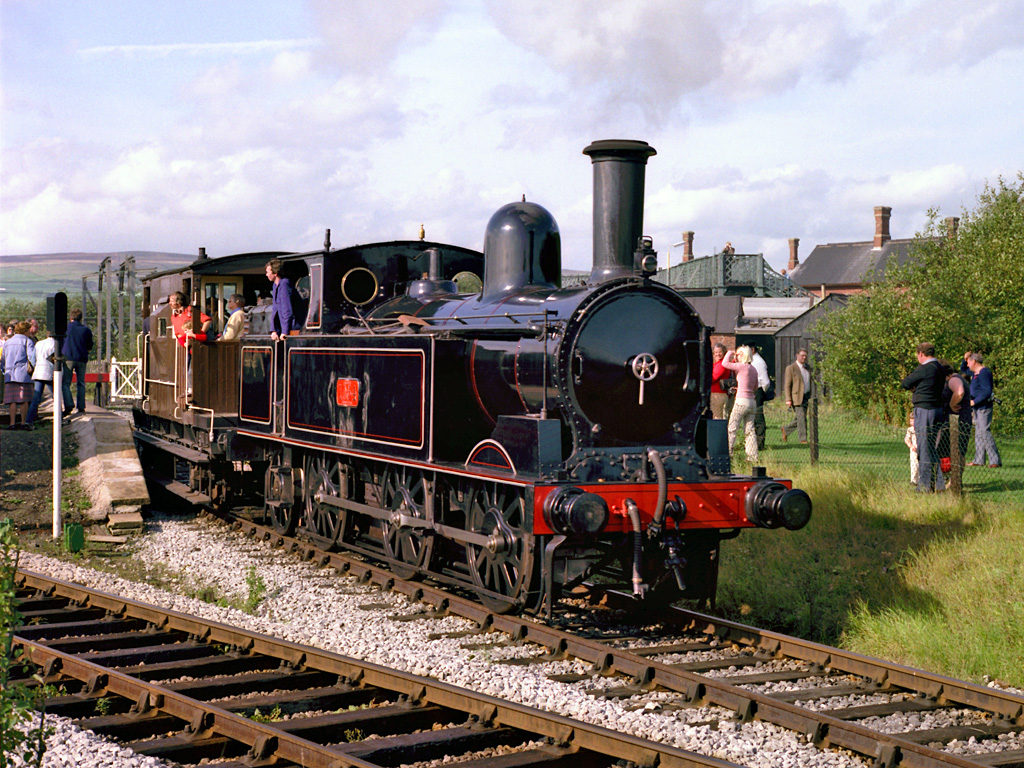
LNWR Webb Coal Tank
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR) Webb Coal Tank is a class of 0-6-2T steam locomotive. They were called "Coal Tanks" because they were a side tank version of Webb's standard LNWR 17in Coal Engine, an 0-6-0 tender engine for slow freight trains. Design The design was introduced in 1881 by F.W. Webb and had the same cheaply produced cast iron wheels and H-section spokes as the tender engines. A trailing radial axle supporting the bunker was added also with two similarly cast iron wheels. Three hundred were built between 1881 and 1897. Operational history Four (LNWR nos. 178, 484, 1257, 69) were withdrawn in January–February 1920 and a further four (LNWR nos. 142, 994, 782, 1012) in July and November 1922, so at the 1923 grouping, 292 passed to the London Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS). They were renumbered from the LNWR's random allocation based on vacant numbers, to a solid block sequence 7550–7841, and given the power classification 1F. Many locomotives st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordnance Survey National Grid
The Ordnance Survey National Grid reference system (OSGB) (also known as British National Grid (BNG)) is a system of geographic grid references used in Great Britain, distinct from latitude and longitude. The Ordnance Survey (OS) devised the national grid reference system, and it is heavily used in their survey data, and in maps based on those surveys, whether published by the Ordnance Survey or by commercial map producers. Grid references are also commonly quoted in other publications and data sources, such as guide books and government planning documents. A number of different systems exist that can provide grid references for locations within the British Isles: this article describes the system created solely for Great Britain and its outlying islands (including the Isle of Man); the Irish grid reference system was a similar system created by the Ordnance Survey of Ireland and the Ordnance Survey of Northern Ireland for the island of Ireland. The Universal Transverse Merca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)