|
Liutbert (archbishop Of Mainz)
Liutbert (or Ludbert) (died 889) was the Archbishop of Mainz from 863 until his death. He also became Ellwangen Abbey, Abbot of Ellwangen in 874 and is reckoned the first Archchancellor, Archchancellor of Germany. He was one of the major organisers—along with Henry of Franconia—of the vigorous and successful defence of East Francia against Viking attack during his last decade. In May 868, Liutbert presided over the Synod of Worms (868), synod of Worms, which condemned the Ecumenical Patriarchate, Greek church for heresy and laid down punishments for rebels. In 870, he became the archchaplain of Louis the German until 876 and thereafter of Louis the Younger until the latter's death in 882. Under Charles the Fat, however, he did not retain this position, rather it was preserved for Liutward of Vercelli. Liutbert did not accept his lack of position at court initially; he had himself referred to as "archchaplain," though he was not, in an 882 document of Wissembourg, Weissenburg, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop Of Mainz
The Elector of Mainz was one of the seven Prince-electors of the Holy Roman Empire. As both the Archbishop of Mainz and the ruling prince of the Electorate of Mainz, the Elector of Mainz held a powerful position during the Middle Ages. The Archbishop-Elector was president of the electoral college, archchancellor of the empire, and the Primate of Germany as the papal legate north of the Alps, until the dissolution of the empire in 1806. The origin of the title dates back to 747, when the city of Mainz was made the seat of an archbishop, and a succession of able and ambitious prelates made the district under their rule a strong and vigorous state. Among these men were important figures in the history of Germany such as Hatto I, Adalbert of Mainz, Siegfried III, Peter of Aspelt and Albert of Brandenburg. There were several violent contests between rivals for the archbishopric, and their power struggles occasionally moved the citizens of Mainz to revolt. The lands of the elector la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard, Son Of Charles The Fat
Bernard or Bernhard (c. 870 – 891/2) was the only child of Emperor Charles the Fat. He was born of an unknown concubine and was thus considered illegitimate. Charles tried to make him his heir, but failed in two attempts. Charles tried to have Bernard recognised as his heir in 885, but met the opposition of several bishops. He had the support of Pope Adrian III, whom he invited to an assembly in Worms in October 885, but who died on the way, just after crossing the river Po.Reuter, pp 116–117. AF(M), 885 (pp 98&99 and nn6&7) and AF(B), 885 (p. 111 and n2). Adrian was going to depose the obstructing bishops, as Charles doubted he could do this himself, and legitimise Bernard. Based on the unfavouring attitude of the chronicler of the Mainz continuation of the ''Annales Fuldenses'', the chief of Charles' opponents in the matter was probably Liutbert, Archbishop of Mainz. Because Charles had called together the "bishops and counts of Gaul" as well as the pope to meet him at Worm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishops Of Mainz
The Elector of Mainz was one of the seven Prince-electors of the Holy Roman Empire. As both the Archbishop of Mainz and the ruling prince of the Electorate of Mainz, the Elector of Mainz held a powerful position during the Middle Ages. The Archbishop-Elector was president of the electoral college, archchancellor of the empire, and the Primate of Germany as the papal legate north of the Alps, until the dissolution of the empire in 1806. The origin of the title dates back to 747, when the city of Mainz was made the seat of an archbishop, and a succession of able and ambitious prelates made the district under their rule a strong and vigorous state. Among these men were important figures in the history of Germany such as Hatto I, Adalbert of Mainz, Siegfried III, Peter of Aspelt and Albert of Brandenburg. There were several violent contests between rivals for the archbishopric, and their power struggles occasionally moved the citizens of Mainz to revolt. The lands of the elector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunderolt, Archbishop Of Mainz
Sunderolt (or Sunderhold) (died 25 June 891) was the Archbishop of Mainz from 889 until his death. Sunderolt had not held the primatial see of Germany for long when a Viking invasion of West Francia attracted his attention. He led an army of Rhenish and Lotharingian troops against the Vikings. He was killed in the ensuing battle, for which the ''Annales Fuldenses'' castigated his rashness. He was succeeded by Hatto I of Reichenau. Sources *The Annals of Fulda'. (Manchester Medieval series, Ninth-Century Histories, Volume II.) Reuter, Timothy Timothy Alan Reuter (25 January 1947 – 14 October 2002), grandson of the former mayor of Berlin Ernst Reuter, was a German-British historian who specialized in the study of medieval Germany, particularly the social, military and ecclesiastical i ... (trans.) Manchester: Manchester University Press, 1992. 891 deaths Archbishops of Mainz 9th-century archbishops Military personnel killed in action Year of birth unknown { ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles, Archbishop Of Mainz
Charles (825/830 – 4 June 863) was the second son of Pepin I of Aquitaine and Engelberga. He lived at the court of his uncle Lothair until 848, when, hearing of the deposition of his brother, he set out in March 849 with a band of followers to claim the Aquitainian realm. He was captured by Vivian, count of Maine at the Loire and sent to Charles the Bald. He was put in the monastery of Corbie as either a monk or a deacon. He escaped in 854 to recruit an army to fight for his brother. He had little success and fled to the court of Louis the German, who made him the archbishop of Mainz and archchancellor on 8 March 856. He made a respectable bishop and died on 4 June 863 and was buried in St. Alban's Abbey, Mainz. Sources *''Dictionnaire de Biographie Française''. Roman d'Amat and R. Limousin-Lamothe (ed). Paris Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franconia
Franconia (german: Franken, ; Franconian dialect: ''Franggn'' ; bar, Frankn) is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and Franconian dialect (German: ''Fränkisch''). The three administrative regions of Lower, Middle and Upper Franconia (largest cities, respectively: Würzburg, Nuremberg and Bamberg) in the State of Bavaria are part of the cultural region of Franconia, as are the adjacent Franconian-speaking South Thuringia, south of the Rennsteig ridge (largest city: Suhl), Heilbronn-Franconia (largest city: Schwäbisch Hall) in the state of Baden-Württemberg, and small parts of the state of Hesse. Those parts of the Vogtland lying in the state of Saxony (largest city: Plauen) are sometimes regarded as Franconian as well, because the Vogtlandian dialects are mostly East Franconian. The inhabitants of Saxon Vogtland, however, mostly do not consider themselves as Franconian. On the other hand, the inhabitants of the Hessian-speaking parts of Lower Franconia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
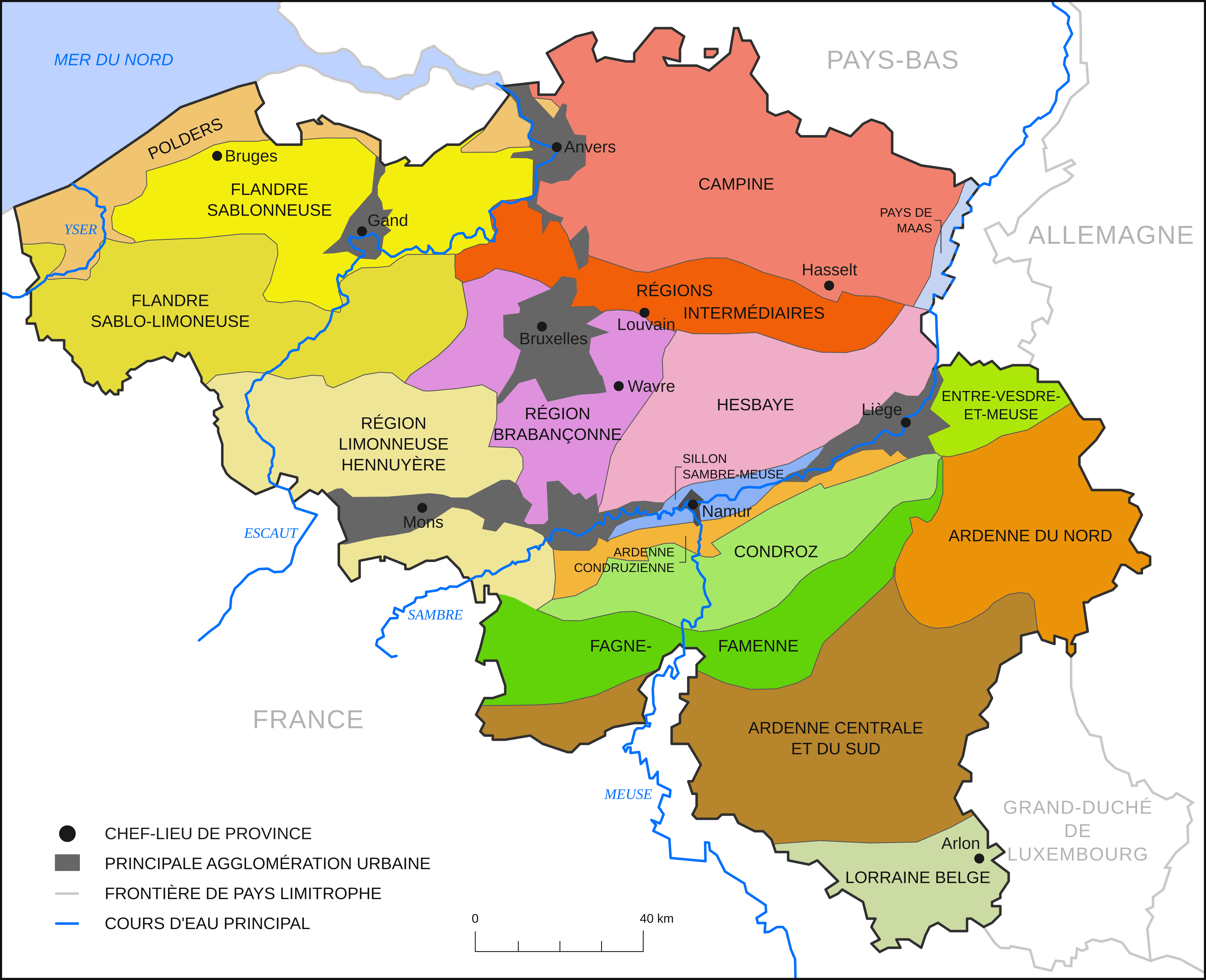
Hesbaye
The Hesbaye ( French, ), or Haspengouw (Dutch and Limburgish, ) is a traditional cultural and geophysical region in eastern Belgium. It is a loamy plateau region which forms a watershed between the Meuse and Scheldt drainage basins. It has been one of the main agricultural regions in what is now Belgium since before Roman times, and specifically named in records since the Middle Ages, when it was an important Frankish ''pagus'' or gau, called ''Hasbania'' in medieval Latin. Location Major parts of three Belgian provinces are dominated by the Hesbaye landscape, important for both tourism and agriculture, and by some definitions it stretches further: *The southern half of the province of Limburg, including the cities of Tongeren, Sint-Truiden, Bilzen and Borgloon. *Liège province north of the Meuse, including for example the towns of Hannut and Waremme. *Eastern Walloon Brabant including Jodoigne and Perwez. *Easternmost Flemish Brabant, including Tienen, Hoegaarden, Lande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
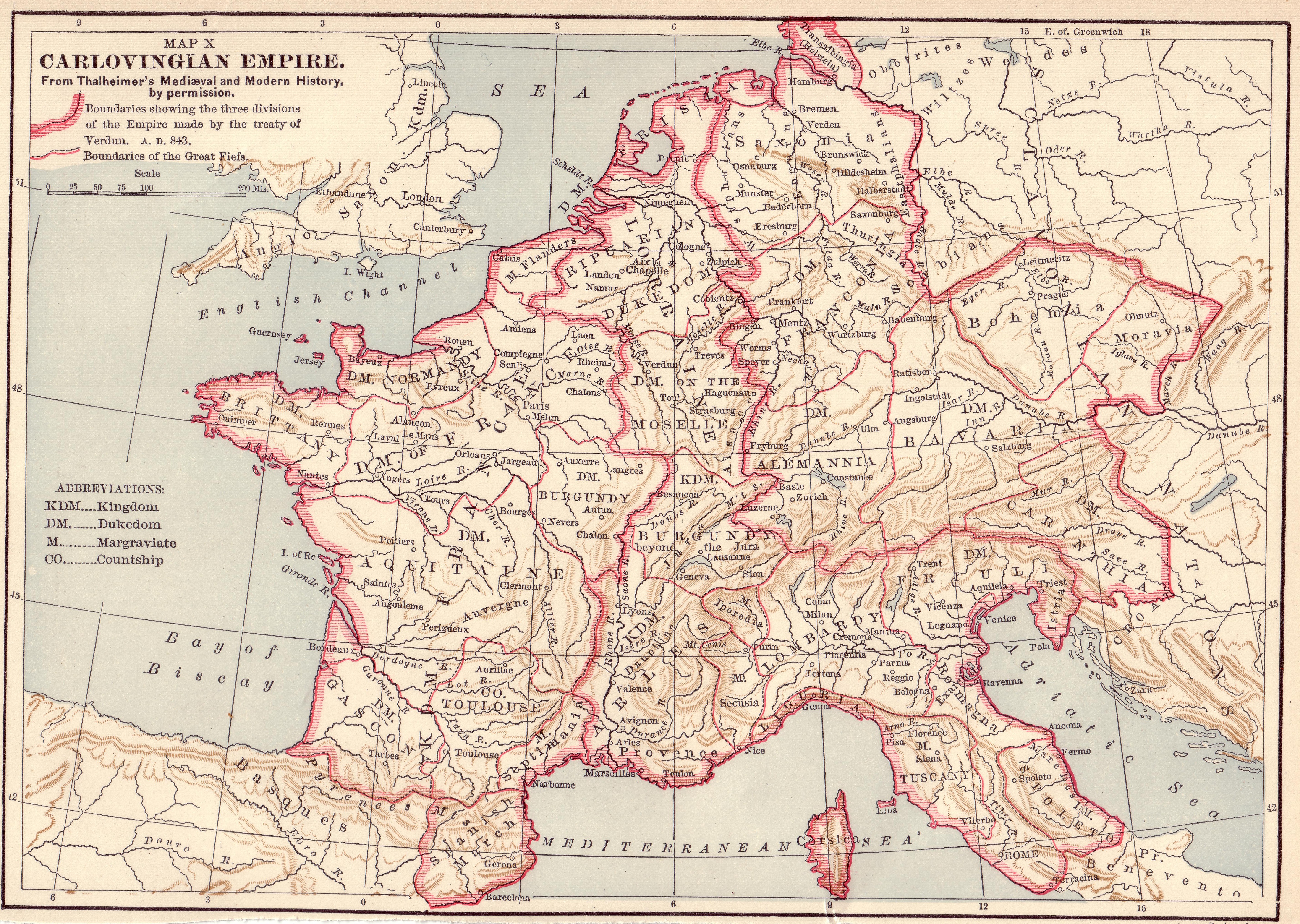
West Francia
In medieval history, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by Charlemagne. It represents the earliest stage of the Kingdom of France, lasting from about 840 until 987. West Francia emerged from the partition of the Carolingian Empire in 843 under the Treaty of Verdun following the death of Charlemagne's son, Louis the Pious. It is considered the first polity in French history. West Francia extended further north and south than modern metropolitan France, but it did not extend as far east. It did not include such future French holdings as Lorraine, the County and Kingdom of Burgundy (the duchy was already a part of West Francia), Alsace and Provence in the east and southeast for example. It also did not include the Brittany peninsula in the west. In addition, by the 10th century the authority of the West Frankish monarchs was greatly reduced. This was contrasted by the evergrowing power of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cologne
Cologne ( ; german: Köln ; ksh, Kölle ) is the largest city of the German western States of Germany, state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with 1.1 million inhabitants in the city proper and 3.6 million people in the Cologne Bonn Region, urban region. Centered on the left bank of the Rhine, left (west) bank of the Rhine, Cologne is about southeast of NRW's state capital Düsseldorf and northwest of Bonn, the former capital of West Germany. The city's medieval Catholic Cologne Cathedral (), the third-tallest church and tallest cathedral in the world, constructed to house the Shrine of the Three Kings, is a globally recognized landmark and one of the most visited sights and pilgrimage destinations in Europe. The cityscape is further shaped by the Twelve Romanesque churches of Cologne, and Cologne is famous for Eau de Cologne, that has been produced in the city since 1709, and "col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland , source1_coordinates= , source1_elevation = , source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein , source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland , source2_coordinates= , source2_elevation = , source_confluence = Reichenau , source_confluence_location = Tamins, Graubünden, Switzerland , source_confluence_coordinates= , source_confluence_elevation = , mouth = North Sea , mouth_location = Netherlands , mouth_coordinates = , mouth_elevation = , progression = , river_system = , basin_size = , tributaries_left = , tributaries_right = , custom_label = , custom_data = , extra = The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label= Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label= Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waldaha
Vltava ( , ; german: Moldau ) is the longest river in the Czech Republic, running southeast along the Bohemian Forest and then north across Bohemia, through Český Krumlov, České Budějovice and Prague, and finally merging with the Labe at Mělník. It is commonly referred to as the "Czech national river". Both the Czech name ' and the German name ' are believed to originate from the old Germanic words ' 'wild water' (compare Latin '). In the ' (872 AD) it is called '; from 1113 AD it is attested as '. In the ' (1125 AD) it is attested for the first time in its Bohemian form, '. Course The Vltava River is long and drains an area of in size, over half of Bohemia and about a third of the Czech Republic's entire territory. As it runs through Prague, the river is crossed by 18 bridges (including the Charles Bridge) and covers within the city. The water from the river was used for drinking until 1912 when the Vinohrady Water Tower ceased pumping operations. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |