|
Lithuanian Territorial Defense Force (1944)
The Lithuanian Territorial Defense Force or LTDF ( lt, Lietuvos vietinė rinktinė, LVR, german: Litauische Sonderverbände) was a short-lived, Lithuanian, volunteer armed force created and disbanded in 1944 during the German occupation of Lithuania. LTDF was subordinate to the authorities of Nazi Germany and Its goal was to fight the approaching Red Army, provide security and conduct Nazi security warfare within the territory, claimed by Lithuanians (see also Nazi German occupation of Lithuania, Generalbezirk Litauen of Reichskommissariat Ostland). LTDF had some autonomy and was staffed by Lithuanian officers, their most notable commander being Lithuanian General Povilas Plechavičius. LTDF quickly reached the size of about 10,000 men. After brief engagements against the Soviet and Polish partisans (Armia Krajowa), the force self-disbanded, its leaders were arrested and sent to concentration camps, and numerous of its members were executed by the Nazis. Many others were either dra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armed Force
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zivilverwaltung
Chief of Civil Administration (german: 'Chef der Zivilverwaltung, CdZ') was an office introduced in Nazi Germany, operational during World War II. Its task was to administer civil issues according to occupation law, with the primary purpose being the support of the military command in the operational areas of the German Army. CdZ would pass his authority to a corresponding civil government after the territory in question became in the rear of the operating armed forces. Responsibility According to German law, all executive powers in the deployment areas passed to the Wehrmacht armed forces. Overstrained and incapable to construct a civil administration, the German Army High Command willingly put these tasks to the CdZ. In the capacity as ''Reichsstatthalter'' governor, the office was under the authority of the Reich Ministry of the Interior, but operationally CdZ was under the commander-in-chief of the German Army and ultimately of Adolf Hitler as supreme commander. Hitler generall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
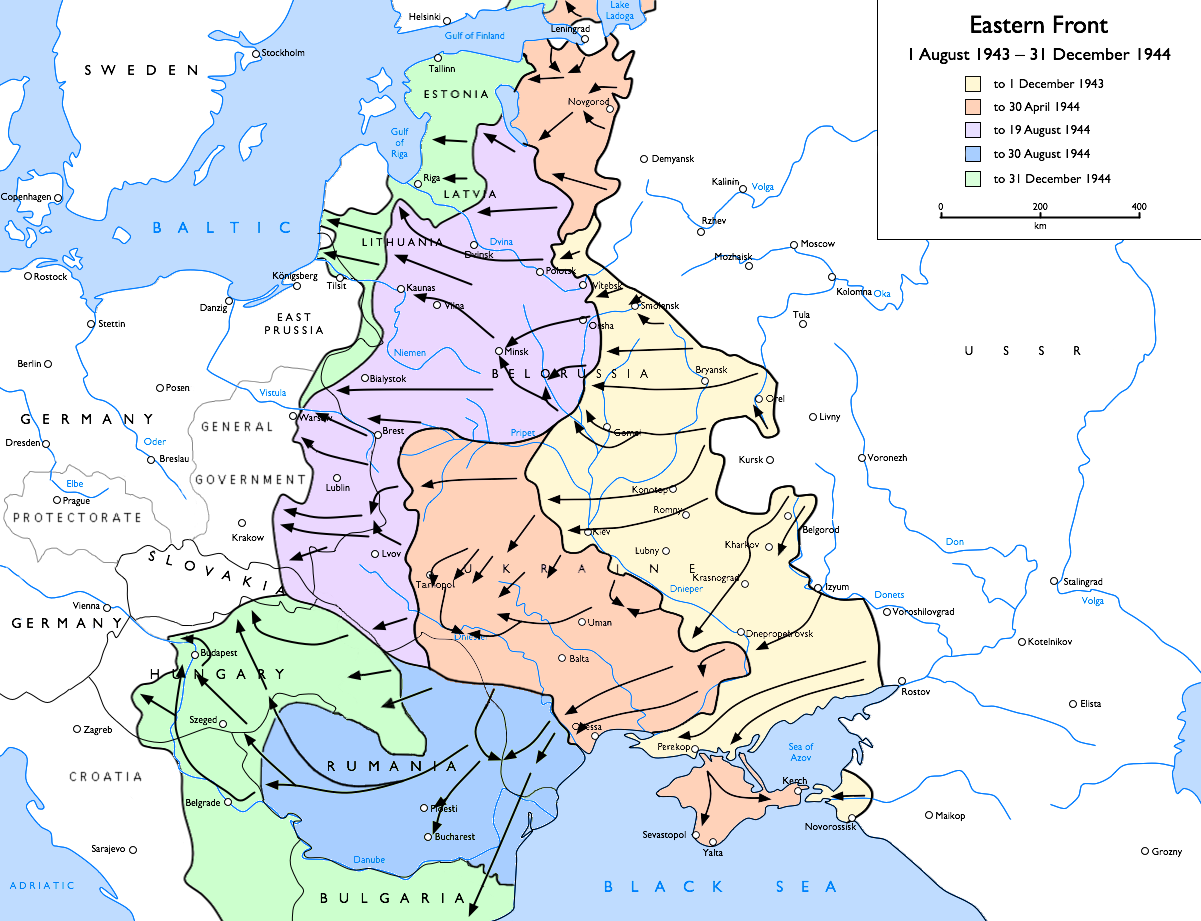
Lithuanian Partisans (1944–1953)
The Lithuanian partisans () were partisans who waged a guerrilla warfare in Lithuania against the Soviet Union in 1944–1953. Similar anti-Soviet resistance groups, also known as Forest Brothers and cursed soldiers, fought against Soviet rule in Estonia, Latvia and Poland. It is estimated that a total of 30,000 Lithuanian partisans and their supporters were killed. The Lithuanian partisan war lasted almost for a decade, thus being one of the longest partisan wars in Europe. At the end of World War II, the Red Army pushed the Eastern Front towards Lithuania. The Soviets invaded and occupied Lithuania by the end of 1944. As forced conscription into Red Army and Stalinist repressions intensified, thousands of Lithuanians used forests in the countryside as a natural refuge. These spontaneous groups became more organized and centralized culminating in the establishment of the Union of Lithuanian Freedom Fighters in February 1948. In their documents, the partisans emphasized that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian Riflemen Union
The Lithuanian Riflemen's Union (LRU, lt, Lietuvos šaulių sąjunga), also referred to as Šauliai ( lt, šaulys for ''rifleman''), is a paramilitary non-profit organisation supported by the State. The activities are in three main areas: military training, sport, and culture. History Establishment The Lithuanian Riflemen's Union was established in Kaunas on 27 June 1919 as a shooting section within the Lithuanian Sport Union. Several historic events determined the establishment of the Union – Lithuania had just declared independence and was asserting it in the wars against the Bolshevik Red Army, the Western Russian Volunteer Army and the young Polish Armed Forces. Vladas Putvinskis and Matas Šalčius were the most important activists behind the idea to form a Union, and Putvinskis became the first Commander of the LRU and its main ideologue. Both of them came up with the idea to form a paramilitary group at almost the same time, but the scope that they envisioned was diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuanian Wars Of Independence
The Lithuanian Wars of Independence, also known as the Freedom Struggles ( lt, Laisvės kovos), refer to three wars Lithuania fought defending its independence at the end of World War I: with Bolshevik forces (December 1918 – August 1919), Bermontians (June 1919 – December 1919), and Poland (August 1920 – November 1920). The wars delayed international recognition of independent Lithuania and the formation of civil institutions. Background After the Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1795, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania was annexed by the Russian Empire. The Lithuanian National Revival emerged during the 19th century and the movement to establish an independent nation-state intensified during the early 20th century. During World War I, Lithuanian territory was occupied by Germany from 1915 until the war ended in November 1918. On February 16, 1918, the Council of Lithuania declared the re-establishment of independence from all previous legal bonds with othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatherland Defense Force
The Fatherland Defense Force ( lt, Tėvynės apsaugos rinktinė or TAR) or Kampfgruppe Mäder (german: Kampfgruppe Mäder) was a short-lived military unit hastily formed in northwestern Lithuania towards the end of World War II to combat Operation Bagration, approaching Soviet forces. Formed from local Lithuanians, the unit was directly subordinate to the Wehrmacht. Their German commander was Hellmuth Mäder who was hoping to raise a Division (military), division. However, only two ill-equipped and ill-trained regiments were actually formed. The total membership is estimated at 6,000 men. On October 7, TAR took defensive positions in Seda, Lithuania, Seda against the of the 6th Guards Army. TAR suffered heavy losses and retreated towards Klaipėda (Memel). In East Prussia, the remaining men were reassigned to various Pioneer (military), pioneer units. Formation As a result of the Operation Bagration, Soviet 1st Baltic Front reached eastern borders of Lithuania in summer 1944 and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forced Labor In Germany During World War II
The use of slave and forced labour in Nazi Germany (german: Zwangsarbeit) and throughout German-occupied Europe during World War II took place on an unprecedented scale. It was a vital part of the German economic exploitation of conquered territories. It also contributed to the mass extermination of populations in occupied Europe. The Germans abducted approximately 12 million people from almost twenty European countries; about two thirds came from Central Europe and Eastern Europe.Part1 an Part 2 . Many workers died as a result of their living conditionsextreme mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrian Von Renteln
file:Adrian von Renteln.jpg, Theodor Adrian von Renteln Theodor Adrian von Renteln (15 September 1897 – 1946 (disputed)) was an activist and politician in Nazi Germany. During World War II, he was General Commissioner of ''Generalbezirk Litauen'' and was involved in perpetrating the Holocaust in Lithuania. Of Baltic German origin, von Renteln studied law and economics in Berlin and Rostock, but became a journalist. In 1928, he joined the NSDAP and the following year, he became the founder and head of the National Socialist Schoolchildren's League (NSS). In 1931, he was appointed the head of the Hitler Youth, but he gave up leadership of the two organizations upon his election to the Reichstag (Weimar Republic), Reichstag in 1932. In 1932–1933 he led the Combat League of the Commercial Middle Class (''NS-Kampfbund für den Gewerblichen Mittelstand''), an organisation allegedly "Deflecting Jewish Atrocity and Boycott-Mongering", participating in the boycott of Jewish businesses an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walther Model
Otto Moritz Walter Model (; 24 January 1891 – 21 April 1945) was a German field marshal during World War II. Although he was a hard-driving, aggressive panzer commander early in the war, Model became best known as a practitioner of defensive warfare. His relative success as commander of the Ninth Army in the battles of 1941–1942 determined his future career path. Model first came to Hitler's attention before World War II, but their relationship did not become especially close until 1942. His tenacious style of fighting and loyalty to the Nazi regime won him plaudits from Hitler, who considered him one of his best field commanders and repeatedly sent him to salvage apparently desperate situations on the Eastern Front. Their relationship broke down by the end of the war after the German defeat at the Battle of the Bulge. In the aftermath of the encirclement and defeat of Army Group B at the Ruhr Pocket, Model committed suicide on 21 April 1945. Early life and career ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Jeckeln
Friedrich Jeckeln (2 February 1895 – 3 February 1946) was a German SS commander during the Nazi era. He served as a Higher SS and Police Leader in the occupied Soviet Union during World War II. Jeckeln was the commander of one of the largest collection of ''Einsatzgruppen'' death squads and was personally responsible for ordering and organizing the deaths of over 100,000 Jews, Romani, and others designated by the Nazis as "undesirables". After the end of World War II in Europe, Jeckeln was convicted of war crimes by a Soviet military tribunal in Riga and executed in 1946. SS career Jeckeln served in World War I as an officer. After being discharged following Germany's defeat, Jeckeln worked as an engineer before joining the Nazi Party on 1 October 1929. In January 1931, he was accepted into the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS). By the end of 1931 he was placed in charge of a regiment and then a brigade. In 1932, Jeckeln was elected as a member of the Reichstag. In January 1933, when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obergruppenführer
' (, "senior group leader") was a paramilitary rank in Nazi Germany that was first created in 1932 as a rank of the ''Sturmabteilung'' (SA) and adopted by the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) one year later. Until April 1942, it was the highest commissioned SS rank after only ''Reichsführer-SS''. Translated as "senior group leader", the rank of ''Obergruppenführer'' was senior to '' Gruppenführer''. A similarly named rank of ''Untergruppenführer'' existed in the SA from 1929 to 1930 and as a title until 1933. In April 1942, the new rank of ''SS-Oberst-Gruppenführer'' was created which was above ''Obergruppenführer'' and below ''Reichsführer-SS''. Creation and history The rank of ''Obergruppenführer'' was created in 1932 by Ernst Röhm and was intended as a seniormost rank of the Nazi stormtroopers for use by Röhm and his top SA generals. In its initial concept, the rank was intended to be held by members of the ''Oberste SA-Führung'' (Supreme SA Command) and also by veteran c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Harm
Hermann Harm ( 30 September 1894 – 28 November 1985) was a Nazi German SS-''Brigadeführer'' and a ''Generalmajor'' of Police who served as an SS and Police Leader (SSPF) in occupied Ukraine and Lithuania during the Second World War. Early life Harm was born in Halle (Saale), the son of a railway inspector. He studied electronics until the outbreak of the First World War in July 1914 when he joined the Imperial German Army. He served in an artillery unit, was commissioned as a ''Leutnant'' in September 1915 and earned the Iron Cross, 1st and 2nd class. After the end of the war, he trained in agriculture and became an estate manager. He joined the Nazi Party on 1 February 1930 (membership number 204,385). He also became a member of its paramilitary wing, the ''Sturmabteilung'' (SA), on 1 August of the same year and was commissioned an SA-''Sturmführer'' on 15 June 1931. Peacetime SS career Harm left the SA to join the SS (SS number 21,342) and was made an SS-''Sturmführ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |