|
Lithium Hybrid Organic Battery
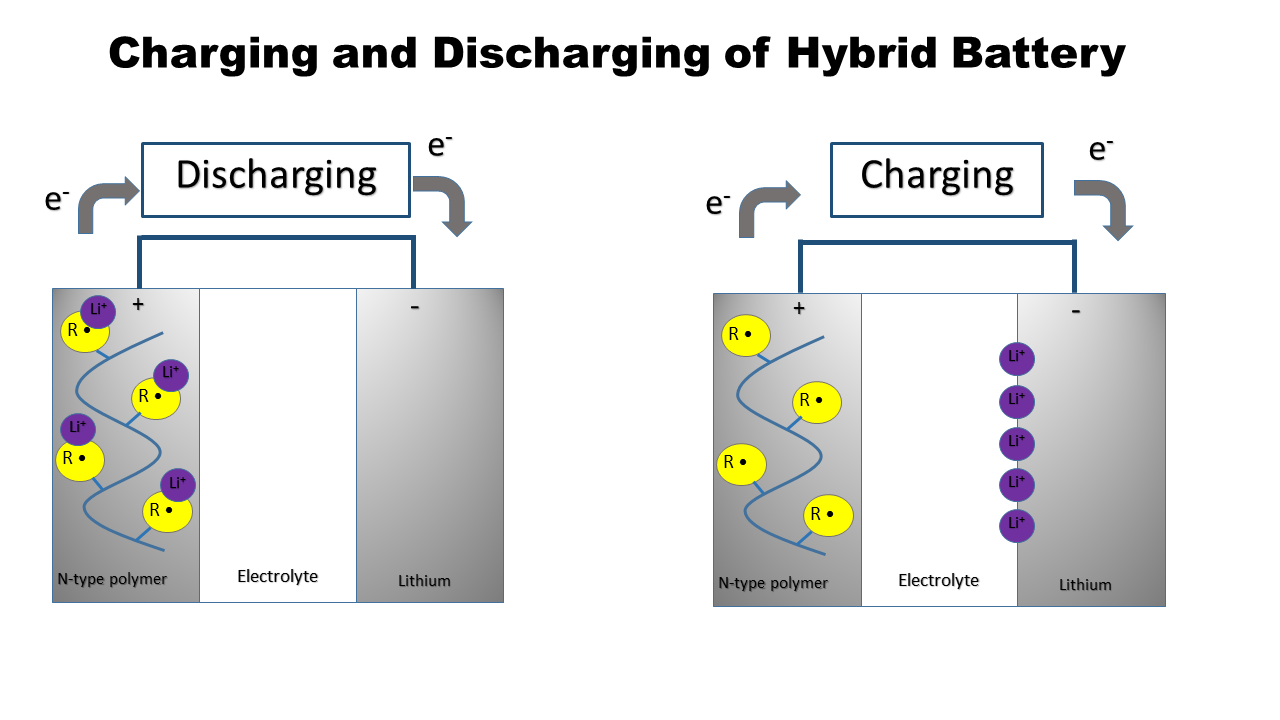
Lithium hybrid organic batteries are an energy storage device that combines lithium with an organic polymer. For example, polyaniline vanadium (V) oxide (PAni/V2O5) can be incorporated into the nitroxide-polymer lithium iron phosphate battery, PTMA/LiFePO4. Together, they improve the lithium ion intercalation capacity, cycle life, electrochemical performances, and conductivity of batteries. PAni/V2O5 Oxides, like V2O5, are used as cathodes in rechargeable lithium batteries. Crystalline V2O5 has a weaker rechargeability or cyclability than amorphous V2O5 because the crystal structure is damaged during discharge/charge cycles. However, amorphous oxides, in particular the V2O5 xerogel, allows lithium ions to diffuse faster and thus have a better cyclability. Hybrid is formed by combining a conducting organic polymer (e.g. polyaniline) with an oxide (e.g. V2O5). V2O5 gels are prepared using the ion-exchange method. Vanadium (V) polymerizes aniline. Before synthesis of a hybrid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactive and flammable, and must be stored in vacuum, inert atmosphere, or inert liquid such as purified kerosene or mineral oil. When cut, it exhibits a metallic luster, but moist air corrodes it quickly to a dull silvery gray, then black tarnish. It never occurs freely in nature, but only in (usually ionic) compounds, such as pegmatitic minerals, which were once the main source of lithium. Due to its solubility as an ion, it is present in ocean water and is commonly obtained from brines. Lithium metal is isolated electrolytically from a mixture of lithium chloride and potassium chloride. The nucleus of the lithium atom verges on instability, since the two stable lithium isotopes foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Figure
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of Units ( SI) is more precise:The second ..is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the caesium frequency, Δ''ν''Cs, the unperturbed ground-state hyperfine transition frequency of the caesium 133 atom, to be when expressed in the unit Hz, which is equal to s−1. This current definition was adopted in 1967 when it became feasible to define the second based on fundamental properties of nature with caesium clocks. Because the speed of Earth's rotation varies and is slowing ever so slightly, a leap second is added at irregular intervals to civil time to keep clocks in sync with Earth's rotation. Uses Analog clocks and watches often have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Conductivity
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows electric current. Resistivity is commonly represented by the Greek letter (rho). The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm-meter (Ω⋅m). For example, if a solid cube of material has sheet contacts on two opposite faces, and the resistance between these contacts is , then the resistivity of the material is . Electrical conductivity or specific conductance is the reciprocal of electrical resistivity. It represents a material's ability to conduct electric current. It is commonly signified by the Greek letter ( sigma), but ( kappa) (especially in electrical engineering) and ( gamma) are sometimes used. The SI unit of electrical conductivity is siemens per metre (S/m). Resistivity and conductivity are inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation State
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. Conceptually, the oxidation state may be positive, negative or zero. While fully ionic bonds are not found in nature, many bonds exhibit strong ionicity, making oxidation state a useful predictor of charge. The oxidation state of an atom does not represent the "real" formal charge on that atom, or any other actual atomic property. This is particularly true of high oxidation states, where the ionization energy required to produce a multiply positive ion is far greater than the energies available in chemical reactions. Additionally, the oxidation states of atoms in a given compound may vary depending on the choice of electronegativity scale used in their calculation. Thus, the oxidation state of an atom in a compound is purely a formalism. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aniline
Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine In organic chemistry, an aromatic amine is an organic compound consisting of an aromatic ring attached to an amine. It is a broad class of compounds that encompasses aniline Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consi .... It is an industrially significant Commodity chemicals, commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It Combustion, ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds. It is toxic to humans. Relative to benzene, it is electron-rich. It thus participates more rapidly in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Likewise, it is also prone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyaniline
Polyaniline (PANI) is a conducting polymer and organic semiconductor of the semi-flexible rod polymer family. The compound has been of interest since the 1980s because of its electrical conductivity and mechanical properties. Polyaniline is one of the most studied conducting polymers. Historical development Polyaniline was discovered in the 19th century by F. Ferdinand Runge (1794–1867), Carl Fritzsche (1808–1871), John Lightfoot (1831–1872), and Henry Letheby (1816–1876). Lightfoot studied the oxidation of aniline, which had been isolated only 20 years previously. He developed the first commercially successful route to the dye called Aniline black. The first definitive report of polyaniline did not occur until 1862, which included an electrochemical method for the determination of small quantities of aniline. From the early 20th century on, occasional reports about the structure of PANI were published. Polymerized from the inexpensive aniline, polyaniline can be found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion Coefficient
Diffusivity, mass diffusivity or diffusion coefficient is a proportionality constant between the molar flux due to molecular diffusion and the gradient in the concentration of the species (or the driving force for diffusion). Diffusivity is encountered in Fick's law and numerous other equations of physical chemistry. The diffusivity is generally prescribed for a given pair of species and pairwise for a multi-species system. The higher the diffusivity (of one substance with respect to another), the faster they diffuse into each other. Typically, a compound's diffusion coefficient is ~10,000× as great in air as in water. Carbon dioxide in air has a diffusion coefficient of 16 mm2/s, and in water its diffusion coefficient is 0.0016 mm2/s. Diffusivity has dimensions of length2 / time, or m2/s in SI units and cm2/s in CGS units. Temperature dependence of the diffusion coefficient Solids The diffusion coefficient in solids at different temperatures is generally found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Conductivity
Electrical resistivity (also called specific electrical resistance or volume resistivity) is a fundamental property of a material that measures how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows electric current. Resistivity is commonly represented by the Greek letter (rho). The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm-meter (Ω⋅m). For example, if a solid cube of material has sheet contacts on two opposite faces, and the resistance between these contacts is , then the resistivity of the material is . Electrical conductivity or specific conductance is the reciprocal of electrical resistivity. It represents a material's ability to conduct electric current. It is commonly signified by the Greek letter ( sigma), but ( kappa) (especially in electrical engineering) and ( gamma) are sometimes used. The SI unit of electrical conductivity is siemens per metre (S/m). Resistivity and conductivity are inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercalation (chemistry)
In chemistry, intercalation is the reversible inclusion or insertion of a molecule (or ion) into layered materials with layered structures. Examples are found in graphite and transition metal dichalcogenides. : Examples Graphite One famous intercalation host is graphite, which intercalates potassium as a guest. Intercalation expands the van der Waals gap between sheets, which requires energy. Usually this energy is supplied by charge transfer between the guest and the host solid, i.e., redox. Two potassium graphite compounds are KC8 and KC24. Carbon fluorides (e.g., (CF)x and (C4F)) are prepared by reaction of fluorine with graphitic carbon. The color is greyish, white, or yellow. The bond between the carbon and fluorine atoms is covalent, thus fluorine is not intercalated. Such materials have been considered as a cathode in various lithium batteries. Treating graphite with strong acids in the presence of oxidizing agents causes the graphite to oxidise. Graphite bisulfate, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mole (chemistry)
The mole, symbol mol, is the unit of amount of substance in the International System of Units (SI). The quantity amount of substance is a measure of how many elementary entities of a given substance are in an object or sample. The mole is defined as containing exactly elementary entities. Depending on what the substance is, an elementary entity may be an atom, a molecule, an ion, an ion pair, or a subatomic particle such as an electron. For example, 10 moles of water (a chemical compound) and 10 moles of mercury (a chemical element), contain equal amounts of substance and the mercury contains exactly one atom for each molecule of the water, despite the two having different volumes and different masses. The number of elementary entities in one mole is known as the Avogadro number, which is the approximate number of nucleons (protons or neutrons) in one gram of ordinary matter. The previous definition of a mole was simply the number of elementary entities equal to that of 12 grams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Stability
In thermodynamics, thermal stability describes the stability of a water body and its resistance to mixing.Schmidt, W. 1928. Über Temperatur und Stabilitätsverhältnisse von Seen. Geogr. Ann 10: 145 - 177. It is the amount of work needed to transform the water to a uniform water density. The Schmidt stability "S" is commonly measured in joule The joule ( , ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). It is equal to the amount of work done when a force of 1 newton displaces a mass through a distance of 1 metre in the direction of the force applied ...s per square meter (J/m). References Further reading * Molecular physics {{engineering-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aniline
Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine In organic chemistry, an aromatic amine is an organic compound consisting of an aromatic ring attached to an amine. It is a broad class of compounds that encompasses aniline Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consi .... It is an industrially significant Commodity chemicals, commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It Combustion, ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds. It is toxic to humans. Relative to benzene, it is electron-rich. It thus participates more rapidly in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Likewise, it is also prone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |