|
Lithium Battery
Lithium battery may refer to: * Lithium metal battery, a non-rechargeable battery with lithium as an anode ** Rechargeable lithium metal battery, a rechargeable counterpart to the lithium metal battery * Lithium-ion battery, a rechargeable battery in which lithium ions move from the negative electrode to the positive electrode during discharge and back when charging ** Thin-film lithium-ion battery, a solid-state lithium-ion battery constructed as a thin-film ** Aqueous lithium-ion battery ** Lithium-ion flow battery ** Lithium ion manganese oxide battery * Lithium polymer battery * Lithium–sulfur battery * Lithium-titanate battery * Lithium–air battery * Lithium iron phosphate battery * Nickel–lithium battery * Lithium–silicon battery * Lithium vanadium phosphate battery * Lithium hybrid organic battery See also *List of battery types *Lithium batteries in China *High capacity oceanographic lithium battery pack *Glass battery, which may use a lithium metal electrode *Sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Metal Battery
Lithium metal batteries are primary batteries that have metallic lithium as an anode. These types of batteries are also referred to as lithium-metal batteries after lithium-ion batteries had been invented. Most lithium metal batteries are non-rechargeable. However, rechargeable lithium metal batteries are also under development. Since 2007, Dangerous Goods Regulations differentiate between lithium metal batteries (UN 3090) and lithium-ion batteries (UN 3480). They stand apart from other batteries in their high charge density and high cost per unit. Depending on the design and chemical compounds used, lithium cells can produce voltages from (comparable to a zinc–carbon or alkaline battery) to about . Disposable primary lithium batteries must be distinguished from secondary lithium-ion or a lithium-polymer, which are rechargeable batteries and contain no metallic lithium. Lithium is especially useful, because its ions can be arranged to move between the anode and the catho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel–lithium Battery
The nickel–lithium battery, also known as Ni–Li, is a battery using a nickel hydroxide cathode and lithium anode. The two metals cannot normally be used together in a battery, as there are no electrolytes compatible with both. The LISICON design uses a layer of porous glass to separate two electrolytes in contact with each metal. The battery is predicted to hold more than twice as much energy per kilogram as lithium-ion batteries A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also se ..., and to be safer. However, the battery will be complex to manufacture and durability issues have yet to be resolved. Ni-Li has a very high cell potential, but is limited in capacity by the cathode material. References Rechargeable batteries {{Energy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
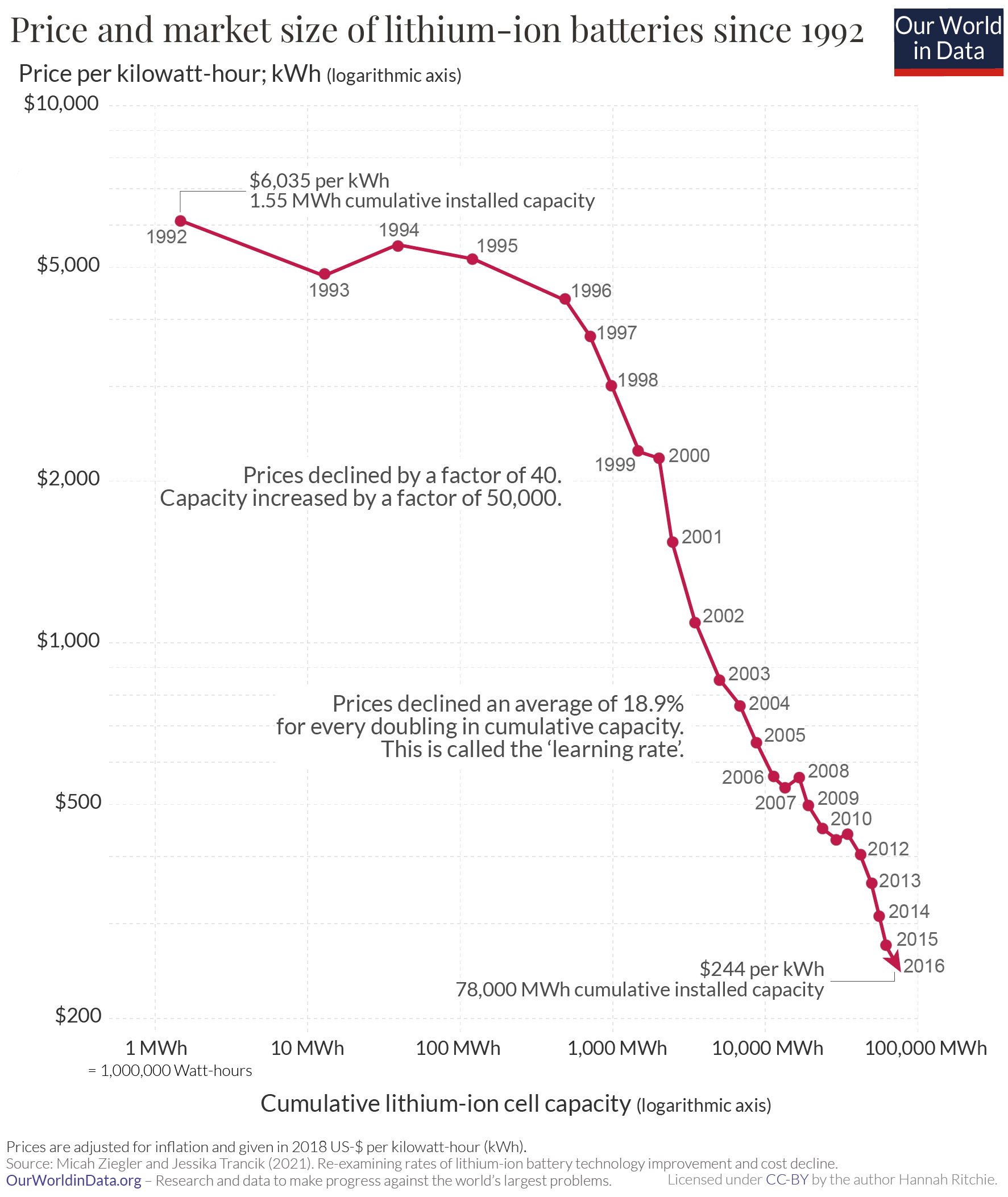
History Of The Lithium-ion Battery
Varta lithium-ion battery, Museum Autovision, Altlussheim">Museum_Autovision.html" ;"title="Varta lithium-ion battery, Museum Autovision">Varta lithium-ion battery, Museum Autovision, Altlussheim, Germany This is a history of the lithium-ion battery. Prior work Much of the basic research that led to the development of the Intercalation (chemistry), intercalation compounds that form the core of lithium-ion batteries was carried out in the 1960s by Robert Huggins and Carl Wagner, who studied the movement of ions in solids. Reversible intercalation of lithium ions into graphite as anodes and intercalation of lithium ions into cathodic oxide as cathodes was discovered during 1974–76 by Jürgen Otto Besenhard at TU Munich. Besenhard proposed its application in lithium cells. Electrolyte decomposition and solvent co-intercalation into graphite were severe early drawbacks for battery life. British chemist M. Stanley Whittingham, then a researcher at ExxonMobil, first reported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Impacts Of Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium batteries are primary batteries that use lithium as an anode. This type of battery is also referred to as a lithium-ion battery and is most commonly used for electric vehicles and electronics. The first type of lithium battery was created by the British chemist M. Stanley Whittingham in the early 1970s and used titanium and lithium as the electrodes. Unfortunately, applications for this battery were limited by the high prices of titanium and the unpleasant scent that the reaction produced. Today's lithium ion battery, modeled after the Whittingham attempt by Akira Yoshino, was first developed in 1985. Environmental impact While safe for landfills, the physical mining of lithium and the production of lithium-ion are both labor-intensive processes. Additionally, most batteries are not properly recycled. Extraction The extraction process of lithium is very resource demanding and specifically uses a lot of water in the extraction process. It is estimated that 500,000 gallo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Battery
The glass battery is a type of solid-state battery. It uses a glass electrolyte and lithium or sodium metal electrodes. The battery was invented by John B. Goodenough, inventor of the lithium cobalt oxide and lithium iron phosphate electrode materials used in the lithium-ion battery (Li-ion), and Maria H. Braga, an associate professor at the University of Porto and a senior research fellow at Cockrell School of Engineering at The University of Texas. The paper describing the battery was published in ''Energy & Environmental Science'' in December 2016; a number of follow-up works have also been published since. Hydro-Québec is researching the battery for possible production. Glass Electrolyte Research In September 2016 Iowa State University was granted U.S. $1.6 million to develop new lithium-ion-conducting glassy solid electrolytes. In August 2019, it was announced that GM was awarded U.S. $2 million by the United States Department of Energy for research into the "fundame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Capacity Oceanographic Lithium Battery Pack
A High capacity oceanographic lithium battery pack is a type of battery pack used by oceanographers. Physical Oceanographers use high capacity lithium battery packs for long term deployments to extend the duration of the deployments and gather more data. Oceanographers often work in far away sites that are difficult to get to. The cost of getting to these remote sites, often by ship, can dominate the cost of an investigation. This motivates oceanographers to extend the duration of their deployments so that they can visit them less often. This means, among other things, increasing the capacity of their battery packs. Reasons for use When possible, oceanographers use alkaline batteries because they are inexpensive and readily available. However, when alkaline batteries provide insufficient capacity, oceanographers turn to lithium battery packs, which can supply three times the capacity. Battery packs based on lithium thionyl chloride chemistry cost more than alkaline battery pack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Batteries In China
China produced more than 15 billion units of lithium-ion batteries in 2019, which accounts for 73% of the world’s 316 giga watt-hours capacity. China is a major producer of both lithium batteries and electric vehicles, with favorable policies for manufacturers and consumers. Chinese made lithium-ion batteries were exported mainly to Hong Kong, the United States, Germany, Korea, and Vietnam. One of the major drivers of the demand for lithium-ion batteries comes from the electric vehicle industry since lithium-ion batteries have high energy density for their weight. In the decade since 2008, the production of lithium batteries has tripled. Background Prior to lithium-ion battery technologies, rechargeable batteries for cars were mostly of the lead-acid type. Although the production cost is cheaper, lead-acid batteries are inferior in their capacity, depth of recharge, efficiency, and lifespan. Charging lithium-ion batteries are four times faster than lead-acid batteries, makin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Battery Types ...
This list is a summary of notable electric battery types composed of one or more electrochemical cells. Three lists are provided in the table. The primary (non-rechargeable) and secondary (rechargeable) cell lists are lists of battery chemistry. The third list is a list of battery applications. Battery cell types See also * Baghdad Battery * Battery nomenclature * Carnot battery * Comparison of commercial battery types * History of the battery * List of battery sizes * List of energy densities * ''Search for the Super Battery'' (2017 PBS film) * Fuel cell References {{Battery sizes * Battery Battery most often refers to: * Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power * Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact Battery may also refer to: Energy source *Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
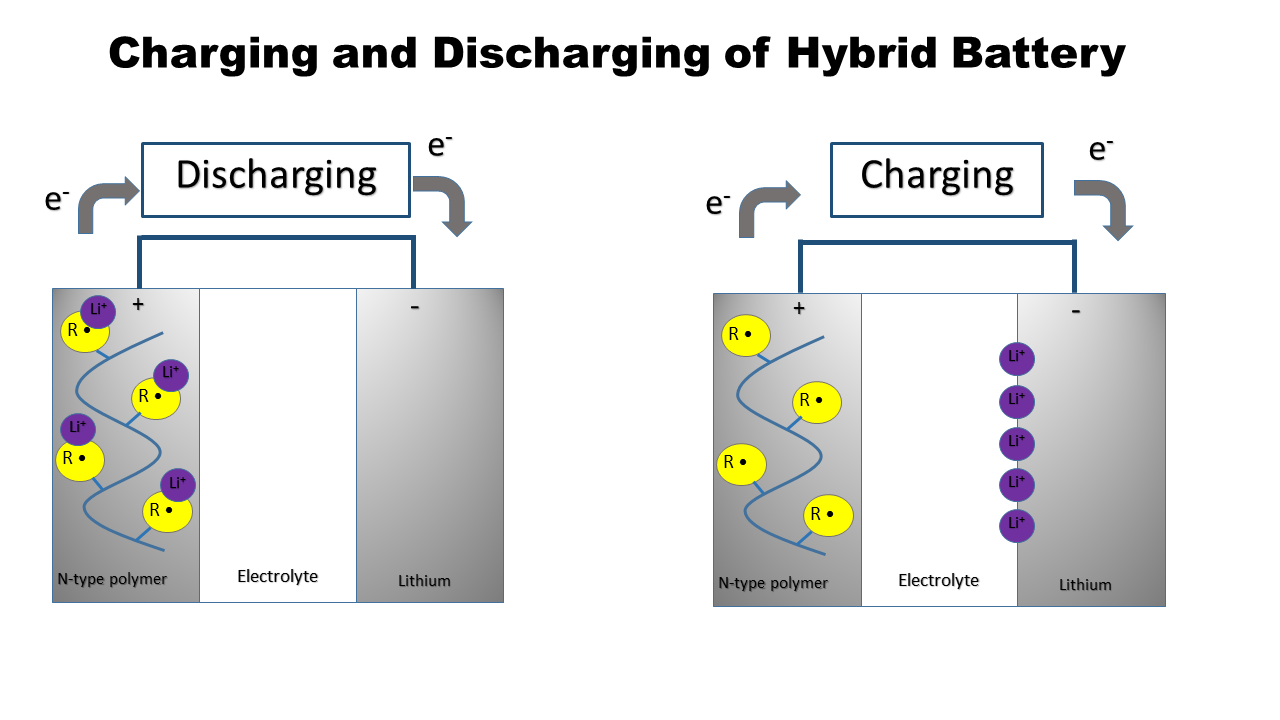
Lithium Hybrid Organic Battery
Lithium hybrid organic batteries are an energy storage device that combines lithium with an organic polymer. For example, polyaniline vanadium (V) oxide (PAni/V2O5) can be incorporated into the nitroxide-polymer lithium iron phosphate battery, PTMA/LiFePO4. Together, they improve the lithium ion intercalation capacity, cycle life, electrochemical performances, and conductivity of batteries. PAni/V2O5 Oxides, like V2O5, are used as cathodes in rechargeable lithium batteries. Crystalline V2O5 has a weaker rechargeability or cyclability than amorphous V2O5 because the crystal structure is damaged during discharge/charge cycles. However, amorphous oxides, in particular the V2O5 xerogel, allows lithium ions to diffuse faster and thus have a better cyclability. Hybrid is formed by combining a conducting organic polymer (e.g. polyaniline) with an oxide (e.g. V2O5). V2O5 gels are prepared using the ion-exchange method. Vanadium (V) polymerizes aniline. Before synthesis of a hybrid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Vanadium Phosphate Battery
A lithium vanadium phosphate (LVP) battery is a proposed type of lithium ion battery that uses a vanadium phosphate in the cathode. they have not been commercialized. Research Vanadium phosphates have been investigated as potential cathodes for Li-ion batteries: including lithium vanadium phosphate, Li3V2(PO4)3; the same material prepared by sol gel Sol or SOL may refer to: Astronomy * The Sun Currency * SOL Project, a currency project in France * French sol, or sou * Argentine sol * Bolivian sol, the currency of Bolivia from 1827 to 1864 * Peruvian sol, introduced in 1991 * Peruvian sol ( ... methods showed lithium insertion/removal over a 3.5 to 4.1 V range, with evidence of three stages of insertion/removal. ɛ-VOPO4 has been studied as a cathode material and has a two stage lithium insertion/removal process. Nanostructured ɛ-VOPO4 has been studied as a potential redox material. References {{Lithium compounds Lithium-ion batteries Phosphates Vanadium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium–silicon Battery
Lithium–silicon battery is a name used for a subclass of lithium-ion battery technology that employs a silicon-based anode#Battery or galvanic cell anode, anode and lithium ions as the charge carriers. Silicon based materials generally have a much larger specific capacity, for example 3600 mAh/g for pristine silicon, relative to graphite, which is limited to a maximum theoretical capacity of 372 mAh/g for the fully lithiated state LiC6.Shao, Gaofeng, et al. ''Polymer derived SiOC integrated with graphene aerogel as highly stable Li-ion battery anodes'' ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 41, 46045–46056 Silicon's large volume change (approximately 400% based on crystallographic densities) when lithium is inserted is one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery
The lithium iron phosphate battery (LFP (lithium ferro-phosphate), or Li-IP) is a type of lithium-ion battery using lithium iron phosphate () as the cathode material, and a graphitic carbon electrode with a metallic backing as the anode. Because of their lower cost, high safety, low toxicity, long cycle life and other factors, LFP batteries are finding a number of roles in vehicle use, utility-scale stationary applications, and backup power. LFP batteries are cobalt-free. As of Q1 2021, LFP type battery market share reached 24.1%, with Chinese manufacturers holding a near monopoly, and is expected to rise further to surpass NMC type batteries in 2028. The energy density of an LFP battery is lower than that of other common lithium ion battery types such as nickel manganese cobalt (NMC) and nickel cobalt aluminum (NCA), and also has a lower operating voltage; CATL's LFP batteries are currently at 125 watt hours (Wh) per kg, up to possibly 160 Wh/kg with improved packing techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |