|
List Of Volcanic Craters In Alaska
The United States National Geodetic Survey lists thirteen craters in the state of Alaska Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., .... Aleutians East Borough, Alaska, Aleutians East Borough *Fisher Caldera is located on Unimak Island and named for American geologist Bernard Fisher (geologist), Bernard Fisher, who died on June 22, 1946, while exploring the Umnak Pass. It is by in area. Aleutians West Census Area, Alaska, Aleutians West Census Area *Mount Okmok, Okmok Caldera Bethel Census Area, Alaska, Bethel Census Area *Binalik Crater is located on Nunivak Island. It was named by the Yupik peoples, Yupik people, and reported in 1937. It is across. *Ikathiwik Crater *Nanwaksjiak Crater Kodiak Island *Kaguyak Crater Lake and Peninsula Borough, Alaska, Lake and Peni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kodiak Island
Kodiak Island (Alutiiq: ''Qikertaq''), is a large island on the south coast of the U.S. state of Alaska, separated from the Alaska mainland by the Shelikof Strait. The largest island in the Kodiak Archipelago, Kodiak Island is the second largest island in the United States and the 80th largest island in the world, with an area of , slightly larger than Cyprus. It is long and in width ranges from . Kodiak Island is the namesake for Kodiak Seamount, which lies off the coast at the Aleutian Trench. The largest community on the island is the city of Kodiak, Alaska. Kodiak Island is mountainous and heavily forested in the north and east, but fairly treeless in the south. The island has many deep, ice-free bays that provide sheltered anchorages for boats. The southwestern two-thirds of the island, like much of the Kodiak Archipelago, is part of Kodiak National Wildlife Refuge. Kodiak Island is part of the Kodiak Island Borough and Kodiak Archipelago of Alaska. The town of Kodiak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrow, Alaska
Utqiagvik ( ik, Utqiaġvik; , , formerly known as Barrow ()) is the borough seat and largest city of the North Slope Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. Located north of the Arctic Circle, it is one of the northernmost cities and towns in the world and the northernmost in the United States, with nearby Point Barrow which is the country's northernmost land. Utqiagvik's population was 4,927 at the 2020 census, an increase from 4,212 in 2010. It is the 12th-most populated city in Alaska. Name The location has been home to the Iñupiat, an indigenous Inuit ethnic group, for more than 1,500 years. The city's Iñupiaq name refers to a place for gathering wild roots. It is derived from the Iñupiat word , also used for '' Claytonia tuberosa'' (" Eskimo potato"). The name was first recorded, by European explorers, in 1853 as "Ot-ki-a-wing" by Commander Rochfort Maguire, Royal Navy. John Simpson's native map dated 1855 has the name "Otkiawik", which was later misprinted on a Briti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avak Crater
Avak is an impact crater centered approximately southeast of Utqiagvik, Alaska, United States. Avak is a subcircular structure about in diameter and deep. In the structure, metamorphic basement rocks and regionally flat lying sedimentary rocks are uplifted and intensely deformed. The Avak structure has no surface expression in the swampy, lake-dotted tundra of the Arctic coastal plain. The structure is covered by a thin veneer of permanently frozen Pliocene and Pleistocene rock. This means that the age of the impact took place anywhere between 3 million and 95 million years ago. Palynological data on its ejecta suggest Middle–Late Turonian age of the impact (about 90 million years ago). The Avak structure provides the structural trap for the natural gas in the adjacent South Barrow and East Barrow gas fields. These fields have accumulated about 37 bcf of natural gas in Jurassic sandstones. History The Avak structure was first recognized from seismic surveys in the National Pet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Crater
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography. Etymology The word ''north'' is related to the Old High German ''nord'', both descending from the Proto-Indo-European unit *''ner-'', meaning "left; below" as north is to left when facing the rising sun. Similarly, the other cardinal directions are also related to the sun's position. The Latin word ''borealis'' comes from the Greek '' boreas'' "north wind, north", which, according to Ovid, was personified as the wind-god Boreas, the father of Calais and Zetes. ''Septentrionalis'' is from ''septentriones'', "the seven plow oxen", a name of '' Ursa Major''. The Greek ἀρκτικός (''arktikós'') is named for the same constellation, and is the source of the English word '' Arctic''. Other languages have other derivations. For example, in Lezgian, ''kefe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Wrangell
Mount Wrangell, in Ahtna K’ełt’aeni or K’ełedi when erupting, is a massive shield volcano located in Wrangell-St. Elias National Park and Preserve in southeastern Alaska, United States. The shield rises over above the Copper River to its southwest. Its volume is over , making it more than twice as massive as Mount Shasta in California, the largest stratovolcano by volume in the Cascades. It is part of the Wrangell Volcanic Field, which extends for more than across Southcentral Alaska into the Yukon Territory in Canada, and has an eruptive history spanning the time from Pleistocene to Holocene. Description Modern Mount Wrangell, built upon the remnants of a mid-Pleistocene volcano, has an eruptive history spanning from 750,000 years ago to minor phreatic eruptions in 1884.Volcanoes of North America, Wood and Kienle The shield volcano features an ice-filled caldera in diameter at the top of Wrangell's broad summit. The caldera was apparently formed by subsidence rathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Crater
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth. Etymology As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that east is the direction where the Sun rises: ''east'' comes from Middle English ''est'', from Old English ''ēast'', which itself comes from the Proto-Germanic *''aus-to-'' or *''austra-'' "east, toward the sunrise", from Proto-Indo-European *aus- "to shine," or "dawn", cognate with Old High German ''*ōstar'' "to the east", Latin ''aurora'' 'dawn', and Greek ''ēōs'' 'dawn, east'. Examples of the same formation in other languages include Latin oriens 'east, sunrise' from orior 'to rise, to originate', Greek ανατολή anatolé 'east' from ἀνατέλλω 'to rise' and Hebrew מִזְרָח mizraḥ 'east' from זָרַח zaraḥ 'to rise, to shine'. ''Ēostre'', a Germanic goddess of dawn, might have been a personification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin Calderas
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of TwinLast Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two embryos, or ''dizygotic'' ('non-identical' or 'fraternal'), meaning that each twin develops from a separate egg and each egg is fertilized by its own sperm cell. Since identical twins develop from one zygote, they will share the same sex, while fraternal twins may or may not. In rare cases twins can have the same mother and different fathers (heteropaternal superfecundation). In contrast, a fetus that develops alone in the uterus, womb (the much more common case, in humans) is called a ''singleton'', and the general term for one offspring of a multiple birth is a ''multiple''. Unrelated look-alikes whose resemblance parallels that of twins are referred to as doppelgängers. Statistics The human twin birth rate in the United States rose 7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nome Census Area, Alaska
Nome Census Area is a census area located in the U.S. state of Alaska, mostly overlapping with the Seward Peninsula. As of the 2020 census, the population was 10,046, up from 9,492 in 2010. It is part of the unorganized borough and therefore has no borough seat. Its largest community by far is the city of Nome. Geography According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the census area has a total area of , of which is land and (18.8%) is water. It also includes the large offshore St. Lawrence Island, which has about 14 percent of the census area's population and two of its larger cities in Gambell and Savoonga. Nome Census Area is the 7th largest county-equivalent in the state of Alaska. Adjacent boroughs and census areas * Northwest Arctic Borough, Alaska - north * Yukon-Koyukuk Census Area, Alaska - east * Kusilvak Census Area, Alaska - south * Chukotsky District, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug - west National protected areas * Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge (part of the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukinrek Maars
The Ukinrek Maars are two volcanic craters on the north side of the Aleutian Range in Alaska that were formed by a phreatomagmatic eruption in 1977. The maars are 1.5 km south of Becharof Lake and 12 km northwest of Peulik Volcano, on a low area of the range, bordering the Bering Sea. The western of the two is elliptical in shape and up to 170 m in diameter and 35 m deep. The other lies 600 m to the east and is circular and up to 300 m in diameter and 70 m deep. The east maar has a 49 m-high lava dome within its crater lake. The eruption occurred in March–April 1977 and lasted for ten days. There was no previous eruption. The magmatic material was olivine basalt from a mantle source. Pyroclastic surge from the eruptions traveled to the northwest. The volume of lava erupted was 9×105 m3 and the volume of tephra expelled was 2.6×107 m3. The Quaternary age Gas Rocks dacite domes some three km to the northeast were the site of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
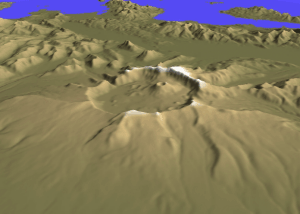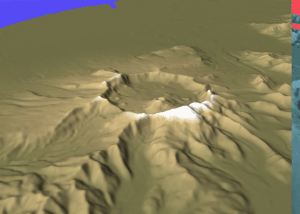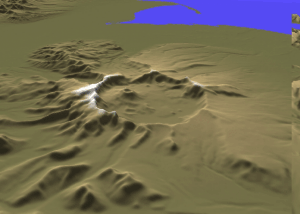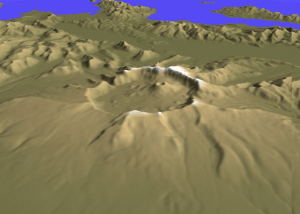
Mount Aniakchak
Mount Aniakchak (russian: Аниакчак) is a 3,700-year-old volcanic caldera approximately in diameter, located in the Aleutian Range of Alaska, United States. Although a stratovolcano by composition, the pre-existing mountain collapsed in a major eruption forming the caldera. The area around the volcano is the Aniakchak National Monument and Preserve, maintained by the National Park Service. In November 1967, Aniakchak Caldera was designated as a National Natural Landmark by the National Park Service. Geological history Mount Aniakchak was previously a glacially eroded stratovolcano of andesitic composition, with a pre-caldera volume of . Andesitic material in the volcano included basalt and dacite. The mountain collapsed, forming the present day caldera, during a major eruption of VEI=6, which left evidence in ice cores dated to 1645 BC. which was later moved to 1641 BC in the Greenland Ice Core Chronology 2005 (GICC05) time scale. Recently, McAneney and Baillie have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |