|
List Of Stars With Resolved Images
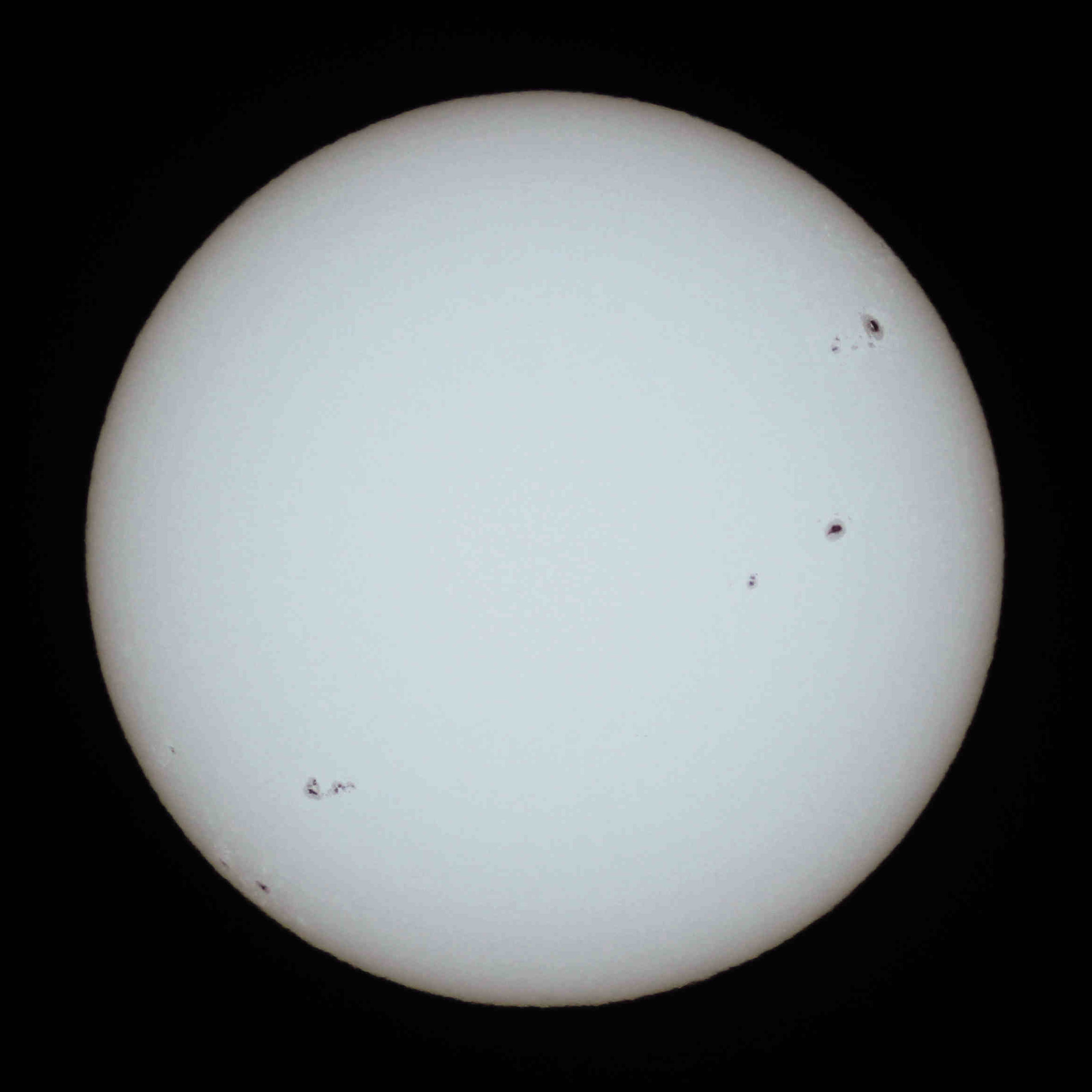
The following is a list of stars with resolved images, that is, stars whose images have been resolved beyond a point source. Aside from the Sun, observed from Earth, stars are exceedingly small in apparent size, requiring the use of special high-resolution equipment and techniques to image. For example, Betelgeuse, the first star other than the Sun to be directly imaged, has an angular diameter of only 50 milliarcseconds (mas). List See also *Doppler imaging which produces maps of the surfaces of stars *Zeeman–Doppler imaging which maps the magnetic fields of stars *List of directly imaged exoplanets *Angular resolution *Angular diameter *List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs References {{Reflist, 30em Images An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensiona ... Astrono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sky, night, but their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed stars, fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterism (astronomy), asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye, all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life star formation, begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Its stellar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
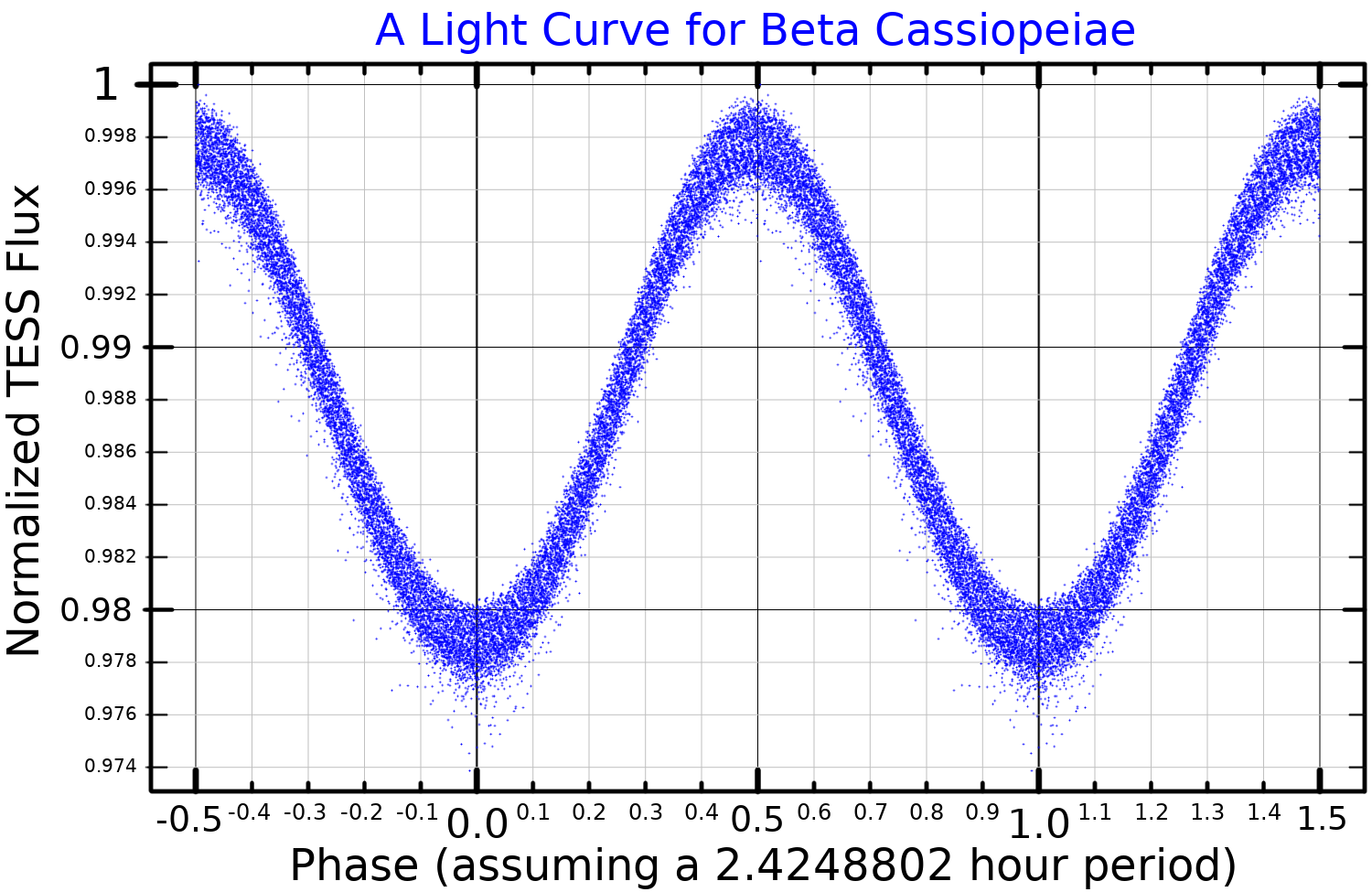
Beta Cassiopeiae
Beta Cassiopeiae (β Cassiopeiae, abbreviated Beta Cas or β Cas), officially named Caph , is a Delta Scuti variable star in the constellation of Cassiopeia. It is a giant star belonging to the spectral class F2. The white star of second magnitude (+2.28 mag, variable) has an absolute magnitude of +1.3 mag. Nomenclature ''Beta Cassiopeiae'' is the star's Bayer designation. It also bore the traditional names ''Caph'' (from the Arabic word ', "palm" - ''i.e.'' reaching from the Pleiades), ''Chaph'' and ''Kaff'', as well as ''al-Sanam al-Nakah'' "the Camel's Hump". In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016 included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN; which included ''Caph'' for this star. Originally, the pre-Islamic Arabic term ''al-Kaff al-Khadib'' "the stained hand" referred to the five stars comprisin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R Doradus ESO
R, or r, is the eighteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ar'' (pronounced ), plural ''ars'', or in Ireland ''or'' . The letter is the eighth most common letter in English and the fourth-most common consonant (after , , and ). The letter is used to form the ending "-re", which is used in certain words such as ''centre'' in some varieties of English spelling, such as British English. Canadian English also uses the "-re" ending, unlike American English, where the ending is usually replaced by "-er" (''center''). This does not affect pronunciation. Name The name of the letter in Latin was (), following the pattern of other letters representing continuants, such as F, L, M, N and S. This name is preserved in French and many other languages. In Middle English, the name of the letter changed from to , following a pattern exhibited in many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R Doradus
R Doradus (HD 29712 or P Doradus) is a red giant variable star in the far-southern constellation Dorado. Its distance from Earth is . Having a uniform disk diameter of , it is thought to be the extrasolar star with the largest apparent size as viewed from Earth. Variability The visible magnitude of R Doradus varies between 4.8 and 6.6, which means it is usually visible to the naked eye, but in the infrared it is one of the brightest stars in the sky. With a near-infrared J band magnitude of −2.6, only Betelgeuse at −2.9 is brighter. In the infrared K band, it is sometimes the brightest star in the sky, although usually Betelgeuse is brighter. It is classified as a semiregular variable star of type SRb, indicating giants with slow poorly-defined variations, often alternating between periodic and irregular brightness changes. Some studies show it alternating between periods of about 175 and 332 days, and a period of 117.3 days has also been identified. It ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starspot
Starspots are stellar phenomena, so-named by analogy with sunspots. Spots as small as sunspots have not been detected on other stars, as they would cause undetectably small fluctuations in brightness. The commonly observed starspots are in general much larger than those on the Sun: up to about 30% of the stellar surface may be covered, corresponding to starspots 100 times larger than those on the Sun. Detection and measurements To detect and measure the extent of starspots one uses several types of methods. *For rapidly rotating stars – Doppler imaging and Zeeman-Doppler imaging. With the Zeeman-Doppler imaging technique the direction of the magnetic field on stars can be determined since spectral lines are split according to the Zeeman effect, revealing the direction and magnitude of the field. *For slowly rotating stars – Line Depth Ratio (LDR). Here one measures two different spectral lines, one sensitive to temperature and one which is not. Since starspots have a low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada–France–Hawaii Telescope
The Canada–France–Hawaii Telescope (CFHT) is located near the summit of Mauna Kea mountain on Hawaii's Big Island at an altitude of 4,204 meters (13,793 feet), part of the Mauna Kea Observatory. Operational since 1979, the telescope is a Prime Focus/ Cassegrain configuration with a usable aperture diameter of . CFHT currently planning a refurbishment to the facility in the 2020s. The facility will be reconstructed with a new 11-m telescope to produce the Maunakea Spectroscopic Explorer, retaining the same base building and infrastructure. First light is expected in 2029. Funding The corporation is bound by a tripartite agreement between the University of Hawaii at Manoa, in the United States, the National Research Council (NRC) in Canada and the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) in France. CFHT also has partnerships with the National Astronomical Observatory of China (NAOC), the Academia Sinica Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics (ASIAA) in Taiwan, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeta Andromedae
Zeta Andromedae (Zeta And, ζ Andromedae, ζ And) is a star system in the constellation Andromeda (constellation), Andromeda. It is approximately 189 light-years from Earth. Zeta Andromedae is the star's Bayer designation. It also has the Flamsteed designation 34 Andromedae and multiple other designations in stellar catalogues. Location The star's location is in the northern constellation Andromeda, in which it is the second-most southerly of the stars in this often drawn characteristic shape representing the mythical princess asterism (astronomy), asterism, after η Andromedae. System The system is a spectroscopic binary whose is classified as an orange K-type star, K-type giant star, giant with a mean apparent magnitude of +4.08. Due to brightness changes caused by the ellipsoidal shape of that object, the system is also an RS Canum Venaticorum variable, RS Canum Venaticorum-type variable star. Its brightness varies from magnitude +3.92 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Tauri
Beta Tauri is the second-brightest star in the constellation of Taurus (constellation), Taurus. It has the official name Elnath; ''Beta Tauri'' is the current Bayer designation, which is Latinisation of names, Latinised from β Tauri and abbreviated Beta Tau or β Tau. The original designation of Gamma Aurigae is now rarely used. It is a chemically peculiar star, chemically peculiar B7 giant star, 134 light years away from the Sun with an apparent magnitude of 1.65. Nomenclature This star has two Bayer designations: β Tauri (Latinised to Beta Tauri) and γ Aurigae (Latinised to Gamma Aurigae). Ptolemy considered the star to be shared by Auriga (constellation), Auriga, and Johann Bayer assigned it a designation in both constellations. When the modern constellation boundaries were fixed in 1930, the designation γ Aurigae largely dropped from use. The traditional name ''Elnath'', variously ''El Nath'' or ''Alnath'', comes from the Arabic word النطح ''an-naţħ'', mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Pegasi
Alpha Pegasi (α Pegasi, abbreviated Alpha Peg, α Peg), formally named Markab , is the third-brightest star in the constellation of Pegasus and one of the four stars in the asterism known as the Great Square of Pegasus. Properties Alpha Pegasi has a stellar classification of A0 IV, indicating that it is an A-type subgiant star that has exhausted the hydrogen at its core and has evolved beyond the main sequence. Its spectrum has also been classified as B9V and B9.5III. It is rotating rapidly, with a projected rotational velocity of 130 km/s giving a lower bound on the azimuthal velocity along the star's equator. The effective temperature of the photosphere is about 10,000 K and the star has expanded to nearly five times the radius of the Sun, emitting 165 times as much energy as the sun. Nomenclature ''α Pegasi'' ( Latinised to ''Alpha Pegasi'') is the star's Bayer designation. It bore the traditional name ''Markab'' (or ''Marchab''), which derived fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eta Ursae Majoris
Eta Ursae Majoris ( Latinised from η Ursae Majoris, abbreviated Eta UMa, η UMa), formally named Alkaid , is a star in the constellation of Ursa Major. It is the most eastern (leftmost) star in the Big Dipper (or Plough) asterism. However, unlike most stars of the Big Dipper, it is not a member of the Ursa Major moving group. With an apparent visual magnitude of +1.84, it is the third-brightest star in the constellation and one of the brightest stars in the night sky. Physical properties Eta Ursae Majoris is a 10-million-year-old B-type main sequence star with a stellar classification of B3 V. Since 1943, the spectrum of this star has served as one of the stable anchor points by which other stars are classified. It has six times the mass; 3.4 times the radius, and is radiating around 594 times as much energy as the Sun. Its outer atmosphere has an effective temperature of about 15,540 K, giving it the blue-white hue of a B-type star. This star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandwidth Smearing
Bandwidth smearing is a chromatic aberration of the reconstructed image of a celestial body observed by an astronomical interferometer that occurs because of the frequency bandwidth. In Fourier terms, the different frequencies of the bandwidth probe different spatial frequencies which results in a reconstruct map containing elongated radial features. It is overcome by going to higher spectral resolutions or, in radioastronomy Radio astronomy is a subfield of astronomy that studies celestial objects at radio frequencies. The first detection of radio waves from an astronomical object was in 1933, when Karl Jansky at Bell Telephone Laboratories reported radiation coming f ..., by using different centres of phase for image reconstruction. References * Bridle, Alan H. and Schwab, Frederic R., ''Wide Field Imaging I: Bandwidth and Time-Average Smearing'' in ''Synthesis imaging in radio astronomy'' (1989), eds. Richard A. Perley, Frederic R. Schwab, Astronomical Society of the Pacific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algol Triple Star System Imaged With The CHARA Interferometer
ALGOL (; short for "Algorithmic Language") is a family of imperative computer programming languages originally developed in 1958. ALGOL heavily influenced many other languages and was the standard method for algorithm description used by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) in textbooks and academic sources for more than thirty years. In the sense that the syntax of most modern languages is "Algol-like", it was arguably more influential than three other high-level programming languages among which it was roughly contemporary: FORTRAN, Lisp, and COBOL. It was designed to avoid some of the perceived problems with FORTRAN and eventually gave rise to many other programming languages, including PL/I, Simula, BCPL, B, Pascal, and C. ALGOL introduced code blocks and the begin...end pairs for delimiting them. It was also the first language implementing nested function definitions with lexical scope. Moreover, it was the first programming language which gave detailed atte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |