|
List Of Ships Named Albatross
This is a list of ships that have carried the name ''Albatros'' or ''Albatross'', after the seabird. Merchant ships * – an American-owned ship that brought news of the outbreak of the War of 1812 to W. P. Hunt. * – a fisheries research ship in service with the United States Commission of Fish and Fisheries from 1882 to 1898 and from 1898 to 1903 and with the United States Bureau of Fisheries from 1903 to 1917 and from 1919 to 1921 which saw service in the United States Navy as USS ''Albatross'' in 1898 and from 1917 to 1919. * – a ketch which was the last sailing vessel trading commercially in Europe. Now a sail training vessel. * – a Dutch/German sailing ship that was later used as a training ship, inspiring the film ''White Squall''. * – a fisheries research ship in service with the United States Bureau of Fisheries from 1926 to 1932 which saw service in the United States Navy as the tug USS ''Patuxent'' (AT-11) from 1909 to 1924. * – a fisheries research ship built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albatross
Albatrosses, of the biological family Diomedeidae, are large seabirds related to the procellariids, storm petrels, and diving petrels in the order Procellariiformes (the tubenoses). They range widely in the Southern Ocean and the North Pacific. They are absent from the North Atlantic, although fossil remains show they once occurred there and occasional vagrants are found. Albatrosses are among the largest of flying birds, and species of the genus ''Diomedea'' (great albatrosses) have the longest wingspans of any extant birds, reaching up to . The albatrosses are usually regarded as falling into four genera, but disagreement exists over the number of species. Albatrosses are highly efficient in the air, using dynamic soaring and slope soaring to cover great distances with little exertion. They feed on squid, fish, and krill by either scavenging, surface seizing, or diving. Albatrosses are colonial, nesting for the most part on remote oceanic islands, often with several spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albatros (1964 Hydrofoil)
''Albatros'' was an Italian-built hydrofoil in service with the Compagnie générale de navigation sur le lac Léman (CGN), commissioned for Expo 64. After initial success, technical difficulties and a flagging number of users led to her decommissioning. She was then sold to a French company in 1972. History In the early 1960, the imminence of Expo 64 led to a number of engineering projects being started in the vicinity of Lausanne. In the contexte, the Compagnie générale de navigation sur le lac Léman (CGN), which operates both historical steam paddle ships and modern liners on the Lake of Geneva, was studying the commissioning of a modern unit. On 10 May 1962, its extraordinary assembly of shareholders decided on ordering a hydrofoil. The chosen design was by Leopoldo Rodriquez, from Messina, for a 1.2 million CHF budget. ''Albatros'' was built during the year 1963. On 8 February 1964, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
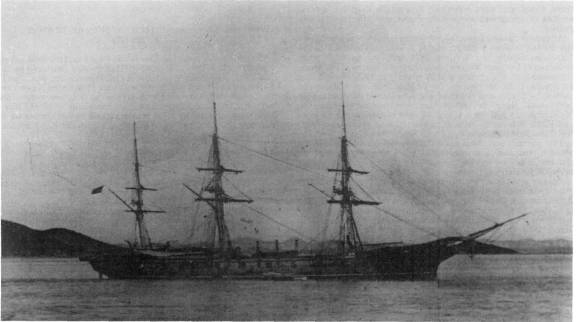
Albatross Expedition
The ''Albatross'' expedition (''Albatrossexpeditionen'') was a Swedish oceanographic expedition that between July 4, 1947, and October 3, 1948, sailed around the world during 15 months covering 45 000 nautical miles. The expedition is considered the second largest Swedish research expedition after the ''Vega'' expedition. The expedition was very successful, received international attention, and is considered one of the important steps in the history of oceanography. The ''Albatross'' The expedition was carried out on board the newly built training ship ''Albatross''. The 70 meter long and 11 meter wide vessel was a combined motor and sailing vessel. The Boström line (''Broströmskoncernen'') had just built the student ship to train prospective ship's officers and this vessel with associated crew was lent to the expedition. Since the Boström line lent the ship at almost no cost, the expedition could be financed and carried out with only private donations. The leader o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
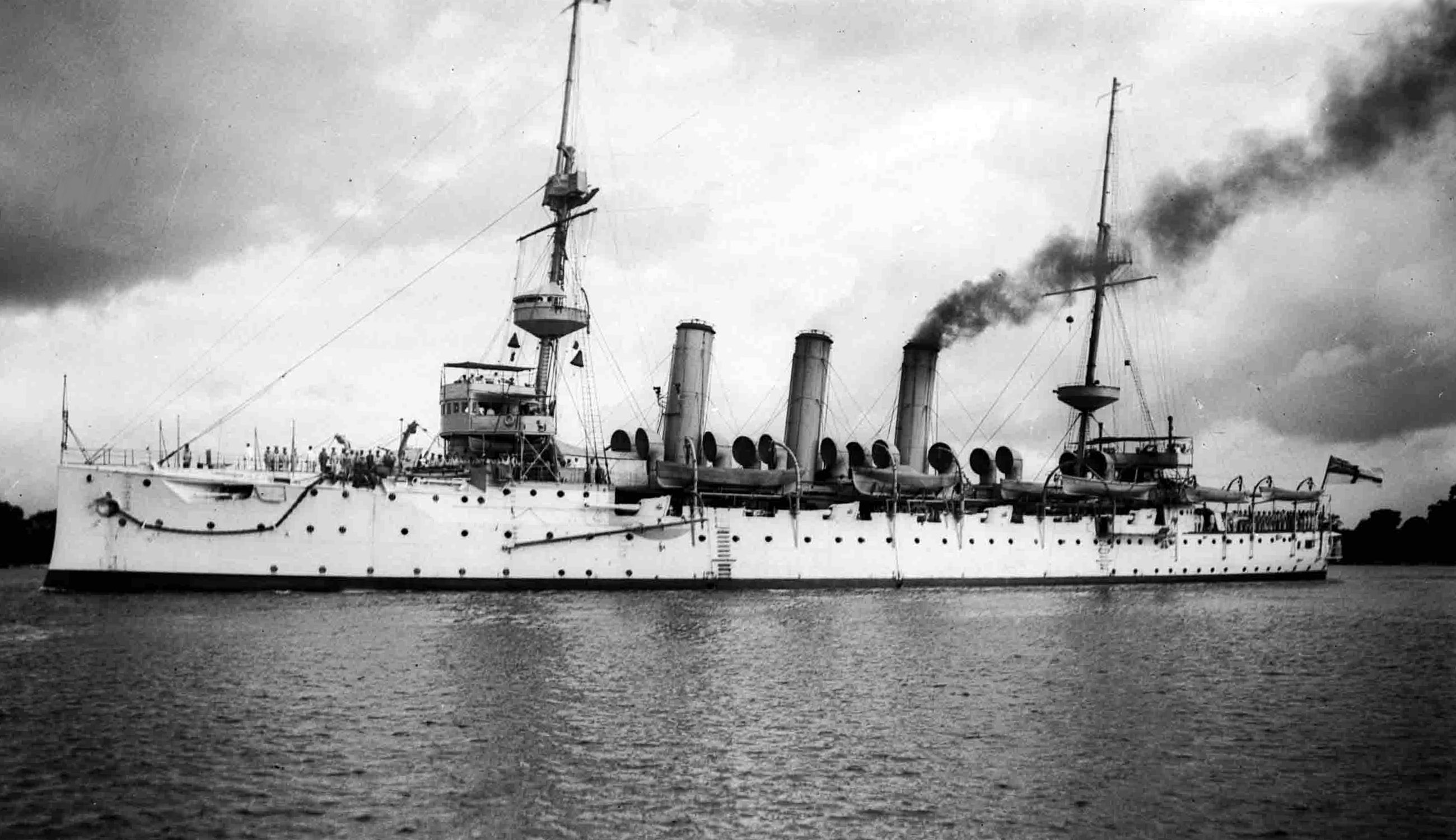
German Torpedo Boat Albatros
''Albatros'' was the fourth of six Type 23 torpedo boats built for the German Navy (initially called the ''Reichsmarine'' and renamed the ''Kriegsmarine'' in 1935). Completed in 1927, ''Albatros'' often served as a flagship of torpedo boat units. The ship made multiple non-intervention patrols during the Spanish Civil War in the late 1930s. After an attack by aircraft of the Spanish Republican Air Force killed German sailors in 1937, she participated in the retaliatory bombardment of Almería. At the beginning of World War II in 1939, ''Albatros'' helped to lay minefields and made anti-shipping patrols before participating in Operation Weserübung, the German invasion of Norway in April 1940. The ship fired the first shots of the campaign when she encountered and crippled a Norwegian patrol boat. She was lightly damaged during the Battle of Horten Harbor. ''Albatros'' then ran aground and was wrecked. Design and armament Derived from the World War I-era torpedo boat ,)., g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 23 Torpedo Boat
The Type 23 torpedo boat (also known as the ''Raubvogel'' (bird of prey) or the ''Möwe'' class) was a group of six torpedo boats built for the ''Reichsmarine'' during the 1920s. As part of the renamed ''Kriegsmarine'', the boats made multiple non-intervention patrols during the Spanish Civil War in the late 1930s. During World War II, they played a minor role in the Norwegian Campaign of 1940, being lost when she ran aground. The Type 23s spent the next several months escorting minelayers as they laid minefields and escorting ships before the ships were transferred to France around September. was torpedoed during this time and did not return to service until 1942. They started laying minefields themselves in September and continued to do so for the rest of the war. After refits in early 1941, the boats were transferred to the Skaggerak where they were assigned escort duties. Most of the surviving ships returned to France in 1942 and helped to escort the capital ships sailing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schooner
A schooner () is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schooner also has a square topsail on the foremast, to which may be added a topgallant. Differing definitions leave uncertain whether the addition of a fore course would make such a vessel a brigantine. Many schooners are gaff-rigged, but other examples include Bermuda rig and the staysail schooner. The origins of schooner rigged vessels is obscure, but there is good evidence of them from the early 17th century in paintings by Dutch marine artists. The name "schooner" first appeared in eastern North America in the early 1700s. The name may be related to a Scots word meaning to skip over water, or to skip stones. The schooner rig was used in vessels with a wide range of purposes. On a fast hull, good ability to windward was useful for priv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brig-sloop
In the 18th century and most of the 19th, a sloop-of-war in the Royal Navy was a warship with a single gun deck that carried up to eighteen guns. The rating system covered all vessels with 20 guns and above; thus, the term ''sloop-of-war'' encompassed all the unrated combat vessels, including the very small gun-brigs and cutters. In technical terms, even the more specialised bomb vessels and fireships were classed as sloops-of-war, and in practice these were employed in the sloop role when not carrying out their specialised functions. In World War I and World War II, the Royal Navy reused the term "sloop" for specialised convoy-defence vessels, including the of World War I and the highly successful of World War II, with anti-aircraft and anti-submarine capability. They performed similar duties to the American destroyer escort class ships, and also performed similar duties to the smaller corvettes of the Royal Navy. Rigging A sloop-of-war was quite different from a civilian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screw Sloop
A screw sloop is a propeller-driven sloop-of-war. In the 19th century, during the introduction of the steam engine, ships driven by propellers were differentiated from those driven by paddle-wheels by referring to the ship's ''screws'' (propellers). Other propeller-driven warships included screw frigates and screw corvette A corvette is a small warship. It is traditionally the smallest class of vessel considered to be a proper (or " rated") warship. The warship class above the corvette is that of the frigate, while the class below was historically that of the slo ...s. See also * CSS ''Alabama'' * USS ''Alaska'' * USS ''Contoocook'' * HMS ''Gannet'', now a museum ship. * USS ''Housatonic'', sunk by the first successful submarine attack. * USS ''Wyoming'' * * Ship types {{navy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo Boat Destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in 1885 by Fernando Villaamil for the Spanish NavySmith, Charles Edgar: ''A short history of naval and marine engineering.'' Babcock & Wilcox, ltd. at the University Press, 1937, page 263 as a defense against torpedo boats, and by the time of the Russo-Japanese War in 1904, these "torpedo boat destroyers" (TBDs) were "large, swift, and powerfully armed torpedo boats designed to destroy other torpedo boats". Although the term "destroyer" had been used interchangeably with "TBD" and "torpedo boat destroyer" by navies since 1892, the term "torpedo boat destroyer" had been generally shortened to simply "destroyer" by nearly all navies by the First World War. Before World War II, destroyers were light vessels with little endurance for unattended oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seaplane Tender
A seaplane tender is a boat or ship that supports the operation of seaplanes. Some of these vessels, known as seaplane carriers, could not only carry seaplanes but also provided all the facilities needed for their operation; these ships are regarded by some as the first aircraft carriers and appeared just before the First World War. Terminology In maritime parlance a tender is a vessel that is used to support the operation of other vessels. In British usage, the term tender was used for small craft, with the term depot ship being used for large seagoing vessels. Flying boats and float planes even when based at home in ports and harbour had a need for small support vessels to operate.p British tenders were small craft of launch to pinnace size. These were used to ferry crews, stores and supplies between shore and the aircraft, to maintain the buoys used to mark out "taxiways" and "runways" and to keep these clear of debris to prevent foreign object damage, and in the case of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Australian Navy
The Royal Australian Navy (RAN) is the principal naval force of the Australian Defence Force (ADF). The professional head of the RAN is Chief of Navy (CN) Vice Admiral Mark Hammond AM, RAN. CN is also jointly responsible to the Minister of Defence (MINDEF) and the Chief of Defence Force (CDF). The Department of Defence as part of the Australian Public Service administers the ADF. Formed in 1901, as the Commonwealth Naval Forces (CNF), through the amalgamation of the colonial navies of Australia following the federation of Australia. Although it was originally intended for local defence, it became increasingly responsible for regional defence as the British Empire started to diminish its influence in the South Pacific. The Royal Australian Navy was initially a green-water navy, and where the Royal Navy provided a blue-water force to the Australian Squadron, which the Australian and New Zealand governments helped to fund, and that was assigned to the Australia Station. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albatross (other)
An albatross is one of a family of large winged seabirds. Albatross or Albatros may also refer to: Animals * Albatross (butterfly) or ''Appias'', a genus of butterfly * Albatross (horse) (1968–1998), a Standardbred horse Literature * Albatross Books, a German publishing house that produced the first modern mass market paperback books * Albatros Literaturpreis, a literary award * "L'albatros" (poem) ("The Albatross"), 1859 poem by Charles Baudelaire * ''The Albatross'', a 1971 novella by Susan Hill * ''The Albatross'', the fictional propeller-sustained airship in Jules Verne's novel ''Robur the Conqueror'' * ''Albatross'' (novel), a 2019 novel by Terry Fallis Film and television * Films Albatros, a French film production company which operated between 1922 and 1939 * ''Albatross'' (2011 film), a British film * ''Albatross'' (2015 film), an Icelandic film * Albatross (Monty Python sketch), a sketch from ''Monty Python's Flying Circus'', first appearing in 1970 * "Albatr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |