|
List Of Science Demonstrations
This is a list of scientific demonstrations used in educational demonstrations and popular science lectures. Physics * Balsa wood bridge — demonstrates compressive strength and tensile strength, teaches engineering thinking * Egg drop competition — demonstrates compressive strength, teaches engineering thinking * Hand boiler — demonstrates vapour-liquid equilibrium and simple heat engine principles * Newton's cradle — demonstrates elastic collision, conservation of momentum, and conservation of energy * Plate trick or Dirac belt trick — demonstrates spinors and the double cover of SO(3) by SU(2) * Prince Rupert's Drop — demonstrates supercooling and tensile stress * Self-siphoning beads — demonstrates momentum, energy and inertia * Water rocket — demonstrates conservation of momentum, conservation of energy, the gas laws and basic rocketry * Franklin bells — demonstrate electric charges * Oxford Electric Bell — an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Demonstrations
A scientific demonstration is a procedure carried out for the purposes of demonstrating scientific principles, rather than for hypothesis testing or knowledge gathering (although they may originally have been carried out for these purposes). Most scientific demonstrations are simple laboratory demonstrations intended to demonstrate physical principles, often in a surprising or entertaining way. They are carried out in schools and universities, and sometimes in public demonstrations in popular science lectures and TV programs aimed at the general public. Many scientific demonstrations are chosen for their combination of educational merit and entertainment value, which is often provided by dramatic phenomena such as explosions. Public scientific demonstrations were a common occurrence in the Age of Enlightenment, and have long been a feature of the British Royal Institution Christmas Lectures, which date back to 1825. In the television era, scientific demonstrations have featured i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
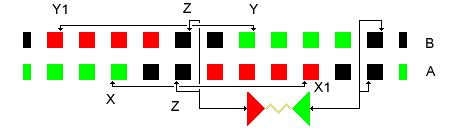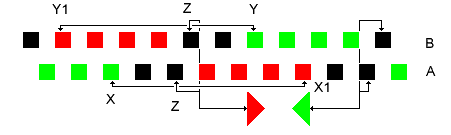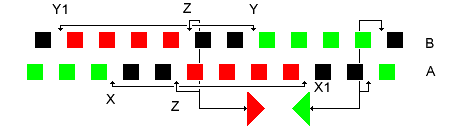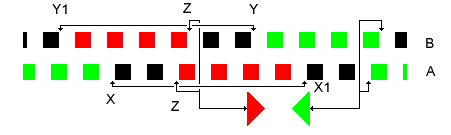
SU(2)
In mathematics, the special unitary group of degree , denoted , is the Lie group of unitary matrices with determinant 1. The more general unitary matrices may have complex determinants with absolute value 1, rather than real 1 in the special case. The group operation is matrix multiplication. The special unitary group is a normal subgroup of the unitary group , consisting of all unitary matrices. As a compact classical group, is the group that preserves the standard inner product on \mathbb^n. It is itself a subgroup of the general linear group, \operatorname(n) \subset \operatorname(n) \subset \operatorname(n, \mathbb ). The groups find wide application in the Standard Model of particle physics, especially in the electroweak interaction and in quantum chromodynamics. The groups are important in quantum computing, as they represent the possible quantum logic gate operations in a quantum circuit with n qubits and thus 2^n basis states. (Alternatively, the more genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barking Dog Reaction
The "Barking Dog" is an exothermic chemical reaction that results from the ignition of a mixture of carbon disulfide and nitrous oxide. When ignited in a cylindrical tube, the reaction produces a bright flash and a loud " woof" - reminiscent of a barking dog. In simple terms, the 'Barking Dog' reaction is a combustion process, in which a fuel (carbon disulfide, CS2) reacts with an oxidizing agent (nitrous oxide, N2O), producing heat and elemental sulfur. The flame front in the reaction is a zone of very hot, luminous gas, produced by the reactants decomposing. :8 N2O + 4 CS2 → S8 + 4 CO2 + 8 N2 In April 1853, Justus von Liebig Justus Freiherr von Liebig (12 May 1803 – 20 April 1873) was a German scientist who made major contributions to agricultural and biological chemistry, and is considered one of the principal founders of organic chemistry. As a professor at t ... performed the demonstration in front of the Bavarian royal family; however, the glass container sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solubility
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution. The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is generally measured as the concentration of the solute in a saturated solution, one in which no more solute can be dissolved. At this point, the two substances are said to be at the solubility equilibrium. For some solutes and solvents, there may be no such limit, in which case the two substances are said to be " miscible in all proportions" (or just "miscible"). The solute can be a solid, a liquid, or a gas, while the solvent is usually solid or liquid. Both may be pure substances, or may themselves be solutions. Gases are always miscible in all proportions, except in very extreme situations,J. de Swaan Arons and G. A. M. Diepen (1966): "Gas—Gas Equilibria". ''Journal of Chemical Physics'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia Fountain
The ammonia fountain is a type of chemical demonstration. The experiment consists of introducing water through an inlet to a container filled with ammonia gas. Ammonia dissolves into the water and the pressure in the container drops. As a result, more water is forced into the container from another inlet creating a fountain effect. The demonstration introduces concepts like solubility and the gas laws at entry level. A different gas of comparable solubility in water, such as hydrogen chloride, can be used instead of ammonia. If the ammonia is replaced by a liquid vapor, such as water vapor, at a pressure higher than its room-temperature vapor pressure, a similar effect is produced. In this case, the reduction in pressure in the container is due to condensation of the vapor as the container cools to room temperature. Another reported variation involves copper sulfate Copper sulfate may refer to: * Copper(II) sulfate, CuSO4, a common compound used as a fungicide and herbicide * Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wimshurst Machine
The Wimshurst influence machine is an electrostatic generator, a machine for generating high voltages developed between 1880 and 1883 by British inventor James Wimshurst (1832–1903). It has a distinctive appearance with two large contra-rotating discs mounted in a vertical plane, two crossed bars with metallic brushes, and a spark gap formed by two metal spheres. Description These machines belong to a class of electrostatic generators called influence machines, which separate electric charges through electrostatic induction, or ''influence'', not depending on friction for their operation. Earlier machines in this class were developed by Wilhelm Holtz (1865 and 1867), August Toepler (1865), J. Robert Voss (1880), and others. The older machines are less efficient and exhibit an unpredictable tendency to switch their polarity, while the Wimshurst machine has neither defect. In a Wimshurst machine, the two insulated discs and their metal sectors rotate in opposite directio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford Electric Bell
The Oxford Electric Bell or Clarendon Dry Pile is an experimental electric bell, in particular a type of bell that uses the electrostatic clock principle that was set up in 1840 and which has run nearly continuously ever since. It was one of the first pieces purchased for a collection of apparatus by clergyman and physicist Robert Walker. It is located in a corridor adjacent to the foyer of the Clarendon Laboratory at the University of Oxford, England, and is still ringing, albeit inaudibly due to being behind two layers of glass. Design The experiment consists of two brass bells, each positioned beneath a dry pile (a form of battery), the pair of piles connected in series, giving the bells opposite electric charges. The clapper is a metal sphere approximately in diameter suspended between the piles, which rings the bells alternately due to electrostatic force. When the clapper touches one bell, it is charged by that pile. It is then repelled from that bell due to having the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franklin Bells
Franklin bells (also known as Gordon's Bells or lightning bells) are an early demonstration of electric charge designed to work with a Leyden jar. Franklin bells are only a qualitative indicator of electric charge and were used for simple demonstrations rather than research. This was the first device that converted electrical energy into mechanical energy in the form of continuous mechanical motion, in this case, the moving of a bell clapper back and forth between two oppositely charged bells. History This device is named for Benjamin Franklin, an early adopter who used it during his experimentation with electricity. It was invented by the Scottish inventor Andrew Gordon, Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Erfurt, Germany. About 1742 he invented a device known as the "electric chimes", which was widely described in textbooks of electricity. Franklin made use of Gordon's idea by connecting one bell to his pointed lightning rod, attached to a chimney, and a sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely from propellant carried within the vehicle; therefore a rocket can fly in the vacuum of space. Rockets work more efficiently in a vacuum and incur a loss of thrust due to the opposing pressure of the atmosphere. Multistage rockets are capable of attaining escape velocity from Earth and therefore can achieve unlimited maximum altitude. Compared with airbreathing engines, rockets are lightweight and powerful and capable of generating large accelerations. To control their flight, rockets rely on momentum, airfoils, auxiliary reaction engines, gimballed thrust, momentum wheels, deflection of the exhaust stream, propellant flow, spin, or gravity. Rockets for military and recreational uses date back to at least 13th-century China. Signific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Laws
The gas laws were developed at the end of the 18th century, when scientists began to realize that relationships between pressure, volume and temperature of a sample of gas could be obtained which would hold to approximation for all gases. Boyle's law In 1662 Robert Boyle studied the relationship between volume and pressure of a gas of fixed amount at constant temperature. He observed that volume of a given mass of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at a constant temperature. Boyle's law, published in 1662, states that, at constant temperature, the product of the pressure and volume of a given mass of an ideal gas in a closed system is always constant. It can be verified experimentally using a pressure gauge and a variable volume container. It can also be derived from the kinetic theory of gases: if a container, with a fixed number of molecules inside, is reduced in volume, more molecules will strike a given area of the sides of the container per unit time, causing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Rocket
A water rocket is a type of model rocket using water as its reaction mass. The water is forced out by a pressurized gas, typically compressed air. Like all rocket engines, it operates on the principle of Newton's third law of motion. Water rocket hobbyists typically use one or more plastic soft drink bottle as the rocket's pressure vessel. A variety of designs are possible including multi-stage rockets. Water rockets are also custom-built from composite materials to achieve world record altitudes. Operation The bottle is partly filled with water and sealed. The bottle is then pressurized with a gas, usually air compressed from a bicycle pump, air compressor, or cylinder up to 125 psi, but sometimes CO2 or nitrogen from a cylinder are used. Water and gas are used in combination, with the gas providing a means to store energy, as it is compressible, and the water increasing the propellant mass fraction and providing greater force when ejected from the rocket's nozzle. Someti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-siphoning Beads
The chain fountain phenomenon, also known as the self-siphoning beads, or Newton's beads is a physical phenomenon observed with a chain placed inside a jar, when one end of the chain is pulled from the jar and is allowed to fall under the influence of gravity. This process establishes a self-sustaining flow of the chain which rises over the edge and goes down to the floor or ground beneath it, as if being sucked out of the jar by an invisible siphon. For chains with small adjacent beads, the arc can ascend into the air over and above the edge of the jar with a noticeable gap; this gap is greater when the chain falls further. History The self-siphoning phenomenon has been known for some time, and had become a topic of public discussion many times in the past. Science entertainer Steve Spangler presented this phenomenon on TV in 2009. This phenomenon is classically known as Newton's beads. The effect is most pronounced when using a long ball chain. The higher the jar containing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |