|
List Of Places Named After Captain James Cook
This is a list of places named after Captain James Cook (1728–1779), the British explorer. {{TOC right Countries *Cook Islands Country subdivisions *Cook County, New South Wales, Australia *Division of Cook, an electoral division in New South Wales, Australia *County of Cook, Queensland, Australia *Electoral district of Cook, Queensland, Australia Towns *Cook, Australian Capital Territory *Cooktown, Queensland, Australia *Cook's Harbour, Newfoundland, Canada *Mount Cook, Wellington, a suburb in New Zealand *Cooks Beach, Coromandel, a town in New Zealand * Captain Cook, Hawaii, United States Geographic features Bodies of water *Cooks River, New South Wales, Australia *Cook's Bay (Ontario), Canada *Cooks Brook (Newfoundland), Canada *Cook Bay (Tierra del Fuego), Chile *Cooks Anchorage, also known as Tautira Bay, Tahiti, French Polynesia *Cook's Bay (Moorea), French Polynesia *Cook Channel, an arm of Dusky Sound, New Zealand *Cook Stream, in Pickersgill Harbour, Dusky S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean and to New Zealand and Australia in particular. He made detailed maps of Newfoundland prior to making three voyages to the Pacific, during which he achieved the first recorded European contact with the eastern coastline of Australia and the Hawaiian Islands, and the first recorded circumnavigation of New Zealand. Cook joined the British merchant navy as a teenager and joined the Royal Navy in 1755. He saw action in the Seven Years' War and subsequently surveyed and mapped much of the entrance to the St. Lawrence River during the siege of Quebec, which brought him to the attention of the Admiralty and the Royal Society. This acclaim came at a crucial moment for the direction of British overseas exploration, and it led to his commission in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cook's Bay (Moorea)
Cook's Bay (also known as Paopao Bay) is a 3-km long bay on the north coast of the island of Mo'orea, Tahiti. It is one of the two principal bays on the island. The other, Opunohu Bay is 4 km west of Cooks Bay. Pao Pao, the largest village on Mo'orea, lies at the head of Cook's Bay. Mo'orea is a tourist destinations, and several hotels lie on the shore of the bay. The University of California, Berkeley maintains the Richard B. Gump South Pacific Research Station on the west coast of Cook's Bay. Cook's Bay was named after the British explorer James Cook. Cook's party visited Mo'orea during First voyage of James Cook, Cook's first voyage in 1769 to observe the transit of Venus, but Cook himself did not visit the island until his Third voyage of James Cook, third voyage. He landed in Opunohu Bay on 30 September 1777, but later visited what is now Cook's Bay by land. References {{Coord, -17.495, -149.822, dim:5000_region:PF, display=title Bays of French Polynesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cook Rock
Cook Rock () is an arched rock, high, lying close east of Trousers Rock and northeast of Vindication Island in the South Sandwich Islands. It was charted in 1930 by Discovery Investigations personnel on the ''Discovery II'' and named for Captain James Cook James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean an .... References Rock formations of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands {{SouthGeorgia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cook Island, South Sandwich Islands
Cook Island is the central and largest island of the Southern Thule island group, part of the South Sandwich Islands in the far south Atlantic Ocean. Southern Thule was discovered by a British expedition under Captain James Cook in 1775. Cook Island was named for Cook by a Russian expedition under Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen, which explored the South Sandwich Islands in 1819–1820. The island was surveyed in 1930 by Discovery Investigations (DI) personnel on ''Discovery II'', who charted and named many of its features. Other names were later applied by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC). Geography Cook Island measures about wide. It is heavily glaciated and uninhabited. Its highest peak, Mount Harmer, rises to . Mount Holdgate rises at the southeast end of the island. Working clockwise from the northwest, the following points are found on the island's coast. All were named by DI personnel unless otherwise specified. Resolution Point is a poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiritimati
Kiritimati (also known as Christmas Island) is a Pacific Ocean atoll in the northern Line Islands. It is part of the Republic of Kiribati. The name is derived from the English word "Christmas" written in Gilbertese according to its phonology, in which the combination ''ti'' is pronounced ''s'', giving kiˈrɪsmæs. Kiritimati has the greatest land area of any atoll in the world, about ; its lagoon is roughly the same size. The atoll is about in perimeter, while the lagoon shoreline extends for over . Kiritimati comprises over 70% of the total land area of Kiribati, a country encompassing 33 Pacific atolls and islands. It lies north of the equator, south of Honolulu, and from San Francisco. Kiritimati is in the world's farthest forward time zone, UTC+14, and is therefore one of the first inhabited places on Earth to experience New Year's Day. (see also Caroline Atoll, Kiribati). Although it lies east of the 180th meridian, the Republic of Kiribati realigned the Internati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cook Island, Tierra Del Fuego
Cook Island, also known as London Island, is an island located in the Tierra del Fuego archipelago. It lies west of Gordon Island, south of O'Brien Island and east of Londonderry Island at the head of Cook Bay, within the Alberto de Agostini National Park. Cook Island is the location of the Fueguino volcanic cones. The island was named after Captain James Cook. Cook did not visit the island, but passed the mouth of Cook Bay on 19 December 1774. The bay was named in 1828 by Captain Henry Foster. See also * List of islands of Chile References External links Islands of Chile @ United Nations Environment ProgrammeWorld island information @ WorldIslandInfo.comSouth America Island High Points above 1000 meters* United States Hydrographic Office The United States Hydrographic Office prepared and published maps, charts, and nautical books required in navigation. The office was established by an act of 21 June 1866 as part of the Bureau of Navigation, Department of the Navy. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cook Island (New South Wales)
__NOTOC__ Cook Island, formerly Cooks Island, Turtle Island and Joong-urra-narrian, is an island in the Australian state of New South Wales located on the state's north coast about north-east of Fingal Head and south-east of the town of Tweed Heads. Description Geology and topography Cook Island is formed of “rocks from the Lismore Basalt Group, formed by lava flows from the Mount Warning Shield Volcano approximately 20 million years ago.” The Island is a “protrusion of eroded basalt” of a maximum height of above sea level and topped with a plateau. The western side of the island has a “gentle” slope while the remaining sides are “sheer cliffs” dropping to “low-lying rock shelves”. The top of the island and its western side are overlaid by a “shallow cover of topsoil.” A “semi-permanent freshwater basin” is located in the island's northern side. Climate In 2011, the average annual rainfall was reported as being . Access Access to the island is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cook Glacier (South Georgia)
Cook Glacier () is a glacier which flows in a north-northeasterly direction to Saint Andrews Bay on the north coast of South Georgia. It was named by the German group of the International Polar Year Investigations based at nearby Moltke Harbour in 1882–83, for Captain James Cook. See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphology, climato ... References * Glaciers of South Georgia {{SouthGeorgia-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
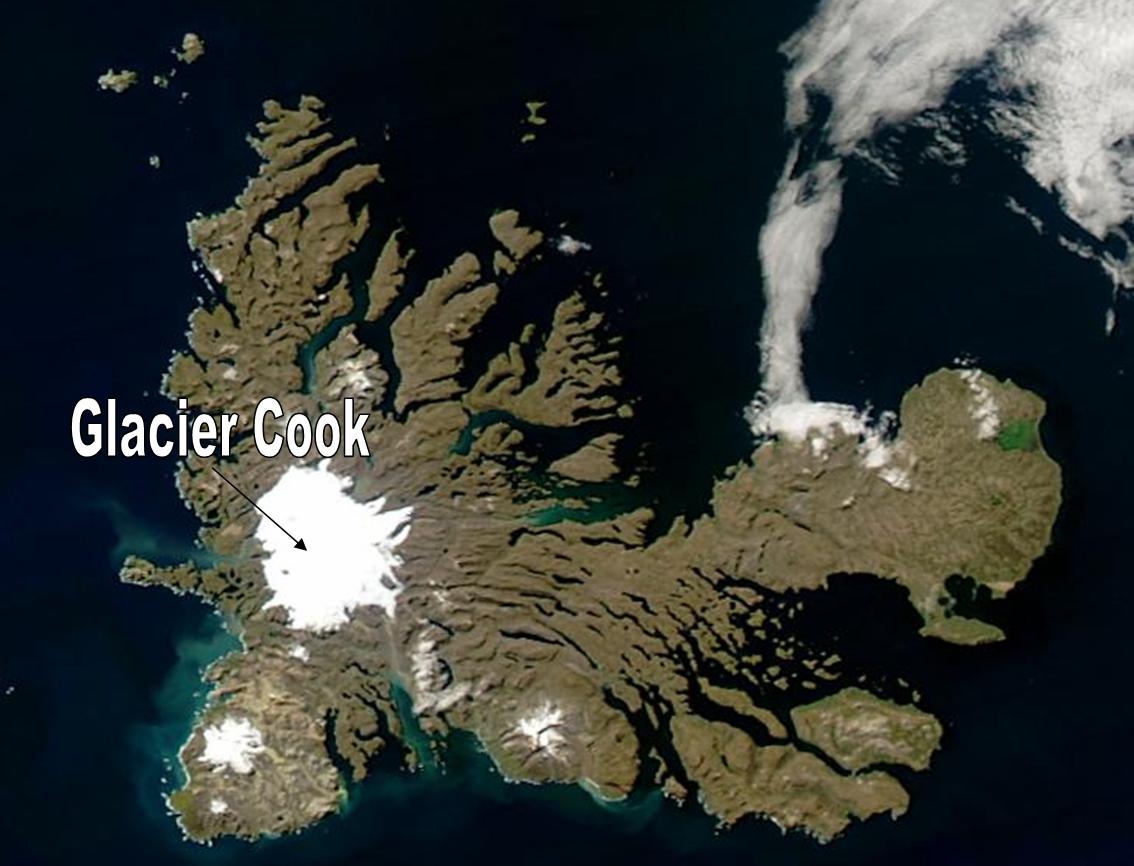
Cook Glacier
The Cook Ice Cap or Cook Glacier ( or ''Glacier Cook'') is a large ice cap in the Kerguelen Islands in the French Southern Territories zone of the far Southern Indian Ocean. Geography The Cook Ice Cap reaches a maximum elevation of in its central area.GoogleEarth It had a surface of approximately in 1963, having shrunk to about in recent times. Named after British explorer James Cook (1728–1779), on French navigational charts of the early 20th century this ice cap appears as 'Glacier Richthofen' '''' 11 September 1909, no 3472 Glaciers About sixty |
Cook Inlet
Cook Inlet ( tfn, Tikahtnu; Sugpiaq: ''Cungaaciq'') stretches from the Gulf of Alaska to Anchorage in south-central Alaska. Cook Inlet branches into the Knik Arm and Turnagain Arm at its northern end, almost surrounding Anchorage. On its southern end, it merges with Shelikof Strait, Stevenson Entrance, Kennedy Entrance and Chugach Passage. The Cook Inlet watershed is the most populated watershed in Alaska. The watershed covers about of southern Alaska, east of the Aleutian Range, south and east of the Alaska Range, receiving water from its tributaries, the Knik River, the Little Susitna River, and the Susitna and Matanuska rivers. The watershed includes the drainage areas of Denali (formerly named Mount McKinley). Within the watershed there are several national parks and the active volcano Mount Redoubt, along with three other historically active volcanoes. Cook Inlet provides navigable access to the port of Anchorage at the northern end, and to the smaller Homer port fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cook Bay (South Georgia)
Cook Bay () is an irregular bay, wide at its entrance between Cape Crewe and Black Head, narrowing into two western arms, Lighthouse Bay and Prince Olav Harbour, along the north coast of South Georgia. It was charted by Discovery Investigations (DI) personnel during the period 1926–30, and named by them for Captain James Cook, who explored South Georgia and landed in this general vicinity in 1775. Features The following notable features of Cook Bay were named by DI personnel, unless otherwise noted. Cape Crewe forms the north side of the entrance to Cook Bay. Cape Crewe is an established name, dating back to about 1912. Crewe Rock, an offshore rock about high, lies 0.1 nautical miles (0.2 km) east of Cape Crewe, for which it is named. Kelp Bank is a shoal, covered with kelp, lying northeast of Cape Crewe. The name appears to be first used on a 1931 British Admiralty chart. A small rock group referred to as the Olav Rocks lies east-southeast of Cape Crewe. It was name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cook Strait
Cook Strait ( mi, Te Moana-o-Raukawa) separates the North and South Islands of New Zealand. The strait connects the Tasman Sea on the northwest with the South Pacific Ocean on the southeast. It is wide at its narrowest point,McLintock, A H, Ed. (1966''Cook Strait''from An Encyclopaedia of New Zealand, updated 18-Sep-2007. Note: This is the distance between the North Island and Arapaoa Island; some sources give a slightly larger reading of around , that between the North Island and the South Island. and is considered one of the most dangerous and unpredictable waters in the world. Regular ferry services run across the strait between Picton in the Marlborough Sounds and Wellington. The strait is named after James Cook, the first European commander to sail through it, in 1770. In Māori it is named ''Te Moana-o-Raukawa'', which means ''The Sea of Raukawa''. Raukawa is a type of woody shrub native to New Zealand. History Approximately 18,000 years ago during the Last Gla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |